Sport тАУ related injuries
Download as pptx, pdf3 likes234 views
This document discusses various types of sports-related injuries including contusions, muscle cramps, strains, sprains, wounds, fractures, head injuries, and spinal cord injuries. It provides details on the causes, symptoms, and typical treatments for each type of injury. For example, it notes that muscle cramps can be very painful but typically only last a few minutes, while strains involve tearing of muscle fibers and should be treated using RICE (rest, ice, compression, and elevation). Prevention tips are also outlined such as warming up, stretching, staying hydrated, and using ice packs as needed.
1 of 19
Download to read offline









Ad
Recommended
Contusions & abrasions
Contusions & abrasionssshssomsen
╠¤
Contusions occur when tissue is injured from blunt force trauma, causing blood vessels to rupture and blood to flow into surrounding tissues. Common causes include contact sports, falls, or crushing the area against a hard surface. Symptoms include pain, bruising, swelling, and decreased mobility. Treatment involves rest, ice, compression, and elevation to reduce swelling. As bleeding and swelling subside, heat treatments can be used, and massage and stretching can aid recovery.Bone injuries
Bone injuriesLen Lapore
╠¤
Common injuries to the skeletal system include fractures, sprains, and dislocations. Fractures are broken bones that can be simple (closed), compound (open), comminuted (broken into multiple pieces), or greenstick (partially broken). Sprains are injuries to ligaments around joints caused by sudden twisting or stretching. Dislocations occur when a bone is forced out of its normal position in a joint, causing pain, swelling, and inability to use the affected area.Abrasions
AbrasionsRUCHIT PATEL
╠¤
Abrasions are mechanical injuries to the superficial layers of the skin caused by blunt force friction against a rough surface. There are several types of abrasions including scratches, grazes, pressure abrasions, and impact abrasions. The age of an abrasion can be determined by the color, which ranges from bright red in fresh abrasions to brown or black scabs in older abrasions. Abrasions have forensic importance as the location, pattern, and age can provide clues about the circumstances of injury.Chapter 14 Bone, Joint, and Muscle Injuries
Chapter 14 Bone, Joint, and Muscle Injuriesjgmedina1
╠¤
Bone, joint, and muscle injuries are common. There are several types of bone fractures including closed (intact skin) and open (broken skin). Joint injuries include dislocations where the bone ends are no longer in contact. Muscle injuries include strains from overstretching and contusions from blows. For all injuries, circulation, sensation, and movement should be checked. RICE procedures (rest, ice, compression, and elevation) and splinting injured areas can help reduce pain and swelling while seeking medical care.Wounds
Woundspdhpemag
╠¤
This document discusses different types of wounds, including open wounds like incisions, lacerations, abrasions, and puncture wounds. It also covers closed wounds such as contusions, hematomas, and crushing injuries. The document provides details on treating minor cuts and scrapes, puncture wounds, and major wounds. It lists signs of infection and specific symptoms for different wound types. Finally, it presents the basic five steps for treating any wound: stop bleeding, wash, remove dirt, close skin, and dress the wound.Tendon and ligament injureies
Tendon and ligament injureiesyter chamrane
╠¤
The document outlines the causes, classification, and management of tendon and ligament injuries, including distinctions between sprains and strains. It details treatment protocols such as the RICE method and provides information on related conditions like tendinitis and bursitis. The document emphasizes the importance of appropriate diagnosis and treatment options based on the severity of the injuries.Sports injuries
Sports injuries SyedAnwar60
╠¤
The document details various types of sports injuries, including soft tissue injuries, bone injuries, and joint injuries, along with their causes, symptoms, and prevention methods. It categorizes athletic injuries into acute, overuse, and chronic types, and describes specific injuries such as contusions, strains, sprains, fractures, and dislocations. Additionally, it provides guidelines for injury prevention through proper conditioning, training, and equipment use.Sports injury
Sports injury SyedAnwar60
╠¤
The document outlines common sports injuries, including their causes, symptoms, and first aid treatments. Injuries covered include muscle strains, torn ligaments, shin splints, fractures, and conditions like plantar fasciitis and concussions. It emphasizes the importance of rest, ice, compression, and elevation for treatment and includes prevention strategies to avoid these injuries.Megan Carter - Resume
Megan Carter - ResumeMegan Carter
╠¤
Megan Carter is a computer science student and experienced waitress seeking a new job. She has worked as a waitress at multiple restaurants, as well as in sales, retail, and cashier roles. Carter enjoys interacting with customers and helping people. She is authorized to work in the US and is willing to relocate to Moline or Peoria, Illinois. Carter is currently pursuing an online bachelor's degree in data analysis and programming while maintaining a flexible schedule.Propery transfer
Propery transferXafar ul hak
╠¤
This document discusses different types of property and rules for transferring property ownership. It covers:
1) The two main types of property are real property (land and buildings) and personal property (movable items). The basic goal of a sales contract is to transfer ownership of property from the seller to the buyer.
2) For property to change ownership, it must be specific and in a deliverable state. If goods are unascertained or not ready for delivery, ownership does not transfer.
3) There are some exceptions where a third party can transfer valid ownership, such as through implied authority from the owner, if they are a mercantile agent, or in cases of joint ownership, voidable contractsSimulacro pedagogiafany garzon
╠¤
Este documento presenta un simulacro de la Prueba de Potencialidad Pedag├│gica (PPP) aplicada por la Universidad Pedag├│gica Nacional de Colombia a sus aspirantes. El simulacro consta de 50 preguntas tipo I y II divididas en potenciales cognitivo, psicosocial y comunicativo. El tiempo m├бximo para resolverlo es de 2 horas y 15 minutos. Al final se encontrar├бn las respuestas correctas y su justificaci├│n. El objetivo es ofrecer a los aspirantes mayor informaci├│n sobre la estructura y caracter├нsticas de la prueba de adProbiotcs
ProbiotcssilGERSIL
╠¤
This document discusses various uses of probiotics in different areas of health. It summarizes that probiotics are live microorganisms that have proven beneficial effects on the host's body when given in sufficient amounts. Some key points made include that certain probiotics like Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG and Saccharomyces boulardii can shorten the duration of acute gastroenteritis by 1 day. Probiotics may also help lower bacterial load of H. pylori but cannot eliminate it completely. Probiotics are also discussed in relation to skin health conditions like acne, bone health, urinary tract infections, and C. difficile treatment.nuevas tecnologiasfany garzon
╠¤
El centro de inter├йs ense├▒a a los estudiantes sobre nuevas tecnolog├нas y el uso de hardware y software, incluyendo dispositivos m├│viles, sistemas operativos, correo electr├│nico, redes sociales y aplicaciones educativas. Los estudiantes aprenden a comunicarse y colaborar utilizando herramientas tecnol├│gicas como Google Drive, wikis y YouTube, adem├бs de desarrollar habilidades de pensamiento cr├нtico y resoluci├│n de problemas. El centro de inter├йs fortalece los valores del colegio y contribuye aPharmacology
PharmacologysilGERSIL
╠¤
Pharmacology is the scientific study of drugs and their effects on the human body. It involves investigating how drugs are absorbed, distributed, metabolized and excreted by the body. Pharmacodynamics examines how drugs act on the body and influence physiological functions, while pharmacokinetics studies the fate of drugs in the body over time. Pharmacology also considers drug sources and classifications, therapeutic uses of drugs, dosages, potential adverse effects, and the drug approval process. The overall goal is to develop effective and safe treatments for diseases.Unit 1_ Orthopedic Nursing^J Educational Platform copy.pptx
Unit 1_ Orthopedic Nursing^J Educational Platform copy.pptxRawalRafiqLeghari
╠¤
The document discusses several common musculoskeletal conditions including sprains, strains, fractures, carpal tunnel syndrome, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, gout, and amputations. It provides information on the etiology, pathophysiology, signs and symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment including nursing considerations for each condition.Fracture and its nursing management
Fracture and its nursing managementDurga Joshi
╠¤
The document provides information about a seminar on fractures presented by Ms. Durga Joshi. It defines a fracture as a break in the bone's continuity. It then lists the objectives of the seminar which are to define fracture, discuss causes and types, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and medical and nursing management. It proceeds to define types of fractures such as complete, incomplete, closed, and open fractures. It also discusses classification, causes, and complications of fractures as well as diagnosis, management including splinting and traction, and nursing care of patients with fractures.Liver abcess
Liver abcessSumreen4
╠¤
A fracture is a break in the continuity of bone that can be caused by direct blows, crushing forces, twisting motions or muscle contractions. There are two main types - complete fractures where the bone is broken across its entire cross-section, and incomplete fractures where the break is only partial. Fractures can be open (compound) if the bone protrudes through skin, or closed (simple) without skin breakage. Clinical signs include pain, deformity, swelling and loss of function. Treatment involves setting and immobilizing the bone through methods like casting, internal/external fixation, or traction to promote healing. Complications can include nonunion, infection and impaired mobility.Fracture
FractureRatheeshkrishnakripa
╠¤
A fracture is a break in the continuity of bone that can be caused by direct blows, crushing forces, twisting motions or muscle contractions. There are two main types - complete fractures where the bone is broken across its entire cross-section, and incomplete fractures where the break is only partial. Fractures can be open (compound) if the bone protrudes through skin, or closed (simple) without skin breakage. Clinical signs include pain, deformity, swelling and loss of function. Treatment involves reduction, immobilization using casts, splints or traction, and restoring mobility while the bone heals. Complications can include nonunion, infection and compartment syndrome.Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures.pptx
Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures.pptxKrishna Krish Krish
╠¤
Tibial shaft fractures, commonly caused by high-energy impacts like motor vehicle collisions, occur along the shinbone and can lead to complications such as infections and healing issues. These fractures are classified by their characteristics, including alignment, type (e.g., transverse, oblique, spiral), and whether they are open or closed. Treatment options vary from non-surgical methods, like splinting and casting, to surgical interventions, depending on the fracture severity and overall health of the patient.The fractures in the children and the types
The fractures in the children and the typesmoonaltayib
╠¤
A fracture is a disruption in the bone structure that can affect adjacent muscles and tissues, resulting in various types including open, closed, greenstick, and comminuted fractures. Causes include direct blows, crushing forces, sudden twisting motions, and extreme muscle contractions, with risks heightened by accidents and poor nutrition. Clinical manifestations include pain, loss of function, deformity, and complications may arise such as hypovolemic shock and compartment syndrome, requiring effective medical management and nursing interventions.Fracture (1)
Fracture (1)Anvin Thomas
╠¤
This seminar discusses fractures, including their definition, causes, classification, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, complications, and medical and nursing management. Fractures are breaks in bone continuity and can be caused by direct blows, twisting motions, or muscle contractions. They are classified based on their relationship to the environment (closed vs open), degree of displacement, fracture pattern (transverse, oblique, etc.), and etiology (traumatic vs pathological). Treatment involves reduction, immobilization using devices like casts, splints, or traction, and restoring function through exercises. Nursing care focuses on pain management, preventing complications like infection or neurovascular issues, and promoting mobility and independence.Ch14 presentation bone_joint_muscle_injuries
Ch14 presentation bone_joint_muscle_injuriesdjorgenmorris
╠¤
This document discusses various types of bone, joint, and muscle injuries. It describes fractures as breaks or cracks in bones that can be closed or open. Fractures include greenstick, transverse, oblique, comminuted, and impacted types. Signs of fractures include deformity, open wounds, tenderness, swelling, loss of function, and crepitus. Treatment involves checking circulation, sensation, and movement (CSM) and stabilizing the injury. Dislocations occur when a joint comes apart. Signs are deformity, tenderness, swelling, and inability to move. Treatment may include holding the part stable and using RICE (rest, ice, compression, and elevation). Sprains result from stretched or01-Sports-Injury-Management-and-Prevention-PPT.pptx
01-Sports-Injury-Management-and-Prevention-PPT.pptxManikandanJayaraman14
╠¤
This document discusses common sports injuries, their causes, symptoms, and treatments. It covers acute injuries which occur suddenly from collisions, strikes, or falls and overuse injuries from repetitive stresses over time like strains or tendonitis. Treatments depend on the type and severity of injury, ranging from RICE (rest, ice, compression, and elevation) for mild sprains to seeking immediate medical attention for serious fractures or dislocations. Proper training, nutrition, hydration, equipment, and injury prevention strategies can help reduce risks.meskuloskeletal injury and its emergency managment.pptx
meskuloskeletal injury and its emergency managment.pptxbirhanudesu
╠¤
The document provides a comprehensive overview of fractures, including definitions, causes, types, pathophysiology, and management strategies. It categorizes fractures into complete and incomplete, closed and open types, along with various specific classifications such as greenstick and spiral fractures. Additionally, it outlines nursing management, treatments for open fractures, and patient care considerations to prevent complications.first_aid_with_injuries_and_fracture..pptx
first_aid_with_injuries_and_fracture..pptxCicilyBibin
╠¤
This document provides comprehensive information on human musculoskeletal structures, including bones, muscles, joints, tendons, ligaments, and cartilage, as well as details on common injuries such as fractures and dislocations. It outlines types of fractures, their causes, symptoms, and first aid measures for different injuries, including specific techniques for addressing fractures of the skull, spine, and limbs. Additionally, the document discusses injury prevention and general first aid protocols for managing musculoskeletal injuries effectively.Musculo-skeletal disorders fracture and dislo.pptx
Musculo-skeletal disorders fracture and dislo.pptxDestaSiyoum
╠¤
The document outlines common musculoskeletal disorders, emphasizing soft tissue injuries like strains and sprains, and conditions such as dislocations and fractures. It details the causes, symptoms, management, and potential complications of these injuries, along with emergency and medical management strategies. Key points include the importance of immobilization, appropriate treatment for fractures, and factors influencing healing.FRACTURE.pptx FOR NURSING STUDENTS CREATED BY KIRAN KARETHA
FRACTURE.pptx FOR NURSING STUDENTS CREATED BY KIRAN KARETHAKIRAN KARETHA
╠¤
A Fracture is defined as a break in the continuity of the bone.
A bone fracture is a crack or break in a bone usually results from a high force impact of stress.
CLINICAL MANIFESTATION:
Pain
Loss of function
Deformity
Shortening
Crepitus
Swelling and dis-coloration
DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION:
History collection
Physical examination
X-ray
CT scan
MRI
MANAGEMENT:
Reduction:
Reduction of a fracture refers to restoration of the fracture fragments to anatomic alignment and rotation.
Immobilization:
immobilization may be accomplished by external or internal fixation.
Methods of external fixation include bandages, casts, splints, continuous traction and external fixators.
Metal implants used for internal fixation serve as internal splints to immobilize the fracture.
Maintaining and restoring function:
Restlessness, anxiety and discomfort are controlled with a variety of approaches such as reassurance, position changes and pain relief strategies including use of analgesics.
Exercises are encouraged to minimize disuse atrophy and to promote circulation.
NURSING MANAGEMENT:
Patient with closed fractures:
encourage patient not to mobilize fracture site.
Exercises to maintain the health of unaffected muscles for using assistive devices (crutches, walker).
Teach patient how to use assistive devices safely.
Patient teaching includes self-care, medication information, monitoring for potential complications and the need for continuing health care supervision.
NURSING MANAGEMENT:
Patient with closed fractures:
encourage patient not to mobilize fracture site.
Exercises to maintain the health of unaffected muscles for using assistive devices (crutches, walker).
Teach patient how to use assistive devices safely.
Patient teaching includes self-care, medication information, monitoring for potential complications and the need for continuing health care supervision.
Patients with open fractures
Wound irrigation and debridement in the operating room are necessary.
Intravenous antibiotics are prescribed to prevent or treat infection.
Wound is cultured.
Any damage to blood vessel, soft tissue, muscles, nerves and tendons is treated.
Acute and Overuse Injuries unlock.nnnpptx
Acute and Overuse Injuries unlock.nnnpptxAAZIZ13
╠¤
The document outlines acute and overuse injuries common in athletes, detailing classifications, clinical features, and management of various injuries such as fractures, ligament sprains, muscle strains, tendon ruptures, and bursitis. It emphasizes the differences between acute and overuse injuries, the complexity of diagnosing and treating overuse injuries, and specific conditions like tendinosis and chronic compartment syndrome. Additionally, it addresses complications associated with these injuries and provides insights on both prevention and treatment strategies.More Related Content
Viewers also liked (7)
Megan Carter - Resume
Megan Carter - ResumeMegan Carter
╠¤
Megan Carter is a computer science student and experienced waitress seeking a new job. She has worked as a waitress at multiple restaurants, as well as in sales, retail, and cashier roles. Carter enjoys interacting with customers and helping people. She is authorized to work in the US and is willing to relocate to Moline or Peoria, Illinois. Carter is currently pursuing an online bachelor's degree in data analysis and programming while maintaining a flexible schedule.Propery transfer
Propery transferXafar ul hak
╠¤
This document discusses different types of property and rules for transferring property ownership. It covers:
1) The two main types of property are real property (land and buildings) and personal property (movable items). The basic goal of a sales contract is to transfer ownership of property from the seller to the buyer.
2) For property to change ownership, it must be specific and in a deliverable state. If goods are unascertained or not ready for delivery, ownership does not transfer.
3) There are some exceptions where a third party can transfer valid ownership, such as through implied authority from the owner, if they are a mercantile agent, or in cases of joint ownership, voidable contractsSimulacro pedagogiafany garzon
╠¤
Este documento presenta un simulacro de la Prueba de Potencialidad Pedag├│gica (PPP) aplicada por la Universidad Pedag├│gica Nacional de Colombia a sus aspirantes. El simulacro consta de 50 preguntas tipo I y II divididas en potenciales cognitivo, psicosocial y comunicativo. El tiempo m├бximo para resolverlo es de 2 horas y 15 minutos. Al final se encontrar├бn las respuestas correctas y su justificaci├│n. El objetivo es ofrecer a los aspirantes mayor informaci├│n sobre la estructura y caracter├нsticas de la prueba de adProbiotcs
ProbiotcssilGERSIL
╠¤
This document discusses various uses of probiotics in different areas of health. It summarizes that probiotics are live microorganisms that have proven beneficial effects on the host's body when given in sufficient amounts. Some key points made include that certain probiotics like Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG and Saccharomyces boulardii can shorten the duration of acute gastroenteritis by 1 day. Probiotics may also help lower bacterial load of H. pylori but cannot eliminate it completely. Probiotics are also discussed in relation to skin health conditions like acne, bone health, urinary tract infections, and C. difficile treatment.nuevas tecnologiasfany garzon
╠¤
El centro de inter├йs ense├▒a a los estudiantes sobre nuevas tecnolog├нas y el uso de hardware y software, incluyendo dispositivos m├│viles, sistemas operativos, correo electr├│nico, redes sociales y aplicaciones educativas. Los estudiantes aprenden a comunicarse y colaborar utilizando herramientas tecnol├│gicas como Google Drive, wikis y YouTube, adem├бs de desarrollar habilidades de pensamiento cr├нtico y resoluci├│n de problemas. El centro de inter├йs fortalece los valores del colegio y contribuye aPharmacology
PharmacologysilGERSIL
╠¤
Pharmacology is the scientific study of drugs and their effects on the human body. It involves investigating how drugs are absorbed, distributed, metabolized and excreted by the body. Pharmacodynamics examines how drugs act on the body and influence physiological functions, while pharmacokinetics studies the fate of drugs in the body over time. Pharmacology also considers drug sources and classifications, therapeutic uses of drugs, dosages, potential adverse effects, and the drug approval process. The overall goal is to develop effective and safe treatments for diseases.Similar to Sport тАУ related injuries (20)
Unit 1_ Orthopedic Nursing^J Educational Platform copy.pptx
Unit 1_ Orthopedic Nursing^J Educational Platform copy.pptxRawalRafiqLeghari
╠¤
The document discusses several common musculoskeletal conditions including sprains, strains, fractures, carpal tunnel syndrome, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, gout, and amputations. It provides information on the etiology, pathophysiology, signs and symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment including nursing considerations for each condition.Fracture and its nursing management
Fracture and its nursing managementDurga Joshi
╠¤
The document provides information about a seminar on fractures presented by Ms. Durga Joshi. It defines a fracture as a break in the bone's continuity. It then lists the objectives of the seminar which are to define fracture, discuss causes and types, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and medical and nursing management. It proceeds to define types of fractures such as complete, incomplete, closed, and open fractures. It also discusses classification, causes, and complications of fractures as well as diagnosis, management including splinting and traction, and nursing care of patients with fractures.Liver abcess
Liver abcessSumreen4
╠¤
A fracture is a break in the continuity of bone that can be caused by direct blows, crushing forces, twisting motions or muscle contractions. There are two main types - complete fractures where the bone is broken across its entire cross-section, and incomplete fractures where the break is only partial. Fractures can be open (compound) if the bone protrudes through skin, or closed (simple) without skin breakage. Clinical signs include pain, deformity, swelling and loss of function. Treatment involves setting and immobilizing the bone through methods like casting, internal/external fixation, or traction to promote healing. Complications can include nonunion, infection and impaired mobility.Fracture
FractureRatheeshkrishnakripa
╠¤
A fracture is a break in the continuity of bone that can be caused by direct blows, crushing forces, twisting motions or muscle contractions. There are two main types - complete fractures where the bone is broken across its entire cross-section, and incomplete fractures where the break is only partial. Fractures can be open (compound) if the bone protrudes through skin, or closed (simple) without skin breakage. Clinical signs include pain, deformity, swelling and loss of function. Treatment involves reduction, immobilization using casts, splints or traction, and restoring mobility while the bone heals. Complications can include nonunion, infection and compartment syndrome.Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures.pptx
Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures.pptxKrishna Krish Krish
╠¤
Tibial shaft fractures, commonly caused by high-energy impacts like motor vehicle collisions, occur along the shinbone and can lead to complications such as infections and healing issues. These fractures are classified by their characteristics, including alignment, type (e.g., transverse, oblique, spiral), and whether they are open or closed. Treatment options vary from non-surgical methods, like splinting and casting, to surgical interventions, depending on the fracture severity and overall health of the patient.The fractures in the children and the types
The fractures in the children and the typesmoonaltayib
╠¤
A fracture is a disruption in the bone structure that can affect adjacent muscles and tissues, resulting in various types including open, closed, greenstick, and comminuted fractures. Causes include direct blows, crushing forces, sudden twisting motions, and extreme muscle contractions, with risks heightened by accidents and poor nutrition. Clinical manifestations include pain, loss of function, deformity, and complications may arise such as hypovolemic shock and compartment syndrome, requiring effective medical management and nursing interventions.Fracture (1)
Fracture (1)Anvin Thomas
╠¤
This seminar discusses fractures, including their definition, causes, classification, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, complications, and medical and nursing management. Fractures are breaks in bone continuity and can be caused by direct blows, twisting motions, or muscle contractions. They are classified based on their relationship to the environment (closed vs open), degree of displacement, fracture pattern (transverse, oblique, etc.), and etiology (traumatic vs pathological). Treatment involves reduction, immobilization using devices like casts, splints, or traction, and restoring function through exercises. Nursing care focuses on pain management, preventing complications like infection or neurovascular issues, and promoting mobility and independence.Ch14 presentation bone_joint_muscle_injuries
Ch14 presentation bone_joint_muscle_injuriesdjorgenmorris
╠¤
This document discusses various types of bone, joint, and muscle injuries. It describes fractures as breaks or cracks in bones that can be closed or open. Fractures include greenstick, transverse, oblique, comminuted, and impacted types. Signs of fractures include deformity, open wounds, tenderness, swelling, loss of function, and crepitus. Treatment involves checking circulation, sensation, and movement (CSM) and stabilizing the injury. Dislocations occur when a joint comes apart. Signs are deformity, tenderness, swelling, and inability to move. Treatment may include holding the part stable and using RICE (rest, ice, compression, and elevation). Sprains result from stretched or01-Sports-Injury-Management-and-Prevention-PPT.pptx
01-Sports-Injury-Management-and-Prevention-PPT.pptxManikandanJayaraman14
╠¤
This document discusses common sports injuries, their causes, symptoms, and treatments. It covers acute injuries which occur suddenly from collisions, strikes, or falls and overuse injuries from repetitive stresses over time like strains or tendonitis. Treatments depend on the type and severity of injury, ranging from RICE (rest, ice, compression, and elevation) for mild sprains to seeking immediate medical attention for serious fractures or dislocations. Proper training, nutrition, hydration, equipment, and injury prevention strategies can help reduce risks.meskuloskeletal injury and its emergency managment.pptx
meskuloskeletal injury and its emergency managment.pptxbirhanudesu
╠¤
The document provides a comprehensive overview of fractures, including definitions, causes, types, pathophysiology, and management strategies. It categorizes fractures into complete and incomplete, closed and open types, along with various specific classifications such as greenstick and spiral fractures. Additionally, it outlines nursing management, treatments for open fractures, and patient care considerations to prevent complications.first_aid_with_injuries_and_fracture..pptx
first_aid_with_injuries_and_fracture..pptxCicilyBibin
╠¤
This document provides comprehensive information on human musculoskeletal structures, including bones, muscles, joints, tendons, ligaments, and cartilage, as well as details on common injuries such as fractures and dislocations. It outlines types of fractures, their causes, symptoms, and first aid measures for different injuries, including specific techniques for addressing fractures of the skull, spine, and limbs. Additionally, the document discusses injury prevention and general first aid protocols for managing musculoskeletal injuries effectively.Musculo-skeletal disorders fracture and dislo.pptx
Musculo-skeletal disorders fracture and dislo.pptxDestaSiyoum
╠¤
The document outlines common musculoskeletal disorders, emphasizing soft tissue injuries like strains and sprains, and conditions such as dislocations and fractures. It details the causes, symptoms, management, and potential complications of these injuries, along with emergency and medical management strategies. Key points include the importance of immobilization, appropriate treatment for fractures, and factors influencing healing.FRACTURE.pptx FOR NURSING STUDENTS CREATED BY KIRAN KARETHA
FRACTURE.pptx FOR NURSING STUDENTS CREATED BY KIRAN KARETHAKIRAN KARETHA
╠¤
A Fracture is defined as a break in the continuity of the bone.
A bone fracture is a crack or break in a bone usually results from a high force impact of stress.
CLINICAL MANIFESTATION:
Pain
Loss of function
Deformity
Shortening
Crepitus
Swelling and dis-coloration
DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION:
History collection
Physical examination
X-ray
CT scan
MRI
MANAGEMENT:
Reduction:
Reduction of a fracture refers to restoration of the fracture fragments to anatomic alignment and rotation.
Immobilization:
immobilization may be accomplished by external or internal fixation.
Methods of external fixation include bandages, casts, splints, continuous traction and external fixators.
Metal implants used for internal fixation serve as internal splints to immobilize the fracture.
Maintaining and restoring function:
Restlessness, anxiety and discomfort are controlled with a variety of approaches such as reassurance, position changes and pain relief strategies including use of analgesics.
Exercises are encouraged to minimize disuse atrophy and to promote circulation.
NURSING MANAGEMENT:
Patient with closed fractures:
encourage patient not to mobilize fracture site.
Exercises to maintain the health of unaffected muscles for using assistive devices (crutches, walker).
Teach patient how to use assistive devices safely.
Patient teaching includes self-care, medication information, monitoring for potential complications and the need for continuing health care supervision.
NURSING MANAGEMENT:
Patient with closed fractures:
encourage patient not to mobilize fracture site.
Exercises to maintain the health of unaffected muscles for using assistive devices (crutches, walker).
Teach patient how to use assistive devices safely.
Patient teaching includes self-care, medication information, monitoring for potential complications and the need for continuing health care supervision.
Patients with open fractures
Wound irrigation and debridement in the operating room are necessary.
Intravenous antibiotics are prescribed to prevent or treat infection.
Wound is cultured.
Any damage to blood vessel, soft tissue, muscles, nerves and tendons is treated.
Acute and Overuse Injuries unlock.nnnpptx
Acute and Overuse Injuries unlock.nnnpptxAAZIZ13
╠¤
The document outlines acute and overuse injuries common in athletes, detailing classifications, clinical features, and management of various injuries such as fractures, ligament sprains, muscle strains, tendon ruptures, and bursitis. It emphasizes the differences between acute and overuse injuries, the complexity of diagnosing and treating overuse injuries, and specific conditions like tendinosis and chronic compartment syndrome. Additionally, it addresses complications associated with these injuries and provides insights on both prevention and treatment strategies.FIRST AID.pptx
FIRST AID.pptxelias de mesa
╠¤
This document provides information on various common injuries and their first aid treatments. It discusses sprains, heat exhaustion, knee injuries, fractures, and dislocations. For sprains and heat exhaustion, it recommends resting, applying cold/elevating the injury, and giving fluids. It also notes that more serious injuries like fractures and dislocations require immediate medical care.1588832907-orthopedic-injuries.pptx
1588832907-orthopedic-injuries.pptxAymanshahzad4
╠¤
This document provides information on orthopedic injuries and fractures. It discusses evaluating injuries through history and examination, classifying fractures, signs of specific fractures like greenstick or Colles fractures, complications, and management techniques like splinting. Key points include classifying fractures as macrotrauma from large forces or microtrauma from small repeated forces, evaluating neurovascular function, and properly splinting and immobilizing fractures to prevent further injury while allowing for transport to a hospital for further treatment.8(2024) POP ╪п ╪│╪╣┘К╪п ╪и╪з┘Е╪┤ ┘Е┘И╪│.ppt
8(2024) POP ╪п ╪│╪╣┘К╪п ╪и╪з┘Е╪┤ ┘Е┘И╪│.pptM H
╠¤
The document discusses the principles and methods of fracture management, including the use of orthopedic casts for healing. It details the materials used, types of casts, indications for their application, and potential complications that can arise during treatment. Guidelines for patient care and monitoring are also provided to prevent complications and ensure effective treatment.Orthopedic Nursing-1.pptx all notes on orthopedic nursing
Orthopedic Nursing-1.pptx all notes on orthopedic nursingwanjikukagunyi2
╠¤
The document covers the comprehensive assessment and management of musculoskeletal function, detailing the history taking, physical examination, diagnostic procedures, and treatment interventions for soft tissue injuries and fractures. It highlights the nursing management principles for fractures, including immobilization techniques such as casts and traction, emergency care protocols, and rehabilitation strategies. Key topics include types of fractures, their classifications, complications, and the importance of timely intervention in managing musculoskeletal injuries.FRACTURES AND DISLOCATION MANAGEMENT.pptx
FRACTURES AND DISLOCATION MANAGEMENT.pptxAntwiBrainard
╠¤
The document discusses fractures, dislocations, and their treatment. It defines fractures and describes different types including closed/open, pathological, and stress fractures. Signs and symptoms of fractures and dislocations are outlined. The principles of diagnosing and treating fractures are described, including reduction, splinting, and casting. Factors that influence fracture healing are also mentioned.Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
Tuberculosis burden , case finding tools and management .pptx
Tuberculosis burden , case finding tools and management .pptxDr. Anu Marhatta
╠¤
This presentation is for educational purposes only. Aspirin powder or Acetyl salicylic acid powder.docx
Aspirin powder or Acetyl salicylic acid powder.docxkopalsharma85
╠¤
pharmacy exercise on aspirin powderinferential statistics Part - 1 i.e Parametric tests
inferential statistics Part - 1 i.e Parametric testsBabitha Devu
╠¤
This part deals with the Inferential Statistics.
Basic Terminologies.
Parametric Test.
T-test
paired & unpaired T -test
Z testwhooping cough community health nursing.
whooping cough community health nursing.ASWIN S
╠¤
Whooping cough for BSC 5th sem community health nursing..
This includes
Introduction
Definition
Incidence
Incubation period
Causes
Clinical manifestations
Diagnostic evaluation
Treatment
Prevention
Complications
Of whooping cough....ELECTROMYOGRAPHY.pptX by GOKULAKRISHNAN.
ELECTROMYOGRAPHY.pptX by GOKULAKRISHNAN.GOKULAKRISHNAN JANARTHANAN
╠¤
Electromyography is basically the study of motor unit activity.
In electromyography, the study of the electrical activity of contracting muscle provides information concerning the structure and function of the motor units.
5-Lift Analysis in ergonomics focuses on evaluating the safety and efficienc...
5-Lift Analysis in ergonomics focuses on evaluating the safety and efficienc...Bolan University of Medical and Health Sciences ,Quetta
╠¤
Lift Analysis in ergonomics focuses on evaluating the safety and efficiency of manual lifting tasks in the workplace. It involves assessing the physical demands placed on the human body during lifting activities to prevent musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs), particularly lower back injuriesINTERPRETATION OF LABORATORY INVESTIGATIONS.pptx
INTERPRETATION OF LABORATORY INVESTIGATIONS.pptxEliLawluvi
╠¤
THE DOCUMENT SUMMARIZES THE KEY COMPONENTS OF INTERPRETING FULL BLOOD CUNTComprehensive Guide on Adsorption and Partition Chromatography Techniques
Comprehensive Guide on Adsorption and Partition Chromatography TechniquesSajini
╠¤
This presentation provides an in-depth overview of chromatography, focusing on adsorption and partition chromatography. It covers the principles, methodologies, types, classification, column preparation, detection methods, advantages, disadvantages, and pharmaceutical applications. A useful resource for pharmacy students and professionals in pharmaceutical chemistry.
How to be and stay healthy: Live Wire Not a Couch Potato
How to be and stay healthy: Live Wire Not a Couch PotatoBiljanaPipovic
╠¤
Live Wire, Not a Couch Potato was an engaging international eTwinning project aimed at promoting physical activity among youth by blending creativity, tradition, and competition. Founded by teachers from Serbia and Portugal, with partners from Turkey and Greece, the project encouraged students to explore the importance of staying active through fun and meaningful challenges. Working within their local contexts, students from all four countries participated in physical activities at school and in their communities. They documented their experiences through photos, videos, and written reflections, which they shared on TwinSpace. The project helped transform exercise from a routine task into an enjoyable, culturally rich experience, while fostering teamwork, creativity, and international exchange.Drmohamedaslam_resident_copd2025_fm.pptx
Drmohamedaslam_resident_copd2025_fm.pptxAslam
╠¤
COPD :LATEST GUIDELINES 2025
REFERENCE: HarrisonтАЩs Principles of Internal Medicine
GOLD -2025 Guidelines
It highlights updated diagnostic criteria, pharmacological and non-pharmacological treatment options, and current best practices for resident doctors and healthcare professionals.
Ideal for medical students, residents, and practitioners seeking an up-to-date, evidence-based reference.
ЁЯСЙ Download, share, and feel free to reach out for related study material!JUNE 2025 ONCOLOGY CARTOONS BY DR KANHU CHARAN PATRO
JUNE 2025 ONCOLOGY CARTOONS BY DR KANHU CHARAN PATROKanhu Charan
╠¤
JUNE 2025 ONCOLOGY CARTOONS BY DR KANHU CHARAN PATROComputer aided formulation development optimization
Computer aided formulation development optimizationSwami ramanand teerth marathwada university
╠¤
Concept of optimization, optimization parameters, factorial design, optimization technology & screening design. Ratricharya according to ayurveda along with day and night pattern in various...
Ratricharya according to ayurveda along with day and night pattern in various...DR DHARMENDRA BINJHWAR
╠¤
This slide are more importents for ayurveda students and teachers because i have mentioned in this slide night time routine in ayurveda the ancient science of India along with day and night pattern in various counteries within in one ppt. thanks for watching i will be greatful for your suggestion and feedback... please like share and suppourtUpdate on Anesthesia for Pediatric Ophthalmic Surgery.pptx
Update on Anesthesia for Pediatric Ophthalmic Surgery.pptxDr.Umang Sharma
╠¤
Based on practices on my hospital and 2021 bja articleFrom Preservation To Regeneration--The Stem Cell Era of Hair Restoration_DrAl...
From Preservation To Regeneration--The Stem Cell Era of Hair Restoration_DrAl...Alan Bauman
╠¤
How can the latest in Regenerative Medicine help those suffering from hair loss? Cell Surgical Conference 2025 featured Dr Alan Bauman as a faculty member once again to discuss all things related to hair loss, hair transplantation and the use of regenerative stem cell therapies for hair restoration. 5-Lift Analysis in ergonomics focuses on evaluating the safety and efficienc...
5-Lift Analysis in ergonomics focuses on evaluating the safety and efficienc...Bolan University of Medical and Health Sciences ,Quetta
╠¤
Ratricharya according to ayurveda along with day and night pattern in various...
Ratricharya according to ayurveda along with day and night pattern in various...DR DHARMENDRA BINJHWAR
╠¤
Ad
Sport тАУ related injuries
- 1. Sport тАУ related injuries Silvia Ger─Н├бkov├б JLF UK UNIcert 2016
- 2. тАв Sports injuries are injuries that occur in athletic activities or exercising. тАв They can result from accidents, poor training technique in practice, inadequate equipment, and overuse of a particular body part. тАв Collisions with the ground, objects, and other players are common, and unexpected dynamic forces on limbs and joints can cause injury.
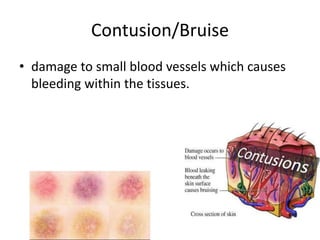
- 3. Contusion/Bruise тАв damage to small blood vessels which causes bleeding within the tissues.
- 4. Muscle cramp тАв a strong muscle contraction that can be very painful lasting in few minutes тАв The symptoms of muscle cramps usually come on quickly and intensely. тАв The most obvious symptom of a muscle cramp is a sharp, acute pain in the affected muscle or muscles. тАв If itтАЩs a large muscle that is involved, like the one in the calf of your leg, you may be able to feel a knot or hard lump in the muscle, just under the skin. тАв There are also cramps that occur after the fact. These delayed or nocturnal cramps can affect athletes.
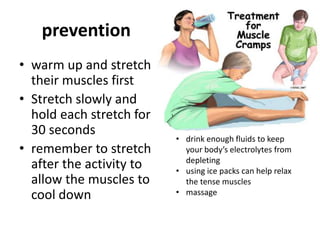
- 5. prevention тАв warm up and stretch their muscles first тАв Stretch slowly and hold each stretch for 30 seconds тАв remember to stretch after the activity to allow the muscles to cool down тАв drink enough fluids to keep your bodyтАЩs electrolytes from depleting тАв using ice packs can help relax the tense muscles тАв massage
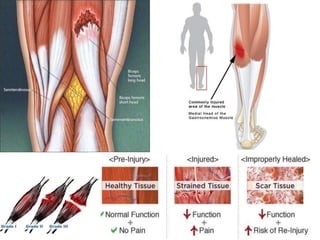
- 6. Muscle strain trauma to a muscle due to overstretching and tearing of muscle fibers тАв Symptoms : яГШSwelling, bruising, or redness due to the injury яГШPain at rest яГШPain when the specific muscle or the joint in relation to that muscle is used яГШWeakness of the muscle or tendons яГШInability to use the muscle at all
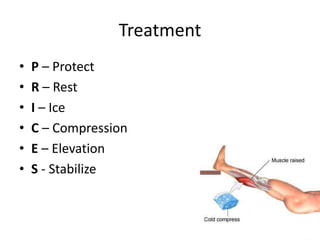
- 8. Treatment тАв P тАУ Protect тАв R тАУ Rest тАв I тАУ Ice тАв C тАУ Compression тАв E тАУ Elevation тАв S - Stabilize
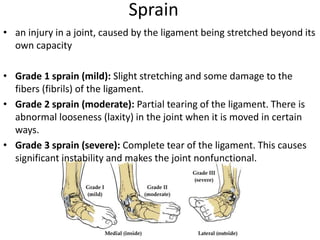
- 9. Sprain тАв an injury in a joint, caused by the ligament being stretched beyond its own capacity тАв Grade 1 sprain (mild): Slight stretching and some damage to the fibers (fibrils) of the ligament. тАв Grade 2 sprain (moderate): Partial tearing of the ligament. There is abnormal looseness (laxity) in the joint when it is moved in certain ways. тАв Grade 3 sprain (severe): Complete tear of the ligament. This causes significant instability and makes the joint nonfunctional.
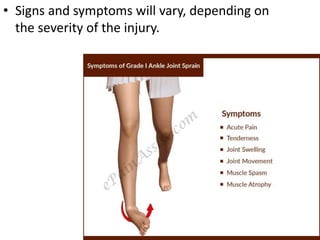
- 10. тАв Signs and symptoms will vary, depending on the severity of the injury.
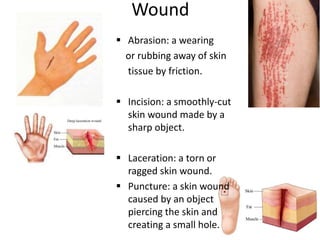
- 11. Wound яВз Abrasion: a wearing or rubbing away of skin tissue by friction. яВз Incision: a smoothly-cut skin wound made by a sharp object. яВз Laceration: a torn or ragged skin wound. яВз Puncture: a skin wound caused by an object piercing the skin and creating a small hole.
- 12. How to help? тАв Washing a cut or scrape with soap, and water and keeping it clean and dry is all that is required to care for most wounds. тАв Cleaning the wound with hydrogen peroxide and iodine is acceptable initially, but can delay healing and should be avoided long-term. тАв Apply antibiotic ointment and keep the wound covered. тАв Seek medical care within 6 hours if the bleeding does not stop, as the wound might need stitches. A delay can increase the rate of wound
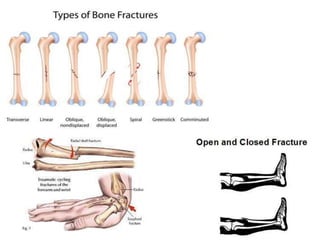
- 13. Bone fracture тАв The most common injuries include fractured wrists, hands, collarbones and bones in the ankle and feet. тАв Stress fractures are very common in sports which involve repetitive movements; long distance runners often suffer from stress fractures in the foot, for example. Symptoms of fractures тАв Common symptoms include swelling, redness and pain; тАв many fractures can be extremely painful and most will swell immediately. тАв More complex fractures may break the skin; in this case the injury will be clearly visible and immediately diagnosable. тАв Fractures generally restrict or prohibit movement in the area for a period of time
- 15. Treating a fracture тАв Application of ice to reduce swelling. тАв Anti-inflammatory medication and pain relief to ease pain and further reduce swelling. тАв immobilisation for a period of time; this may involve having a plaster cast fitted, wearing a sling or using crutches; this will allow the bone time to heal. тАв a course of physiotherapy to strengthen the area and improve flexibility and movement.
- 16. Head injury тАв concussions a type of traumatic brain injury (TBI) that happens when the brain is shaken hard enough to bounce against the skull. тАв Contusion a bruise on the brain that can cause swelling, and a hematoma, which is bleeding in the brain that collects and forms a clot. тАв A skull fracture pieces of bone can cut into the brain and cause bleeding
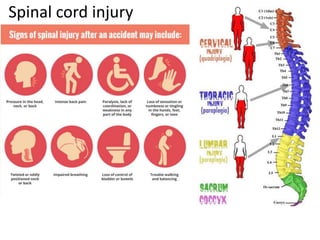
- 17. Indications of severe head trauma тАв Changes in size of pupils тАв Clear or bloody fluid draining from the nose, mouth, or ears тАв Convulsions тАв Distorted facial features тАв Drop in blood pressure тАв Facial bruising тАв Fracture in the skull or face тАв Impaired hearing, smell, taste, or vision тАв Inability to move one or more limbs тАв Irritability тАв Loss of consciousness тАв Low breathing rate тАв Restlessness, clumsiness, or lack of coordination тАв Severe headache тАв Slurred speech or blurred vision тАв Stiff neck or vomiting тАв Sudden worsening of symptoms after initial improvement тАв Swelling at the site of the injury тАв Persistent vomiting Need to be managed by professional medical team!