Spinal Column and Spinal Cord Injuries.pptx
- 2. Spinal Column and Spinal Cord Injuries
- 3. Objectives At the conclusion of this presentation the participant will be able to: ŌĆó Identify the components of the spine ŌĆó Assess for spine and spinal cord injury ŌĆó Discuss the initial management of the spinal cord injured patient ŌĆó Evaluate the long term needs of the spinal cord injured patient ŌĆó Describe effects of spinal cord injury on the rest of the body
- 4. Epidemiology ŌĆó Approx 12,000 new cases per year ŌĆó Average age 40.7 years ŌĆó 80.7% male ŌĆó Increased incidence among African Americans (27%) and Asians (2%) ŌĆó Most common causes - MVC (41%), Falls, Violence
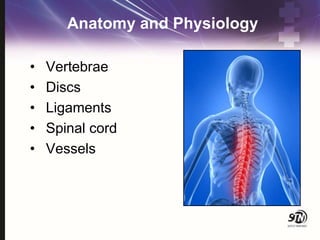
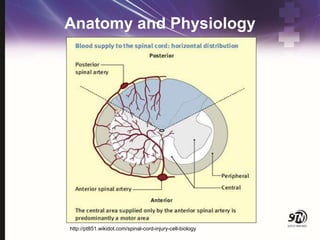
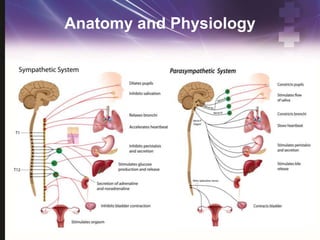
- 5. Anatomy and Physiology ŌĆó Vertebrae ŌĆó Discs ŌĆó Ligaments ŌĆó Spinal cord ŌĆó Vessels
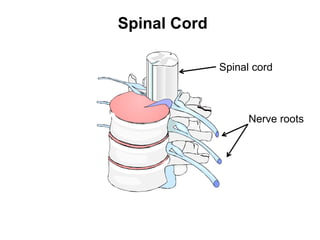
- 9. Spinal Cord Spinal cord Nerve roots
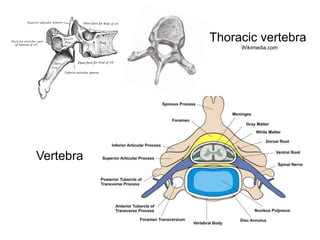
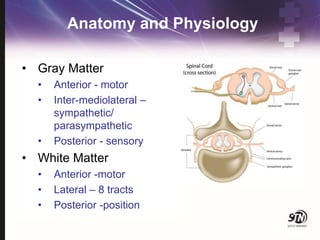
- 10. Anatomy and Physiology ŌĆó Gray Matter ŌĆó Anterior - motor ŌĆó Inter-mediolateral ŌĆō sympathetic/ parasympathetic ŌĆó Posterior - sensory ŌĆó White Matter ŌĆó Anterior -motor ŌĆó Lateral ŌĆō 8 tracts ŌĆó Posterior -position
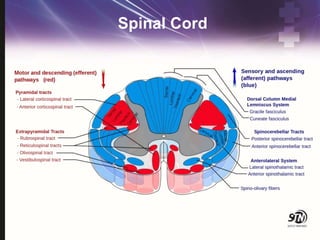
- 11. Spinal Cord
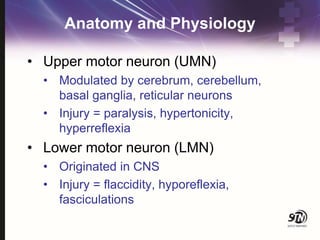
- 12. Anatomy and Physiology ŌĆó Upper motor neuron (UMN) ŌĆó Modulated by cerebrum, cerebellum, basal ganglia, reticular neurons ŌĆó Injury = paralysis, hypertonicity, hyperreflexia ŌĆó Lower motor neuron (LMN) ŌĆó Originated in CNS ŌĆó Injury = flaccidity, hyporeflexia, fasciculations
- 15. Mechanisms of Injury McQuillan, K., Von Rueden, K., Hartsock, R., Flynn, M., & Whalen, E. (eds.). (2002). Trauma Nursing: From Resuscitation Through Rehabilitation. Philadelphia: W. B. Saunders Company. Reprinted with permission.
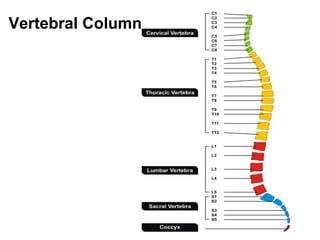
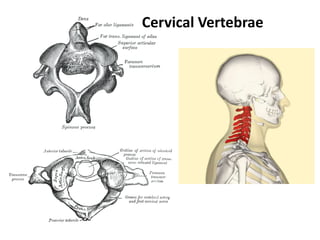
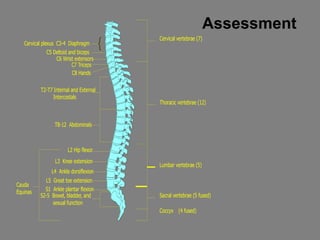
- 17. Assessment Cervical vertebrae (7) Thoracic vertebrae (12) Lumbar vertebrae (5) Sacral vertebrae (5 fused) Coccyx (4 fused) Cervical plexus C3-4 Diaphragm C5 Deltoid and biceps C6 Wrist extensors C8 Hands T2-T7 Internal and External Intercostals T8-12 Abdominals L2 Hip flexor L3 Knee extension L4 Ankle dorsiflexion L5 Great toe extension S1 Ankle plantar flexion S2-5 Bowel, bladder, and sexual function Cauda Equinas
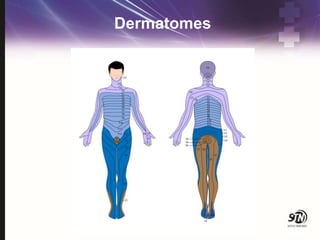
- 18. Dermatomes
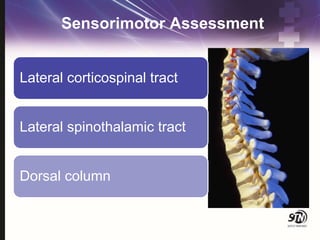
- 19. Sensorimotor Assessment Lateral corticospinal tract Lateral spinothalamic tract Dorsal column
- 20. Reflex Assessment ŌĆó Test for sensory/motor sparing ŌĆó Major deep tendon reflexes (DTR) assessed ŌĆó Biceps (C5) ŌĆó Brachioradialis (C5-6) ŌĆó Triceps (C7-8) ŌĆó Quadriceps (knee-jerk) (L3-4) ŌĆó Achilles (S1-2) ŌĆó Scoring 0 to ++++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++ ++
- 21. Superficial Reflex Assessment Abdominal - umbilicus pulls toward stimulus Cremasteric - scrotum pulls up with stoking inner thigh Bulbocavernosus - anal sphincter contraction with stimulus Superficial anal ŌĆō anal sphincter contraction with stroking peri-anal area Priapism ŌĆō results with tugging on catheter
- 22. Spinal Cord Injury ŌĆó Primary ŌĆó From the time of initial mechanism of injury ŌĆó Secondary ŌĆó Any incidence of hypotension or hypoxia can result in further injury to the spinal cord
- 23. Spinal Cord Injury ŌĆó ASIA Impairment scale ŌĆó Complete (A) ŌĆō lack of motor/sensory function in sacral roots (S4-5) ŌĆó Incomplete (B) ŌĆō sensory preservation, motor loss below injury including S4-5 ŌĆó Incomplete (C) ŌĆō motor preservation below injury, more than ┬Į muscle groups motor strength <3 ŌĆó Incomplete (D) - motor preservation below injury, at least 50% muscle groups motor strength >3 ŌĆó Normal (E) ŌĆō all motor/sensory function present
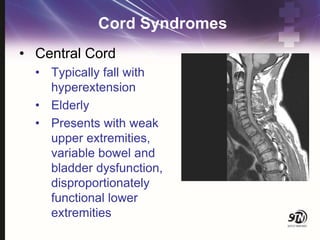
- 24. Cord Syndromes ŌĆó Central Cord ŌĆó Typically fall with hyperextension ŌĆó Elderly ŌĆó Presents with weak upper extremities, variable bowel and bladder dysfunction, disproportionately functional lower extremities
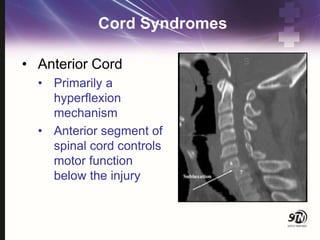
- 25. Cord Syndromes ŌĆó Anterior Cord ŌĆó Primarily a hyperflexion mechanism ŌĆó Anterior segment of spinal cord controls motor function below the injury
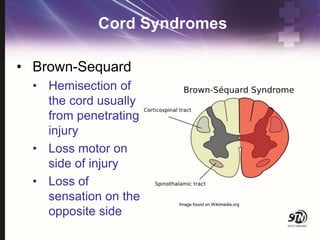
- 26. Cord Syndromes ŌĆó Brown-Sequard ŌĆó Hemisection of the cord usually from penetrating injury ŌĆó Loss motor on side of injury ŌĆó Loss of sensation on the opposite side Image found on Wikimedia.org
- 27. Cord Syndromes ŌĆó Conus Medullaris ŌĆó S4-5 exit at L1; may have L1 fracture ŌĆó Areflexic bowel and bladder, flaccid anal sphincter ŌĆó Variable lower extremity loss ŌĆó Cauda Equina ŌĆó Lumbar sacral nerve roots, with or without fracture ŌĆó Variable loss; areflexia; radicular pain
- 28. Complete Cord Injury ŌĆó Quadriplegia (Tetraplegia) ŌĆó Loss of function below the level of injury ŌĆó Includes sacral roots (bowel and bladder) ŌĆó C1-T1 ŌĆó Paraplegia ŌĆó Loss of function below the level of injury ŌĆó Below T1
- 29. Diagnostics ŌĆó Plain films ŌĆó Lateral, A/P, odontoid; C-T-L spines ŌĆó May be used for rapid identification of gross deformity ŌĆó CT Scan ŌĆó Comprehensive, cervical through sacral ŌĆó Demonstrates degree of compression and cord canal impingement ŌĆó MRI Scan ŌĆó Demonstrates ligamentous, spinal cord injury
- 30. Diagnostics ŌĆó Clearing the Cervical Spine ŌĆó Awake, alert, and oriented ŌĆó NO distracting injuries ŌĆó NO drugs or alcohol that alter experience ŌĆó NO pain or tenderness ŌĆó Clearing spine with films, CT, MRI ŌĆó Complaints of neck pain ŌĆó Neurologic deficit ŌĆó Altered level of consciousness, ventilator
- 31. Fractures-Dislocations ŌĆó Atlanto-occipital dissociation ŌĆó Complete injury; death ŌĆó Atlanto-axial dislocation ŌĆó Complete injury; death ŌĆó Jumped, Jump-locked facets ŌĆó Require reduction; may impinge on cord; unstable due to ligamentous injury
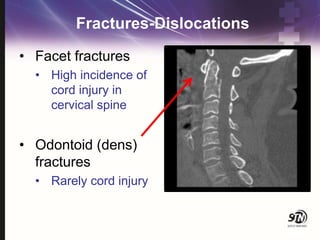
- 32. Fractures-Dislocations ŌĆó Facet fractures ŌĆó High incidence of cord injury in cervical spine ŌĆó Odontoid (dens) fractures ŌĆó Rarely cord injury
- 34. SCIWORA ŌĆó Spinal Cord Injury without Radiographic Abnormality ŌĆó Most frequently children ŌĆó Dislocation occurs with spontaneous relocation ŌĆó Cord injury evident ŌĆó Radiographs negative
- 35. Management ŌĆó Airway ŌĆó C1-4 injuries require definitive airway ŌĆó Injuries below C4 may also require airway due to ŌĆó Work of breathing ŌĆó Weak thoracic musculature ŌĆó Breathing ŌĆó Adequacy of respirations ŌĆó SpO2 ŌĆó Tidal volume ŌĆó Effort ŌĆó Pattern
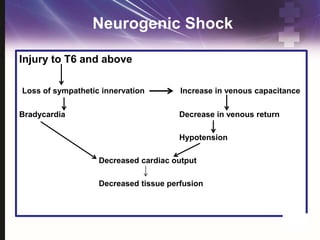
- 36. Management ŌĆó Circulation ŌĆó Neurogenic shock ŌĆó Injuries above T6 ŌĆó Hypotension ŌĆó Bradycardia ŌĆōtreat symptomatic only ŌĆó Warm and dry ŌĆó Poikilothermic ŌĆō keep warm ŌĆó Fluid resuscitation ŌĆó Identify and control any source of bleeding ŌĆó Supplement with vasopressors
- 37. Neurogenic Shock Injury to T6 and above Loss of sympathetic innervation Increase in venous capacitance Bradycardia Decrease in venous return Hypotension Decreased cardiac output Decreased tissue perfusion
- 38. Management ŌĆó Urine output ŌĆó Urinary retention ŌĆó Atonic bladder ŌĆó Foley ŌĆó Initially avoid intermittent catheterization ŌĆó High urine output from resuscitation fluids
- 39. Management ŌĆó Deficit ŌĆó Spinal shock ŌĆó Flaccid paralysis ŌĆó Absence of cutaneous and/or proprioceptive sensation ŌĆó Loss of autonomic function ŌĆó Cessation of all reflex activity below the site of injury ŌĆó Identify level of injury
- 40. Management ŌĆó Pain ŌĆó Frequent physical and verbal contact ŌĆó Explain all procedures to patient ŌĆó Patient-family contact as soon as possible ŌĆó Appropriate short-acting pain medication and sedatives ŌĆó Foster trust
- 41. Management ŌĆó Communication ŌĆó Blink board ŌĆó Adapted call bell system ŌĆó Avoid clicking, provide a better option ŌĆó Speech and occupational therapy ŌĆó Prism glasses ŌĆó Setting limits/boundaries for behavior
- 42. Management ŌĆó Special Treatment ŌĆó Hypothermia ŌĆó Recommends 33oC intravascular cooling ŌĆó Rapid application, Monitor closely ŌĆó Anecdotal papers ŌĆó No peer reviewed/ class I clinical research studies to substantiate ŌĆó High dose methylprednisolone ŌĆó No longer considered standard of care
- 43. Management ŌĆó Pharmacologic agents ŌĆó Lazaroids (21-aminosteroids) ŌĆó Opiate antagonists (Naloxone) ŌĆó EAA receptor antagonists ŌĆó Calcium channel blocker ŌĆó Antioxidants and free radical scavengers ŌĆó Arachidonic acid inhibitors
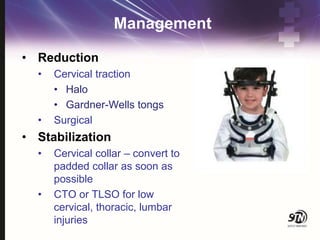
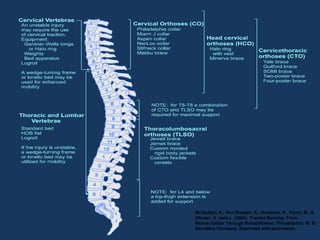
- 44. Management ŌĆó Reduction ŌĆó Cervical traction ŌĆó Halo ŌĆó Gardner-Wells tongs ŌĆó Surgical ŌĆó Stabilization ŌĆó Cervical collar ŌĆō convert to padded collar as soon as possible ŌĆó CTO or TLSO for low cervical, thoracic, lumbar injuries
- 45. McQuillan, K., Von Rueden, K., Hartsock, R., Flynn, M., & Whalen, E. (eds.). (2002). Trauma Nursing: From Resuscitation Through Rehabilitation. Philadelphia: W. B. Saunders Company. Reprinted with permission.
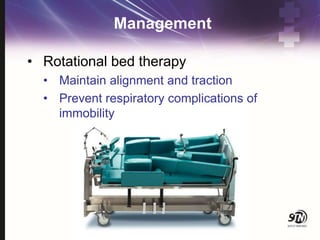
- 46. Management ŌĆó Rotational bed therapy ŌĆó Maintain alignment and traction ŌĆó Prevent respiratory complications of immobility
- 47. Management ŌĆó Surgical ŌĆó Determined by ŌĆó Degree of deficit, location of injury, instability, cord impingement ŌĆó Anterior vs. posterior decompression/ both ŌĆó Emergent ŌĆó Reserved for neurologic deterioration when evidence of cord compression is present ŌĆó SSEP ŌĆōduring procedure to monitor changes ŌĆó Limited to ascending sensory tracts esp.. dorsal columns
- 48. Complication Prevention ŌĆó Respiratory ŌĆó Complications of immobility ŌĆó Atelectasis, Pneumonia ŌĆó Pulmonary embolism ŌĆó Respiratory insufficiency/ failure ŌĆó Level of injury affects phrenic nerve, intercostals ŌĆó Increased work of breathing, fatigue ŌĆó Rate and pattern are altered (accessory muscle use) ŌĆó Monitor breath sounds
- 49. Respiratory Ventilation Early intubation to prevent hypoxia and fatigue C1-4 injuries require tracheostomy and home ventilation training Quad cough training Communication tools Bronchoscopy
- 50. Respiratory ŌĆó Pulmonary management ŌĆó Weaning parameters ŌĆó Monitor SpO2 and ABGs ŌĆó Routine CXR ŌĆó Aggressive pulmonary toilet ŌĆō Postural drainage (PD) ŌĆō Chest physiotherapy (CPT) ŌĆō Kinetic bed therapy ŌĆó Suctioning
- 51. Respiratory ŌĆó Non-ventilated patients ŌĆó Pulmonary function tests ŌĆó Incentive Spirometry ŌĆó Non-invasive ventilation (CPAP, BiPAP) ŌĆó Abdominal binder ŌĆó Early OOB/ mobilization
- 52. Complication Prevention ŌĆó Cardiovascular ŌĆó Neurogenic shock ŌĆó IV fluids ŌĆōincludes vasopressors ŌĆó Atropine or pacing ONLY when bradycardia symptomatic
- 53. Cardiovascular ŌĆó Orthostatic hypotension ŌĆó Decreased BP, possibly increased heart rate, dizziness or lightheadedness, blurred vision, loss of consciousness ŌĆó Provide physical support with hose, abdominal binder; salt tablets; Florinef; sympathomimetics ŌĆó Slowly raise the head of the bed for mobilization ŌĆó Turn slowly ŌĆó Prone to vasovagal response
- 54. Cardiovascular ŌĆó Poikilothermia ŌĆó Inability to shiver/sweat and adjust body temperature ŌĆó Keep patient warm ŌĆó Warm the environment ŌĆó Monitor skin to prevent burns or frostbite from exposure ŌĆó Insensate skin
- 55. Complication Prevention ŌĆó Gastrointestinal ŌĆó Ileus ŌĆó Gastric/ intestinal ulcers ŌĆó Pancreas dysfunction ŌĆó Nutritional deficiencies ŌĆó Constipation/ impaction ŌĆó Cholecystitis
- 56. Gastrointestinal ŌĆó Abdominal distention ŌĆó Nasogatric tube to decompress stomach ŌĆó Monitor bowel sounds ŌĆó Monitor N/G output for bleeding ŌĆó Gastric prophylaxis- ŌĆó Histamine blockers, proton-pump inhibitors, antacids ŌĆó Bowel routine ŌĆó Stool softeners, suppositories; high fiber diet ŌĆó Digital stimulation, fluids, mobilization
- 57. Gastrointestinal ŌĆó Nutrition ŌĆó Early enteral nutrition ŌĆó PO or tube feeding if ventilated ŌĆó Transpyloric tube if slow gastric emptying ŌĆó Hypermetabolic rate ŌĆó Feed as with any critically injured patient
- 58. Complication Prevention ŌĆó Venous thromboembolism ŌĆó Slightly higher risk the first 2-3 months post injury ŌĆó Duplex ultrasonography evaluation ŌĆó Prevention (x 3months) ŌĆó LMWH ŌĆó Apply sequential compression devices ŌĆó Vena cava filter (in patients who cannot be anti- coagulated or have failed anti-coagulation) ŌĆó Monitor for signs and symptoms ŌĆó Early mobilization, hydration
- 59. Complication Prevention ŌĆó Fluid restriction transition to straight cath ŌĆó Condom catheters, SPT ŌĆó Palpate for fullness (approx 5-600ml/4-6hr) Reflexive bladder ŌĆō involuntary contraction
- 60. Urinary ŌĆó Areflexive bladder ŌĆó Valsalva or crede ŌĆó Prone to incontinence/ skin issues ŌĆó Condom catheters, incontinence pads, conduit ŌĆó DSD ŌĆó Results in elevated voiding pressures ŌĆó Annual urodynamic evaluation ŌĆó Pharmacologic management, Surgical intervention (sphincterotomy)
- 61. Urinary Tract Infection ŌĆó Signs and symptoms ŌĆó Fever, spontaneous voiding between catheterizations, Autonomic Dysreflexia, hematuria, cloudy- foul-smelling urine, vague abdominal discomfort, pyuria ŌĆó Prevention ŌĆó Remove indwelling catheter as soon as clinically possible, intermittent cath, hydration
- 62. Urinary Renal calculi ŌĆó Chronic bacteriuria and sediment, long- term indwelling catheters, urinary stasis, chronic calcium loss ŌĆó Signs and symptoms ŌĆō persistent UTI, hematuria, unexplained Autonomic Dysreflexia ŌĆó KUB x-ray, IVP with cystogram, passage of stone ŌĆó Interventions - increased fluid intake, dietary modifications, lithotripsy
- 63. Complication Prevention Skin breakdown ŌĆó Pressure, insensate, dampness ŌĆó PREVENTION ŌĆō frequent turning, specialty beds, remove backboard asap; proper fitting braces ŌĆó Nutrition, mobilization, cushions, massage ŌĆó Early wound care specialist ŌĆó Surgery if deep ŌĆó Can cause delays in stabilization, rehabilitation
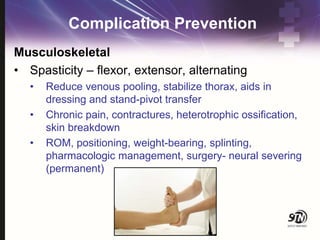
- 64. Complication Prevention Musculoskeletal ŌĆó Spasticity ŌĆō flexor, extensor, alternating ŌĆó Reduce venous pooling, stabilize thorax, aids in dressing and stand-pivot transfer ŌĆó Chronic pain, contractures, heterotrophic ossification, skin breakdown ŌĆó ROM, positioning, weight-bearing, splinting, pharmacologic management, surgery- neural severing (permanent)
- 65. Musculoskeletal Heterotrophic ossification ŌĆó Ectopic bone within connective tissue ŌĆó Below spinal lesion ŌĆó More often complete injuries with spasticity ŌĆó Redness, swelling, warmth, pain, decreased ROM, fever, positive bone scan
- 66. Musculoskeletal Contractures ŌĆó Imbalance of muscle innervation ŌĆó High level cord injury, skin breakdown, concomitant head injury, spasticity, HO, fractures ŌĆó PREVENTION ŌĆō aggressive ROM, mobilization, PT/OT, splinting, positioning, serial casting, anti-spasmodics
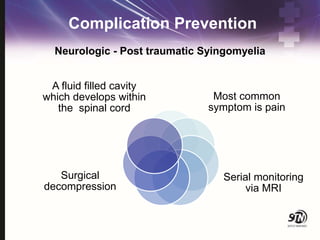
- 67. Complication Prevention A fluid filled cavity which develops within the spinal cord Most common symptom is pain Serial monitoring via MRI Surgical decompression Neurologic - Post traumatic Syingomyelia
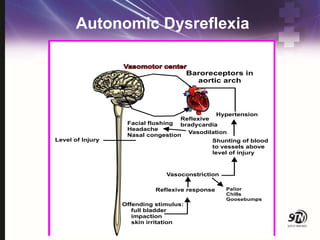
- 68. Complication Prevention Autonomic dysreflexia ŌĆó An uncontrolled, massive sympathetic reflex response to noxious stimuli, below the level of the lesion ŌĆó Precipitating factors ŌĆó Full bladder ŌĆó Distended bowel ŌĆó Skin irritation, ingrown toenail ŌĆó UTI ŌĆó Uterine spasms, penile stimulation ŌĆó Tight clothing, wrinkled sheets
- 70. Autonomic Dysreflexia ŌĆó Sit patient upright to produce orthostatic hypotension ŌĆó Monitor BP every 5 minutes ŌĆó Monitor neurologic status (GCS) ŌĆó Eliminate the offending stimulus ŌĆó Empty bladder, bowel; identify skin lesion ŌĆó Administer anti-hypertensives if the above fails ŌĆó Education ŌĆōfamily and patient
- 71. Psychologic Pain/Depression ŌĆó Nocioceptive ŌĆō noxious stimuli to normally innervated parts ŌĆó Neurogenic ŌĆō nerve tissue injury in CNS or PNS ŌĆó Evaluate for depression associated with pain ŌĆó Counseling, ROM, pharmacologic treatment, TENS
- 72. Sexuality Male sexuality ŌĆó Erection ŌĆō parasympathetic ŌĆó Requires intact sacral reflexes, short- lived ŌĆó Technical aides, pharmacology, prosthesis ŌĆó Ejaculation ŌĆō sympathetic ŌĆó Intrathecal injection, electroejaculation, vibroejaculation ŌĆó Fertility ŌĆō decreased sperm motility and quality ŌĆó Serial ejaculation, in vitro fertilization
- 73. Sexuality Female ŌĆó Lack innervation to pelvic floor ŌĆó Maintain reflex lubrication/ congestion ŌĆó Loss psychogenic/ fantasy response ŌĆó Fertility normal ŌĆó Pregnancy ŌĆō loss of sensation, increased BP, may precipitate AD ŌĆó Decreased respiratory excursion ŌĆó Alter GI/GU management
- 74. Rehabilitation ŌĆó Mobility ŌĆó Tendon transfer ŌĆó Functional electrical stimulation ŌĆó Lower level of injury, more functional ŌĆó Bowel and Bladder Management ŌĆó Prevention of complications
- 75. Summary ŌĆó Spinal cord injury occurrence is decreased with safety equipment use ŌĆó Prevent secondary injury to result in optimal neurologic recovery ŌĆó Spinal column fractures can occur without long term effects ŌĆó Spinal cord injury requires diligence in complication prevention