Speech Compression using LPC
- 1. SPEECH COMPRESSION USING LPC Prepared By, Disha Modi, Roll No: 15MECC12, M.Tech (Communication), Electronics and Communication Department, NU-IT
- 2. Table of Content ŌĆó Objective ŌĆó Introduction to LPC ŌĆó LPC system implementation ŌĆó Applications ŌĆó Simulation results ŌĆó Conclusion
- 3. Objective: ŌĆó The past decade has observed progress towards the submission of low-rate speech coders to public and military communications. ŌĆó In cellular telephony standards, service providers are unceasingly met with the challenge of accommodating more users within a limited allocated bandwidth in mobile communication services. ŌĆó For this object, service providers are constantly in search of low bit-rate speech coders that deliver high-quality speech.
- 4. Introduction to LPC ŌĆó Human speech is produced in the vocal tract. The linear predictive coding (LPC) model is based on the vocal tract characterized by this tube of a varying diameter and it represented in mathematical approximation. ŌĆó The important facet of LPC is the linear predictive filter which determines the value of the next sample by a linear combination of previous samples. ŌĆó One important thing about speech production is that mechanically there is a high correlation between adjacent samples of speech. ŌĆó It is a lossy form of compression.
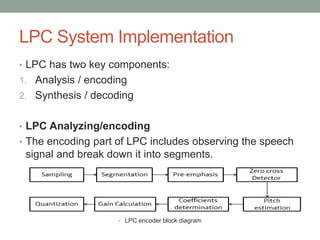
- 5. LPC System Implementation ŌĆó LPC has two key components: 1. Analysis / encoding 2. Synthesis / decoding ŌĆó LPC Analyzing/encoding ŌĆó The encoding part of LPC includes observing the speech signal and break down it into segments. ŌĆó LPC encoder block diagram
- 6. LPC System Implementation ...(contŌĆÖd) ’ü▒Input speech: Under the normal situation, the input signal is sampled at a rate of 8000 samples per second. This input signal is then break down into approx. 180 sample segments and it is transmitted to the receiver. This means that each segment represents 22.5 milliseconds of the input speech signal. ’ü▒Voice/Unvoiced Determination: It is important to determine if a segment is voiced or unvoiced because voiced sounds have a distinct waveform then unvoiced sounds. The LPC encoder informs the decoder if a signal segment is voiced or unvoiced by sending a single bit.
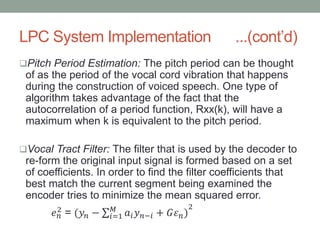
- 7. LPC System Implementation ...(contŌĆÖd) ’ü▒Pitch Period Estimation: The pitch period can be thought of as the period of the vocal cord vibration that happens during the construction of voiced speech. One type of algorithm takes advantage of the fact that the autocorrelation of a period function, Rxx(k), will have a maximum when k is equivalent to the pitch period. ’ü▒Vocal Tract Filter: The filter that is used by the decoder to re-form the original input signal is formed based on a set of coefficients. In order to find the filter coefficients that best match the current segment being examined the encoder tries to minimize the mean squared error. ØæÆ Øæø 2 = (Øæ”Øæø ŌłÆ Øæ¢=1 ØæĆ ØæÄØæ¢ Øæ” ØæøŌłÆØæ¢ + ØÉ║Ø£Ć Øæø) 2
- 8. LPC System Implementation ...(contŌĆÖd) ŌĆó Øææ ØææØæÄ ØæŚ E[(Øæ”Øæø ŌłÆ Øæ¢=1 ØæĆ ØæÄØæ¢ Øæ” ØæøŌłÆØæ¢ + ØÉ║Ø£Ć Øæø) 2 ]=0 ŌĆó -2E[(Øæ”Øæø ŌłÆ Øæ¢=1 ØæĆ ØæÄØæ¢ Øæ” ØæøŌłÆØæ¢ + ØÉ║Ø£Ć Øæø)Øæ” ØæøŌłÆØæŚ]=0 ŌĆó Øæ¢=1 ØæĆ ØæÄØæ¢ ØÉĖ Øæ” ØæøŌłÆØæ¢ Øæ” ØæøŌłÆØæŚ = ØÉĖ Øæ” ØæøŌłÆØæ¢ Øæ” ØæøŌłÆØæŚ ŌĆó In autocorrelation, each E Øæ” ØæøŌłÆØæ¢ Øæ” ØæøŌłÆØæŚ is converted into an autocorrelation function of the form Ryy(k) can be expressed as follows. ŌĆó Using Ryy(k), the M equations that were acquired can be written in matrix form RA = P where A is filter coefficients
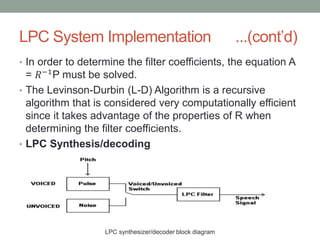
- 9. LPC System Implementation ...(contŌĆÖd) ŌĆó In order to determine the filter coefficients, the equation A = ØæģŌłÆ1P must be solved. ŌĆó The Levinson-Durbin (L-D) Algorithm is a recursive algorithm that is considered very computationally efficient since it takes advantage of the properties of R when determining the filter coefficients. ŌĆó LPC Synthesis/decoding LPC synthesizer/decoder block diagram
- 10. LPC System Implementation ...(contŌĆÖd) ŌĆó The process of decoding a sequence of speech segments is the reverse of the encoding process. Each segment is decoded individually. ŌĆó Each segment of speech has a different LPC filter that is eventually produced using the reflection coefficients and the gain that are received from the encoder. ŌĆó The final step of decoding a segment of speech is to pass the excitement signal through the filter to produce the synthesized speech signal.
- 11. Applications ŌĆó Standard telephone systems ŌĆó Voice mail systems ŌĆó Telephone auto answering machines ŌĆó Text to speech synthesis ŌĆó Multimedia ŌĆó Used in the tonal analysis of violins and other stringed musical instruments ŌĆó SILK audio codec ŌĆó other lossless audio codecs
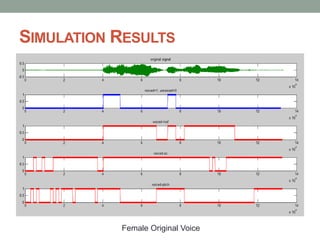
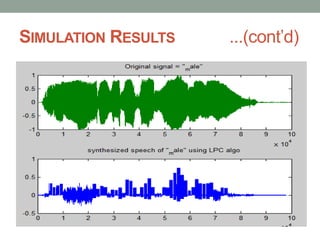
- 12. SIMULATION RESULTS Female Original Voice
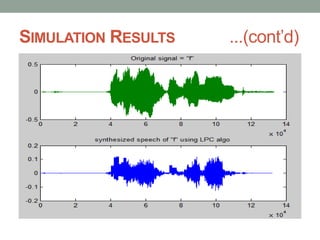
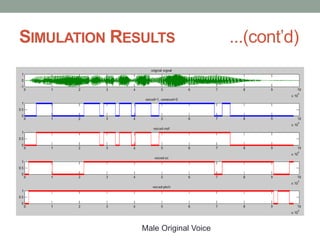
- 14. SIMULATION RESULTS ...(contŌĆÖd) Male Original Voice
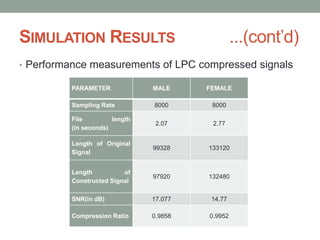
- 16. SIMULATION RESULTS ...(contŌĆÖd) ŌĆó Performance measurements of LPC compressed signals PARAMETER MALE FEMALE Sampling Rate 8000 8000 File length (in seconds) 2.07 2.77 Length of Original Signal 99328 133120 Length of Constructed Signal 97920 132480 SNR(in dB) 17.077 14.77 Compression Ratio 0.9858 0.9952
- 17. SIMULATION RESULTS ...(contŌĆÖd) ŌĆó Looking at the SNR computed in Table, it is obvious that both male and female sounds are noisy as they have a low SNR value. ŌĆó It observed that for all levels of compression the quality is better with male signal than female signal. ŌĆó On the other hand the compression factor with female signal has larger values comparable with these of male signal. This result is expected because the female voice has more high frequencies than male voice. ŌĆó It has observed that no further enhancements can be achieved beyond certain level of decomposition for both signals.
- 18. Conclusion ŌĆó Linear Predictive Coding is an analysis/synthesis technique to lossy speech compression that attempts to model the human production of sound instead of transmitting an estimate of the sound wave. Linear predictive coding achieves a bit rate of 2400 bits/second from 8000vbits/second in cellular communication which makes it ideal for use in secure telephone systems. Secure telephone systems are more concerned that the content and meaning of speech, rather than the quality of speech, be preserved.
- 19. Thank You!
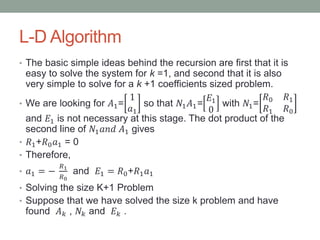
- 20. L-D Algorithm ŌĆó The basic simple ideas behind the recursion are first that it is easy to solve the system for k =1, and second that it is also very simple to solve for a k +1 coefficients sized problem. ŌĆó We are looking for ØÉ┤1= 1 ØæÄ1 so that Øæü1 ØÉ┤1= ØÉĖ1 0 with Øæü1= Øæģ0 Øæģ1 Øæģ1 Øæģ0 and ØÉĖ1 is not necessary at this stage. The dot product of the second line of Øæü1 ØæÄØæøØææ ØÉ┤1 gives ŌĆó Øæģ1+Øæģ0 ØæÄ1 = 0 ŌĆó Therefore, ŌĆó ØæÄ1 = ŌłÆ Øæģ1 Øæģ0 and ØÉĖ1 = Øæģ0+Øæģ1 ØæÄ1 ŌĆó Solving the size K+1 Problem ŌĆó Suppose that we have solved the size k problem and have found ØÉ┤ Øæś , ØæüØæś and ØÉĖ Øæś .
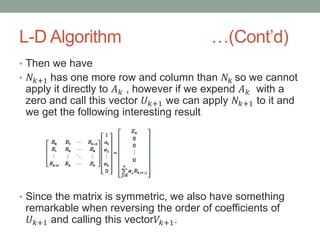
- 21. L-D Algorithm ŌĆ”(ContŌĆÖd) ŌĆó Then we have ŌĆó ØæüØæś+1 has one more row and column than ØæüØæś so we cannot apply it directly to ØÉ┤ Øæś , however if we expend ØÉ┤ Øæś with a zero and call this vector Øæł Øæś+1 we can apply ØæüØæś+1 to it and we get the following interesting result ŌĆó Since the matrix is symmetric, we also have something remarkable when reversing the order of coefficients of Øæł Øæś+1 and calling this vectorØæēØæś+1.
- 22. ŌĆó We can notice that a linear combination Øæł Øæś+1 + Ø£å ØæēØæś+1 is of the form wanted for ØÉ┤ Øæś+1 since the first element is a 1 for all values of Ø£å . Now if there was a value of Ø£å for ŌĆó Calculating ØæüØæś+1 (Øæł Øæś+1+Ø£å) gives





![LPC System Implementation ...(contŌĆÖd)
ŌĆó
Øææ
ØææØæÄ ØæŚ
E[(Øæ”Øæø ŌłÆ Øæ¢=1
ØæĆ
ØæÄØæ¢ Øæ” ØæøŌłÆØæ¢ + ØÉ║Ø£Ć Øæø)
2
]=0
ŌĆó -2E[(Øæ”Øæø ŌłÆ Øæ¢=1
ØæĆ
ØæÄØæ¢ Øæ” ØæøŌłÆØæ¢ + ØÉ║Ø£Ć Øæø)Øæ” ØæøŌłÆØæŚ]=0
ŌĆó Øæ¢=1
ØæĆ
ØæÄØæ¢ ØÉĖ Øæ” ØæøŌłÆØæ¢ Øæ” ØæøŌłÆØæŚ = ØÉĖ Øæ” ØæøŌłÆØæ¢ Øæ” ØæøŌłÆØæŚ
ŌĆó In autocorrelation, each E Øæ” ØæøŌłÆØæ¢ Øæ” ØæøŌłÆØæŚ is converted into an
autocorrelation function of the form Ryy(k) can be
expressed as follows.
ŌĆó Using Ryy(k), the M equations that were acquired can be
written in matrix form RA = P where A is filter coefficients](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/89dbd4f2-394f-4eb4-9ed2-f6bfcb10a4a2-160307063424/85/Speech-Compression-using-LPC-8-320.jpg)