Spintronics ppt
- 1. Spintronics Ą°A Spin to RememberĄą Submitted To:- Presented By:- Er. Pieush Vyas Abhishek Shringi (Associate Professor) 08/33/106 (Unit In charge EC) VIII Sem ECE
- 2. Outline ? Spintronics basics ? The giant magneto resistance ? Applications of GMR ? Spin devices ? Injections & detection of spin ? The MRAM ? Recent trends
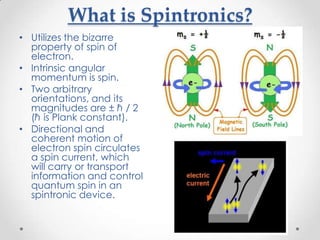
- 3. What is Spintronics? ? Utilizes the bizarre property of spin of electron. ? Intrinsic angular momentum is spin. ? Two arbitrary orientations, and its magnitudes are ĄĀ ? / 2 (? is Plank constant). ? Directional and coherent motion of electron spin circulates a spin current, which will carry or transport information and control quantum spin in an spintronic device.
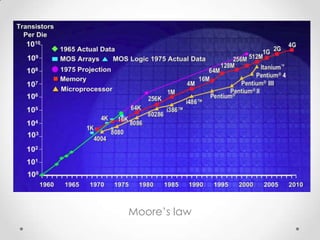
- 4. Why Spintronics? ? MooreĄŊs Law: No. of Transistor doubles in every 18 months. ?Complexity: Complex Chip Design & Power Loss. ? Motivation: Spintronics-Information is carried not by electron charge but by itĄŊs spin.
- 5. MooreĄŊs law
- 6. Combining the best of both worlds Ferro magnets Semiconductors ? Stable Memory ? Bandgap engineering ? Fast switching ? Carrier density & type ? High ordering temp ? Electrical gating ? Long spin lifetime ? Spin transport ? Technological base ? Technological base (Electronics) (magnetic recordings) Can we develop spin based How to create control propagate transistors , switches and logic spin information in semiconductor circuits? structures?
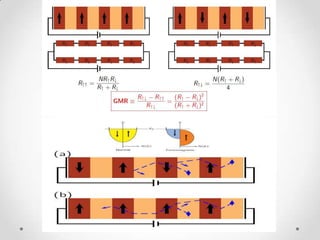
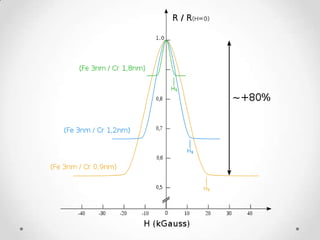
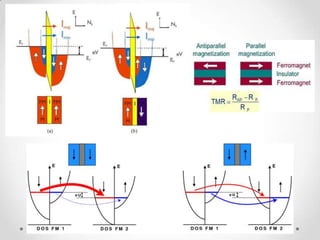
- 7. The Giant Magneto Resistance ? A Nano scale phenomena . ? Giant refers to giant change in resistance due to current. ? It is a quantum mechanical magneto resistance effect observed in thin-film structures composed of alternating ferromagnetic and non-magnetic layers.
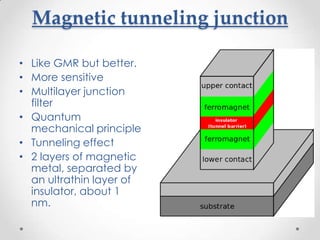
- 10. Magnetic tunneling junction ? Like GMR but better. ? More sensitive ? Multilayer junction filter ? Quantum mechanical principle ? Tunneling effect ? 2 layers of magnetic metal, separated by an ultrathin layer of insulator, about 1 nm.
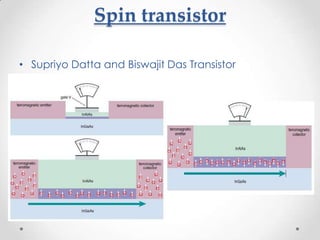
- 12. Spin transistor ? Supriyo Datta and Biswajit Das Transistor
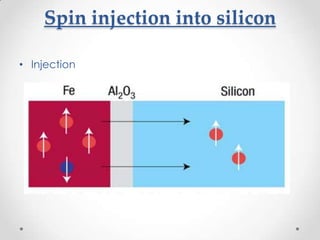
- 13. Spin injection into silicon ? Injection
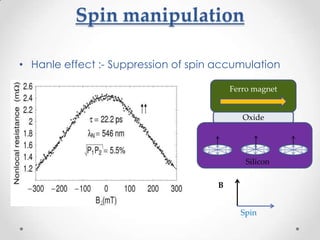
- 14. Spin manipulation ? Hanle effect :- Suppression of spin accumulation Ferro magnet Oxide Silicon B Spin
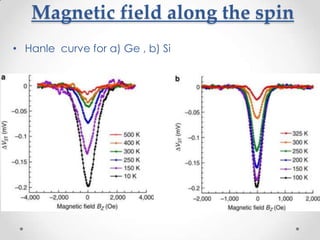
- 15. Magnetic field along the spin ? Hanle curve for a) Ge , b) Si
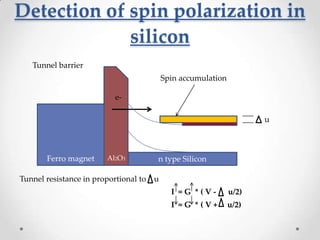
- 16. Detection of spin polarization in silicon Tunnel barrier Spin accumulation e- u Ferro magnet Al2O3 n type Silicon Tunnel resistance in proportional to u I =G *(V- u/2) I =G *(V+ u/2)
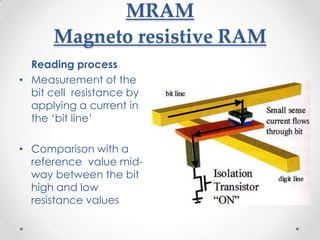
- 17. MRAM Magneto resistive RAM Reading process ? Measurement of the bit cell resistance by applying a current in the ĄŪbit lineĄŊ ? Comparison with a reference value mid- way between the bit high and low resistance values
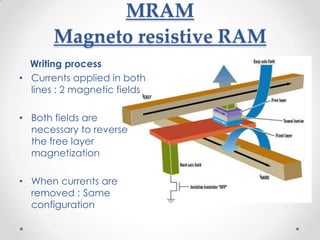
- 18. MRAM Magneto resistive RAM Writing process ? Currents applied in both lines : 2 magnetic fields ? Both fields are necessary to reverse the free layer magnetization ? When currents are removed : Same configuration
- 19. MRAM Magneto resistive RAM Array structure of MRAM ? Reading: transistor of the selected bit cell turned ĄŪonĄŊ + current applied in the bit line ? Writing: transistor of the selected bit cell turned ĄŪoffĄŊ + currents applied in the bit and word lines ? Need of 2 magnetic fields for writing
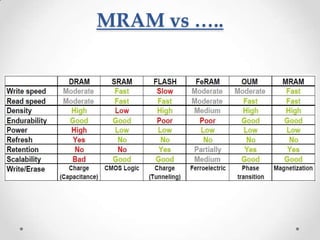
- 20. MRAM vs Ą..
- 21. MRAM Magneto resistive RAM ? MTJ test structures developed at SPINTEC: the die area with 1x5 ĶĖm ? 0.2 ĶĖm width isolated MTJ element after etch
- 22. Advantages of Spintronics ? Low power consumption. ? Less heat dissipation. ? Spintronic memory is non-volatile. ? Takes up lesser space on chip, thus more compact. ? Spin manipulation is faster , so greater read & write speed. ? Spintronics does not require unique and specialized semiconductors. Common metals such as Fe, Al, Ag , etc. can be used.
- 23. Conclusion ? Spin property of electrons are yet to mastered. ? Researcher and scientist are taking keen interest. ? Universities and electronic industries collaborating . ? Span of last two decade major milestones. ? It holds vast opportunities for physics , material & device engineering & technology ? Last year PTB, Germany, have achieved a (2GBit/s) write cycle ? Potential of the field is colossal and continuous development is required.