SONALI CRP.pptx
- 1. PARUL INSTITUTE OF PHARMACY Topic â Informed consent process PRESENTED BY SONALI JAIN MPHARM(PHARMACOLOGY) DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACY GUIDED TO SAGAR PATEL ASSISTANT PROFESSOR 1
- 2. CONTENT 1. Introduction 2. Purpose of consent 3. Definition 4. What is informed consents 5. Basic principle 6. Elements of inform consents 7. Informed consent as a process 8. Documentation 9. Summary 10. reference 2
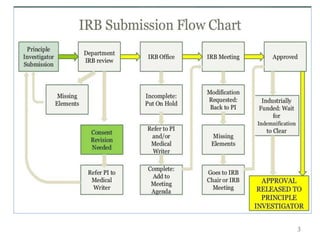
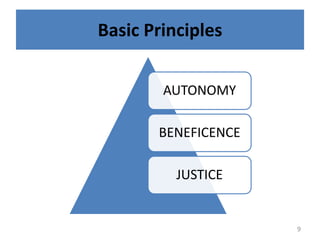
- 3. 3
- 4. Introduction âĒMillions of volunteers participate in government and industry sponsored clinical trial each year. âĒPrior to agreeing to participate, every volunteers has right to know and understand what happen during clinical trial . âĒ This is called as informed consent and this process that can help to decide whether or not participating in a trial is right for you 4
- 5. Purpose of Consent ? âĒ Prospective Subject Will .. ïž Understand nature of research ïž Be informed of purpose, risks, and benefits, and alternative therapies ïž Make a Voluntary Decision about Participation 5
- 6. Definition âĒ A process by which a subject voluntarily confirms his or her willingness to participate in a particular trial, after having been informed of all aspects of the trial that are relevant to the subjectâs decision to participate. âĒ Informed consent is documented by means of a written, signed and dated informed consent form. 6
- 7. What is informed consents..??? âĒ Informed consent is a communication process: ïž Between the researcher and the participant. ïž Starts before the research is initiated . ïž Continues throughout the duration of the study . ïž Providing all relevant information to the volunteer/ patient ïž The patient/ volunteer understanding the information provided Voluntarily agreeing to participate 7
- 8. Informed Consent allows individuals âĒ To determine whether participating in research fits with their values and interests. âĒ To decide whether to contribute to this specific research project. âĒ To protect themselves from risks. âĒ To decide whether they can fulfill the requirements necessary for the research 8
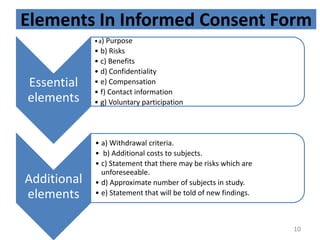
- 10. Elements In Informed Consent Form Essential elements âĒa) Purpose âĒ b) Risks âĒ c) Benefits âĒ d) Confidentiality âĒ e) Compensation âĒ f) Contact information âĒ g) Voluntary participation Additional elements âĒ a) Withdrawal criteria. âĒ b) Additional costs to subjects. âĒ c) Statement that there may be risks which are unforeseeable. âĒ d) Approximate number of subjects in study. âĒ e) Statement that will be told of new findings. 10
- 11. INFORMED CONSENT AS A PROCESS âĒ Informed consent is a communication process: ïž between the researcher and the participant ïž starts before the research is initiated ïž continues throughout the duration of the study 11
- 12. Research Consent Document Readability âĒ Language that is easily understood âĒ Language must be appropriate to the population being studied âĒ Language translators should be qualified and IRB authorized âĒ Consider comprehension as well as readability âĒ Limit medical terminology âĒ Avoid informal speech 12
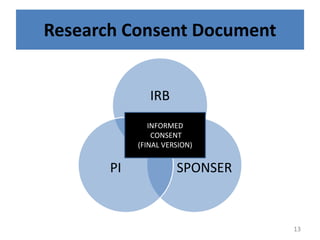
- 13. Research Consent Document IRB SPONSER PI INFORMED CONSENT (FINAL VERSION) 13
- 14. Research Consent Document âĒ When do you need a witness? ïž When presenting the informed consent document orally ïž If required by the IRB âĒ Who can be the witness? ïž A person who is independent of the trial, who cannot be unfairly influenced by people involved in the trial, who attends the informed consent processâĶ Research Consent Document 14
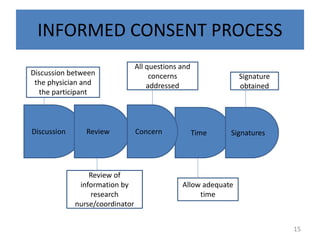
- 15. INFORMED CONSENT PROCESS Discussion Review Time Signatures Concern Discussion between the physician and the participant All questions and concerns addressed Signature obtained Review of information by research nurse/coordinator Allow adequate time 15
- 16. Informed Consent and Screening Procedures âĒ Informed consent must be obtained prior to any protocol specific testing being conducted. âĒ If protocol specific testing done the same day as informed consent document signed, must be clear documentation of the chronological order in the medical record 16
- 17. How does informed consent apply to children? âĒ Children do not have the decision-making capacity to provide informed consent. âĒ Since Therefore, parents or other surrogate decision-makers may give informed permission for diagnosis and treatment of a child, preferably with the assent of the child whenever possible. âĒ Other disagreements in care may result in court orders that specify what treatment should occur (for example, blood transfusions), or in the court-ordered appointment of a guardian to make medical decisions for the child. âĒ Depending on the type of research, the IRB may make provisions for âassentâ of children Assent âA childâs affirmative agreement to be a participant in research. Mere failure to object should not, absent affirmative agreement, be construed as assent.â 17
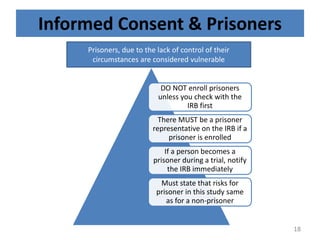
- 18. Informed Consent & Prisoners DO NOT enroll prisoners unless you check with the IRB first There MUST be a prisoner representative on the IRB if a prisoner is enrolled If a person becomes a prisoner during a trial, notify the IRB immediately Must state that risks for prisoner in this study same as for a non-prisoner Prisoners, due to the lack of control of their circumstances are considered vulnerable 18
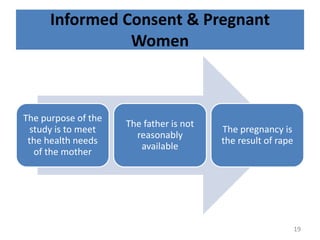
- 19. Informed Consent & Pregnant Women The purpose of the study is to meet the health needs of the mother The father is not reasonably available The pregnancy is the result of rape 19
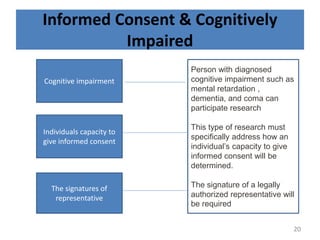
- 20. Informed Consent & Cognitively Impaired Cognitive impairment Individuals capacity to give informed consent The signatures of representative Person with diagnosed cognitive impairment such as mental retardation , dementia, and coma can participate research This type of research must specifically address how an individualâs capacity to give informed consent will be determined. The signature of a legally authorized representative will be required 20
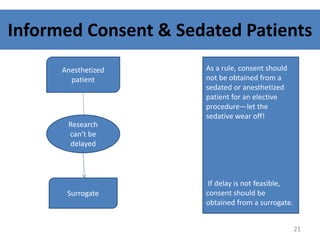
- 21. Informed Consent & Sedated Patients Anesthetized patient Research canât be delayed Surrogate As a rule, consent should not be obtained from a sedated or anesthetized patient for an elective procedureâlet the sedative wear off! If delay is not feasible, consent should be obtained from a surrogate. 21
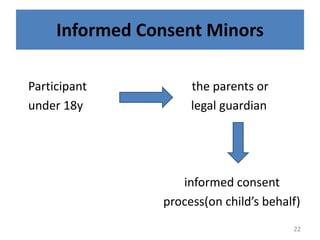
- 22. Informed Consent Minors Participant the parents or under 18y legal guardian informed consent process(on childâs behalf) 22
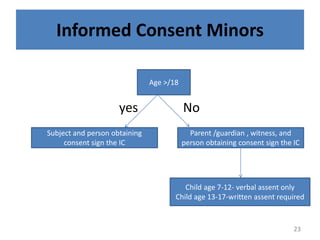
- 23. Informed Consent Minors yes No Age >/18 Subject and person obtaining consent sign the IC Parent /guardian , witness, and person obtaining consent sign the IC Child age 7-12- verbal assent only Child age 13-17-written assent required 23
- 24. Waiver of Informed Consent âĒ Waiving (omitting) or altering some or all the basic elements of informed consent, including the entire informed consent process : ïž Minimal risk ïž Rights and welfare of participants protected ïž Research not possible without a waiver ïž Appropriate information provided 24
- 25. Revocation and Telephone Consent Revocation of Consent Telephone consents are acceptable, but they must be well documented. Patient may revoke at any time, either orally or in writing Telephone Consent 25
- 26. Informed Consent in a Teaching Situation âĒ Have the attending physician and house staff visit the patient together, prior to the procedure. Clarify the residentâs role in the procedure to the patient and his/her family. âĒ Spell out the residentâs qualifications to reinforce patient confidence. âĒ Clarify that the attending physician will be present at all times in a directly supervisory capacity and that he/she is the responsible doctor. âĒ Inform the patient of the identity of personnel in the operating room. âĒ Prepare for some patients to insist on the attending physician performing the procedure. Informed Consent in a Teaching Situation 26
- 27. Informed consent guidelines âĒ ICMR (Indian Council of Medical Research) âEthical Guidelines for Biomedical Research on Human Subjectsâ Published in 2000 and revised in 2006 âĒ ICH Guidelines E6 section 4.8 under GLP (Good Clinical Practice) 27
- 28. Information provision and sharing by research team Discussion and interaction between researchers and potential participants True understanding Acceptance or rejection of participation Agreement to participate End of contract Follow up 28
- 29. SUMMARY âĒ An informed Consent Process should be performed and documented in the manner that is : ïž Clear ïž Complete ïž Accurate 29
- 30. 30