Solid modeling-Sweep Representation and B-representation
- 1. Solid Modeling Presented by Pramod Poudel 1
- 2. Solid Modeling Computer representation of a physical solid object Creation or visualization of digital model 2
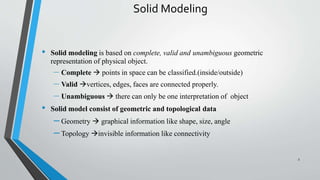
- 3. Solid Modeling • Solid modeling is based on complete, valid and unambiguous geometric representation of physical object. – Complete ïƒ points in space can be classified.(inside/outside) – Valid ïƒ vertices, edges, faces are connected properly. – Unambiguous ïƒ there can only be one interpretation of object • Solid model consist of geometric and topological data – Geometry ïƒ graphical information like shape, size, angle – Topology ïƒ invisible information like connectivity 3
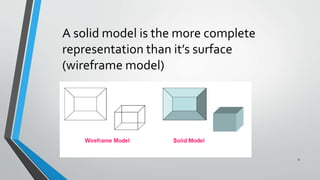
- 5. 5 A solid model is the more complete representation than it’s surface (wireframe model)
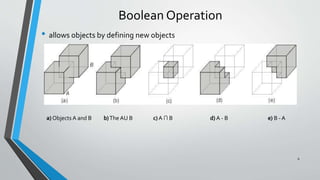
- 6. Boolean Operation • allows objects by defining new objects 6 a) Objects A and B b)The AU B c) A ∩ B d) A - B e) B - A
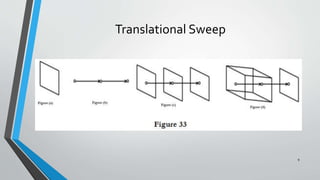
- 7. Sweep representation • Is a method to generate solid with the help of 2D structures • Sweeping an object along a trajectory through space defines a new object called a sweep.The displacement of an object according to a trajectory defines another object 7
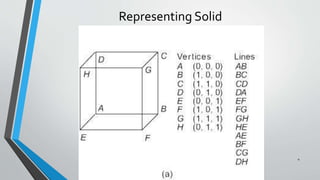
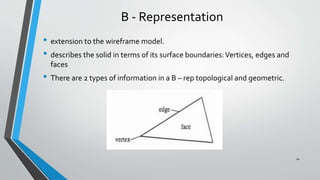
- 10. B - Representation • extension to the wireframe model. • describes the solid in terms of its surface boundaries:Vertices, edges and faces • There are 2 types of information in a B – rep topological and geometric. 10
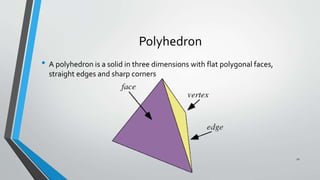
- 11. Polyhedron • A polyhedron is a solid in three dimensions with flat polygonal faces, straight edges and sharp corners 11
- 12. • A simple polyhedron without holes, obeys Euler's formula: 12 V - E + F = 2 V -Vertex E - Edges (edges) F - Faces
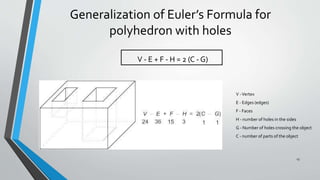
- 13. Generalization of Euler’s Formula for polyhedron with holes 13 V - E + F - H = 2 (C - G) V -Vertex E - Edges (edges) F - Faces H - number of holes in the sides G - Number of holes crossing the object C - number of parts of the object
- 14. 14 ThankYou