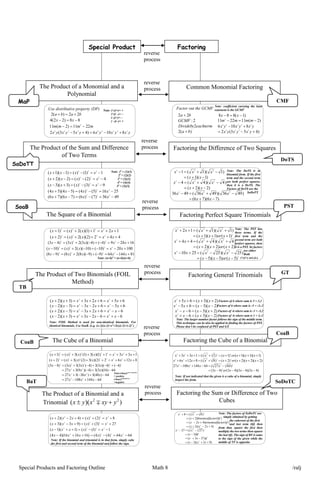
Special Products and Factoring , Rational Algebraic Expressions Concept Map
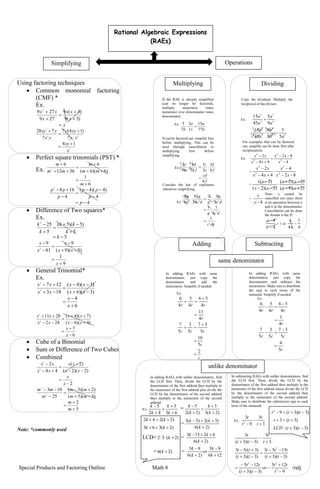
- 1. Special Products and Factoring Outline Math 8 /ralj Special Product Factoring The Product of a Monomial and a Polynomial The Product of the Sum and Difference of Two Terms The Square of a Binomial The Product of Two Binomials (FOIL Method) The Cube of a Binomial The Product of a Binomial and a Trinomial ))(( 22 yxyxyx ’Ć½’é▒ ’üŁ Common Monomial Factoring Factoring the Difference of Two Squares Factoring Perfect Square Trinomials Factoring General Trinomials Factoring the Cube of a Binomial Factoring the Sum or Difference of Two Cubes reverse process MaP SaDoTT SoaB TB CoaB BaT CMF DoTS PST GT CoaB SoDoTC reverse process baba 22)(2 ’Ć½’ĆĮ’Ć½ 88)22(4 ’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ĆŁ xx mmmm 2211)2(11 2 ’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ĆŁ yxyxyxyxyxyx 325462333 8106)453(2 ’Ć½’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’Ć½’ĆŁ Use distributive property (DP) Note: (+)(+)= + (+)( ŌĆō)= ŌĆō (ŌĆō)(+)= ŌĆō ( ŌĆō)(ŌĆō)= + 1)1()()1)(1( 222 ’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ĆŁ’Ć½ xxxx 4)2()()2)(2( 222 ’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ĆŁ’Ć½ xxxx 9)3()()3)(3( 222 ’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’Ć½’ĆŁ xxxx 2516)5()4()54)(54( 222 ’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ĆŁ’Ć½ xxxx 4936)7()6()76)(76( 222 ’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ĆŁ’Ć½ xxxx Note: 12 = (1)(1) 22 = (2)(2) 32 = (3)(3) 42 = (4)(4) 52 = (5)(5) 121)1)((2)()1( 2222 ’Ć½’Ć½’ĆĮ’Ć½’Ć½’ĆĮ’Ć½ xxxxx 442)2)((2)()2( 2222 ’Ć½’Ć½’ĆĮ’Ć½’Ć½’ĆĮ’Ć½ xxxxx 16249)4()4)(3(2)3()43( 2222 ’Ć½’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ĆŁ’Ć½’ĆŁ’Ć½’ĆĮ’ĆŁ xxxxx 10020)10()10)((2)()10( 2222 ’Ć½’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ĆŁ’Ć½’ĆŁ’Ć½’ĆĮ’ĆŁ xxxxx 8114464)9()9)(8(2)8()98( 2222 ’Ć½’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ĆŁ’Ć½’ĆŁ’Ć½’ĆĮ’ĆŁ xxxxx Note: (a+b)2 = (a+b)(a+b) reverse process reverse process reverse process reverse process reverse process 65623)3)(2( 22 ’Ć½’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’Ć½’ĆŁ’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ĆŁ’ĆŁ xxxxxxx 65623)3)(2( 22 ’Ć½’Ć½’ĆĮ’Ć½’Ć½’Ć½’ĆĮ’Ć½’Ć½ xxxxxxx 6623)3)(2( 22 ’ĆŁ’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’Ć½’Ć½’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ĆŁ’Ć½ xxxxxxx 6623)3)(2( 22 ’ĆŁ’Ć½’ĆĮ’ĆŁ’ĆŁ’Ć½’ĆĮ’Ć½’ĆŁ xxxxxxx Note: FOIL Method is used for non-identical binomials. For identical binomials, Use SoaB. (e.g. (x-2)(x-2)=x2 +2(x)(-2)+(-2)2 ) 1331)1)((3)1()(3)()1( 2332233 ’Ć½’Ć½’Ć½’ĆĮ’Ć½’Ć½’Ć½’ĆĮ’Ć½ xxxxxxx 81262)2)((3)2()(3)()2( 2332233 ’Ć½’Ć½’Ć½’ĆĮ’Ć½’Ć½’Ć½’ĆĮ’Ć½ xxxxxxx 6414410827 64)48(3)36(327 64)16)(3(3)4)(9(327 )4()4)(3(3)4()3(3)3()43( 23 23 23 32233 ’ĆŁ’Ć½’ĆŁ’ĆĮ ’ĆŁ’Ć½’ĆŁ’Ć½’ĆĮ ’ĆŁ’Ć½’ĆŁ’Ć½’ĆĮ ’ĆŁ’Ć½’ĆŁ’Ć½’ĆŁ’Ć½’ĆĮ’ĆŁ xxx xxx xxx xxxx Note:(-base)even exponent = positive (-base)oddexponent =negative 8)2()()42)(2( 3332 ’Ć½’ĆĮ’Ć½’ĆĮ’Ć½’ĆŁ’Ć½ xxxxx 27)3()()93)(3( 3332 ’Ć½’ĆĮ’Ć½’ĆĮ’Ć½’ĆŁ’Ć½ xxxxx 1)1()()1)(1( 3332 ’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’Ć½’Ć½’ĆŁ xxxxx 6464)4()4()161616)(44( 3332 ’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’Ć½’Ć½’ĆŁ xxxxx Note: If the binomial and trinomial is in that form, simply cube the first and second term of the binomial and follow the sign. Factor out the GCMF )(2 2 2: 22 ba eachtermDivideby GCMF ba ’Ć½ ’Ć½ )1(888 ’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ĆŁ xx )2(112211 2 ’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ĆŁ mmmm )453(2 8106 2333 32546 ’Ć½’ĆŁ’ĆĮ ’Ć½’ĆŁ yxyxyx yxyxyx Note: coefficient carrying the least exponent is the GCMF )1)(1( )1)(1(1 222 ’ĆŁ’Ć½’ĆĮ ’ĆŁ’Ć½’ĆĮ’ĆŁ xx xxx )2)(2( )4)(4(4 222 ’ĆŁ’Ć½’ĆĮ ’ĆŁ’Ć½’ĆĮ’ĆŁ xx xxx )76)(76( )4936)(4936(4936 222 ’ĆŁ’Ć½’ĆĮ ’ĆŁ’Ć½’ĆĮ’ĆŁ xx xxx Note: The DoTS is in binomial form. If the first term and the second term are both perfect squares, then it is a DoTS. The Factors of DoTS are the SaDoTT. 2 222 )1()1)(1( )1)(1(12 ’Ć½’Ć½’Ć½’ĆĮ ’Ć½’Ć½’ĆĮ’Ć½’Ć½ xorxx xxxx 2 222 )2()2)(2( )4)(4(44 ’Ć½’Ć½’Ć½’ĆĮ ’Ć½’Ć½’ĆĮ’Ć½’Ć½ xorxx xxxx 2 222 )5()5)(5( )25)(25(2510 ’ĆŁ’ĆŁ’ĆŁ’ĆĮ ’ĆŁ’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’Ć½’ĆŁ xorxx xxxx Note: The PST has three terms. If the first term and the second term are both perfect squares, then it is a PST. Its factors are either Both (+)(+) or(-)(-) )2)(3(652 ’Ć½’Ć½’ĆĮ’Ć½’Ć½ xxxx )2)(3(652 ’ĆŁ’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’Ć½’ĆŁ xxxx )2)(3(62 ’Ć½’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ĆŁ’ĆŁ xxxx )2)(3(62 ’ĆŁ’Ć½’ĆĮ’ĆŁ’Ć½ xxxx Factors of 6 where sum is 5 = 3,2 Factors of 6 where sum is -5 = -3,-2 Factors of -6 where sum is -1 = -3,2 Factors of -6 where sum is 1 = 3,-2 Note: The larger number factor follows the sign of the middle term. This technique can be also be applied in finding the factors of PST. Please donŌĆÖt be confused of PST and GT. )1)(1)(1()1()1(133 3333 323 ’Ć½’Ć½’Ć½’Ć½’ĆĮ’Ć½’ĆĮ’Ć½’Ć½’Ć½ xxxorxxxxx )2)(2)(2()2()8(8126 3333 323 ’Ć½’Ć½’Ć½’Ć½’ĆĮ’Ć½’ĆĮ’Ć½’Ć½’Ć½ xxxorxxxxx )43)(43)(43()43( )6427(6414410827 3 333 323 ’ĆŁ’ĆŁ’ĆŁ’ĆŁ’ĆĮ ’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ĆŁ’Ć½’ĆŁ xxxorx xxxx Note: If not indicated that the given is a cube of a binomial, simply inspect the form. )42)(2( )()42( )()2( )8(8 2 333 33 ’Ć½’ĆŁ’Ć½’ĆĮ ’Ć½’ĆŁ’ĆĮ ’Ć½’ĆĮ ’Ć½’ĆĮ’Ć½ xxx tfactortrinomialfxx bfctorbinomialfax xx )93)(3( )273( )3( )27(27 2 333 33 ’Ć½’Ć½’ĆŁ’ĆĮ ’ĆŁ’Ć½’ĆĮ ’ĆŁ’ĆĮ ’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ĆŁ xxx tfxx bfx xx Note: The factors of SoDoTC are simply obtained by getting the cuberoot of the first and last term (bf) then from that, square the first then multiply the two terms then square the last (tf). The sign of BF is same to the sign of the given while the middle of TF is opposite.
- 2. Special Products and Factoring Outline Math 8 /ralj Using factoring techniques ’éĘ Common monomial factoring (CMF) * Ex. x x xx x xx ’ĆĮ ’Ć½ ’Ć½ ’ĆĮ ’Ć½ ’Ć½ )3(9 )3(9 279 279 2 2 22 2 14 7 )14(7 7 728 x xy xy xyy yx yxy ’Ć½ ’ĆĮ ’āŚ ’Ć½ ’ĆĮ ’Ć½ ’éĘ Perfect square trinomials (PST) * Ex. 6 1 )6)(6( 6 3612 6 2 ’Ć½ ’ĆĮ ’Ć½’Ć½ ’Ć½ ’ĆĮ ’Ć½’Ć½ ’Ć½ m mm m mm m 4 4 )4)(4( 4 1682 ’ĆŁ’ĆĮ ’ĆŁ ’ĆŁ’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ ’ĆŁ ’Ć½’ĆŁ p p pp p pp ’éĘ Difference of Two squares* Ex. 5 5 )5)(5( 5 252 ’ĆŁ’ĆĮ ’Ć½ ’ĆŁ’Ć½ ’ĆĮ ’Ć½ ’ĆŁ k k kk k k 9 1 )9)(9( 9 81 9 2 ’Ć½ ’ĆĮ ’ĆŁ’Ć½ ’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ ’ĆŁ ’ĆŁ x xx x x x ’éĘ General Trinomial* Ex. 6 4 )3)(6( )3)(4( 183 127 2 2 ’Ć½ ’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ ’ĆŁ’Ć½ ’ĆŁ’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ ’ĆŁ’Ć½ ’Ć½’ĆŁ x x xx xx xx xx 6 7 )4)(6( )7)(4( 242 2811 2 2 ’ĆŁ ’Ć½ ’ĆĮ ’Ć½’ĆŁ ’Ć½’Ć½ ’ĆĮ ’ĆŁ’ĆŁ ’Ć½’Ć½ x x xx xx xx xx ’éĘ Cube of a Binomial ’éĘ Sum or Difference of Two Cubes ’éĘ Combined 2 )2)(2( )2( 44 2 2 2 ’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ ’ĆŁ’ĆŁ ’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ ’Ć½’ĆŁ ’ĆŁ x x xx xx xx xx 5 2 )5)(5( )2)(5( 25 103 2 2 ’Ć½ ’Ć½ ’ĆĮ ’ĆŁ’Ć½ ’Ć½’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ ’ĆŁ ’ĆŁ’ĆŁ m m mm mm m mm Note: *commonly used Rational Algebraic Expressions (RAEs) Simplifying Operations Multiplying Dividing Adding Subtracting unlike denominator If the RAE is already simplified (can no longer be factored), multiply numerator times numerator over denominator times denominator. Ex: b aa b 77 15 11 3 7 5 ’ĆĮ’āŚ If can be factored out, simplify first before multiplying. This can be used through cancellation or multiplying first before simplifying. Ex: f cd f d e c f d e c 8 4 1 2 1 12 3 10 5 ’ĆĮ ’āŚ’ĆĮ’āŚ 1 2 1 4 Consider the law of exponents whenever simplifying. Ex: dgc dcg dc g gdc g g g 5 5 5253 1 1 11 2 12 24 12 4 8 ’ĆĮ ’āŚ’ĆĮ ’āŚ’ĆĮ’āŚ Copy the dividend. Multiply the reciprocal of the divisor. Ex: 4 7 5 3 9 5 45 15 a a a a ’éĖ 7 4 5 3 5 9 45 15 a a a a ’āŚ = 5 5 3 a Ex: 4 82 44 2 2 2 2 2 ’ĆŁ ’ĆŁ’ĆŁ ’éĖ ’Ć½’ĆŁ ’ĆŁ x xx xx xx = 82 4 44 2 2 2 2 2 ’ĆŁ’ĆŁ ’ĆŁ ’āŚ ’Ć½’ĆŁ ’ĆŁ xx x xx xx = )2)(4( )2)(2( )2)(2( )2( ’Ć½’ĆŁ ’ĆŁ’Ć½ ’āŚ ’ĆŁ’ĆŁ ’ĆŁ xx xx xx xx = 4’ĆŁx x 1 3 3 1 5 For examples that can be factored out, simplify can be done first after reciprocation. Note: x cannot be cancelled out since there is an operation between x and 4 in the denominator. Cancellation can be done the format is the ff: 4 4 ’ĆŁ ’ĆŁ x x = 1 or x x 4 = 4 1 In adding RAEs with same denominator, just copy the denominator and add the numerators. Simplify if needed. In adding RAEs with same denominator, just copy the denominator and subtract the numerators. Make sure to distribute the sign to each terms of the minuend. Simplify if needed.Ex: r rrr 4 11 4 56 4 5 4 6 ’ĆĮ ’Ć½ ’ĆĮ’Ć½ c c ccc 2 5 10 5 37 5 3 5 7 ’ĆĮ ’ĆĮ ’Ć½ ’ĆĮ’Ć½ Ex: r rrr 4 1 4 56 4 5 4 6 ’ĆĮ ’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ’ĆŁ c ccc 5 4 5 37 5 3 5 7 ’ĆĮ ’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ’ĆŁ In adding RAEs with unlike denominators, find the LCD first. Then, divide the LCD by the denominator of the first addend then multiply to the numerator of the first addend plus divide the LCD by the denominator of the second addend then multiply to the numerator of the second addend. In subtracting RAEs with unlike denominators, find the LCD first. Then, divide the LCD by the denominator of the first addend then multiply to the numerator of the first addend minus divide the LCD by the denominator of the second addend then multiply to the numerator of the second addend. Make sure to distribute the subtraction sign to each term of the minuend. Ex. 63 3 42 5 ’Ć½ ’Ć½ ’Ć½ ’Ć½ ’ĆŁ k k k k = )2(3 3 )2(2 5 ’Ć½ ’Ć½ ’Ć½ ’Ć½ ’ĆŁ k k k k )2(363 )2(242 ’Ć½’ĆĮ’Ć½ ’Ć½’ĆĮ’Ć½ kk kk = )2(6 )3(2)5(3 ’Ć½ ’Ć½’Ć½’ĆŁ k kk LCD= )2(32 ’Ć½’āŚ’āŚ k = )2(6 62153 ’Ć½ ’Ć½’Ć½’ĆŁ k kk = )2(6 ’Ć½k = 126 95 )2(6 95 ’Ć½ ’ĆŁ ’Ć½ ’ĆŁ k k or k k Ex. 3 5 9 3 2 ’Ć½ ’ĆŁ ’ĆŁ t t t t )3)(3(: )3(3 )3)(3(92 ’ĆŁ’Ć½ ’Ć½’ĆĮ’Ć½ ’ĆŁ’Ć½’ĆĮ’ĆŁ ttLCD tt ttt 9 125 )3)(3( 125 )3)(3( 1553 )3)(3( )3(53 3 5 )3)(3( 3 2 22 2 ’ĆŁ ’Ć½ ’ĆŁ ’ĆŁ’Ć½ ’ĆŁ’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ ’ĆŁ’Ć½ ’ĆŁ’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ ’ĆŁ’Ć½ ’Ć½’ĆŁ ’Ć½ ’ĆŁ ’ĆŁ’Ć½ t tt or tt tt tt ttt tt ttt t t tt t same denominator