solids, liquids and gases
- 1. KS3 Chemistry 7G Solids, Liquids and Gases
- 2. Contents 7G Solids, Liquids and Gases Properties of solids, liquids and gases Summary activities Diffusion Introducing states of matter The particle model
- 3. Different substances What different types of materials are there? M ercury A luminium T in E thanol R adium I ron A rgon L ead Aluminium Lead Argon Iron Radium Ethanol Tin Mercury What are the names of the substances described in this table? (The first letters spell out another word for ŌĆśsubstanceŌĆÖ.) Solid used by Roman plumbers Unreactive gas Solid that rusts Radioactive solid Intoxicating liquid Solid used to coat steel cans Solid used in aircraft Liquid metal
- 4. Three states of matter solid liquid gas At room temperature most substances exist in one of three physical states.
- 5. Solid, liquid or gas?
- 6. Solid, liquid or gas?
- 7. Contents 7G Solids, Liquids and Gases Properties of solids, liquids and gases Summary activities Diffusion Introducing states of matter The particle model
- 8. The particle model The difference between solids, liquids and gases can be explained by theŌĆ” particle model All substances are made up of particles . The particles are attracted to each other . Some particles are attracted strongly to each other and others weakly. The particles move around . They are described as having kinetic energy. The kinetic energy of the particles increases with temperature.
- 9. Particles in a solid ŌĆō animation
- 10. Particles in a liquid ŌĆō animation
- 11. Particles in a gas ŌĆō animation
- 12. Contents 7G Solids, Liquids and Gases Properties of solids, liquids and gases Summary activities Diffusion Introducing states of matter The particle model
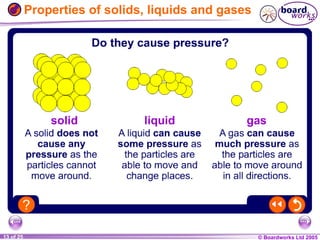
- 13. Properties of solids, liquids and gases
- 14. Which state of matter am I?
- 15. Contents 7G Solids, Liquids and Gases Properties of solids, liquids and gases Summary activities Diffusion Introducing states of matter The particle model
- 16. How do smells spread out? Where is the smell coming from and how does it spread out?
- 17. What is diffusion? Diffusion occurs in liquids and gases but hardly at all in solids. Diffusion is the movement of particles that allows them to spread out and mix with other particles. For example, the smell of aftershave or perfume diffuses and is detected by people on the other side of the room. Use the particle model to explain these facts about diffusion: Diffusion happens more quickly for gases than for liquids. Diffusion happens more quickly at warm temperatures than at cooler temperatures.
- 20. When the gases meet, they react to form a ring of ammonium chloride which is closer to one end of the tube than the other. Diffusion experiment cotton wool soaked in ammonia solution cotton wool soaked in concentrated hydrochloric acid Which gas particles diffuse faster, ammonia or acid, and why? By the time the gases meet, the ammonia particles have travelled further down the tube so they must have diffused at a faster speed. In this experiment, two gases diffuse towards each other in a sealed glass tube. gases meet here
- 21. Contents 7G Solids, Liquids and Gases Properties of solids, liquids and gases Summary activities Diffusion Introducing states of matter The particle model
- 22. Glossary ’ĆĮ diffusion ŌĆō Particles spreading out and mixing in the gas or liquid state. ’ĆĮ gas ŌĆō The state of matter in which particles move quickly in all directions and rarely touch each other. ’ĆĮ liquid ŌĆō The state of matter in which particles are randomly arranged and touch each other. ’ĆĮ matter ŌĆō The stuff that everything is made of. ’ĆĮ particle ŌĆō The smallest unit of matter. ’ĆĮ pressure ŌĆō The f orce produced when particles move against a surface. ’ĆĮ solid ŌĆō The state of matter in which particles are in a fixed arrangement and touch each other.
- 23. Anagrams
- 24. Across: 2. Change from liquid to solid 5. Force caused by collisions of particles 6. Arranged in a 3-dimensional pattern 9. Spacing of particles in solids and liquids 10. All substances are this state at very low temperatures 11. Only liquids and gases do this Crossword Down: 1. Closely packed particles 6. Particles are close but disorganised 3. Change from gas to liquid 7. Particles widely spread out 4. Change from solid to liquid 8. Change from liquid to gas 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11