Species Presentation- Cheetah's
- 1. Ecology and Conservation (Acinonyx jubatus)
- 2. Population NOT EVALUATED [NE] DATA DEFICIENT [DD] LEAST CONCERN [LC] NEAR THREATENED [NT] VULNERABLE [VU] ENDANGERED [EN] CRITICALLY ENDANGERED [CR] EXTINCT IN THE WILD [EW] EXTINCT [EX] CONSERVATION STATUS Estimated 6,700 surviving individuals (IUCN, 2015) Eastern <2000 Southern >4000 Western, Central & Northern <500 Less than 500 found in non- African countries The ‘Asiatic cheetah’ is critically endangered Iran >70 Not to Scale
- 3. Biology of the Cheetah Evolved for speed over aggression Rely on speed and skill to survive Can reach their top speed of 70mph in 3 seconds
- 4. Threats & Solutions Media influence Anti-poaching laws Wildlife reserves Land preserved for cheetah’s- protection from humans Breeding programmes Conflict with humans Loss of habitat as a result of human encroachment Decline in amount of prey Cub mortality as a result of carnivore predators Inbreeding
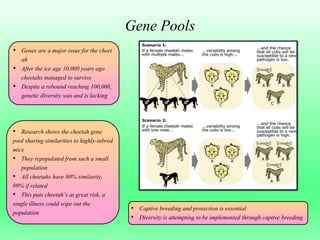
- 5. Gene Pools • Genes are a major issue for the cheet ah • After the ice age 10,000 years ago cheetahs managed to survive • Despite a rebound reaching 100,000, genetic diversity was and is lacking • Research shows the cheetah gene pool sharing similarities to highly-inbred mice • They repopulated from such a small population • All cheetahs have 80% similarity, 99% if related • This puts cheetah’s at great risk, a single illness could wipe out the population • Captive breeding and protection is essential • Diversity is attempting to be implemented through captive breeding
- 6. Conservation An interesting method of conservation for cheetahs is to pair the species with dogs One way to fulfil the cheetah’s instincts is by staging a hunt Additionally, ‘boomer balls’ are also used so animals can stalk and pounce on to satisfy urges


![Population
NOT
EVALUATED
[NE]
DATA
DEFICIENT
[DD]
LEAST
CONCERN
[LC]
NEAR
THREATENED
[NT]
VULNERABLE
[VU]
ENDANGERED
[EN]
CRITICALLY
ENDANGERED
[CR]
EXTINCT IN
THE WILD
[EW]
EXTINCT
[EX]
CONSERVATION
STATUS
Estimated 6,700 surviving individuals (IUCN, 2015)
Eastern
<2000
Southern
>4000
Western,
Central &
Northern
<500
Less than 500 found in non-
African countries
The ‘Asiatic cheetah’ is
critically endangered
Iran
>70
Not to Scale](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cheetahpresentation-160426152311/85/Species-Presentation-Cheetah-s-2-320.jpg)