SQL, Embedded SQL, Dynamic SQL and SQLJ
- 1. Click to add Title Embedded SQL, Dynamic SQL and SQLJ e-Infochips Institute of Training Research and Academics Limited Prepared By:- Dharita Chokshi
- 2. Outlines ŌĆó What is SQL ŌĆó What is Embedded SQL ŌĆó Cursors ŌĆó Dynamic SQL ŌĆó SQLJ ŌĆó Summary
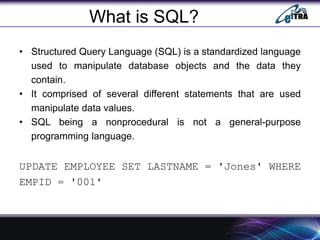
- 3. What is SQL? ŌĆó Structured Query Language (SQL) is a standardized language used to manipulate database objects and the data they contain. ŌĆó It comprised of several different statements that are used manipulate data values. ŌĆó SQL being a nonprocedural is not a general-purpose programming language. UPDATE EMPLOYEE SET LASTNAME = 'Jones' WHERE EMPID = '001'
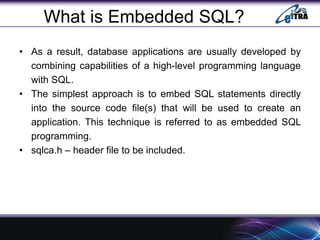
- 4. What is Embedded SQL? ŌĆó As a result, database applications are usually developed by combining capabilities of a high-level programming language with SQL. ŌĆó The simplest approach is to embed SQL statements directly into the source code file(s) that will be used to create an application. This technique is referred to as embedded SQL programming. ŌĆó sqlca.h ŌĆō header file to be included.
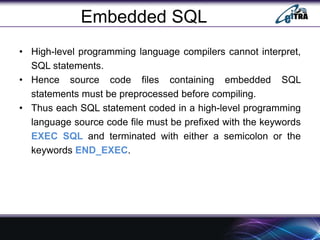
- 5. Embedded SQL ŌĆó High-level programming language compilers cannot interpret, SQL statements. ŌĆó Hence source code files containing embedded SQL statements must be preprocessed before compiling. ŌĆó Thus each SQL statement coded in a high-level programming language source code file must be prefixed with the keywords EXEC SQL and terminated with either a semicolon or the keywords END_EXEC.
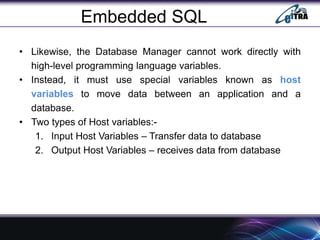
- 6. Embedded SQL ŌĆó Likewise, the Database Manager cannot work directly with high-level programming language variables. ŌĆó Instead, it must use special variables known as host variables to move data between an application and a database. ŌĆó Two types of Host variables:- 1. Input Host Variables ŌĆō Transfer data to database 2. Output Host Variables ŌĆō receives data from database
- 7. Embedded SQL ŌĆó Host variables are ordinary programming language variables. ŌĆó To be set apart, they must be defined within a special section known as a declare section. EXEC SQL BEGIN DECLARE SECTION char EmployeeID[7]; double Salary; EXEC SQL END DECLARE SECTION ŌĆó Each host variable must be assigned a unique name even though declared in different declaration section.
- 8. Embedded SQL main() { EXEC SQL BEGIN DECLARE SECTION; int OrderID, CustID; char SalesPerson[10], Status[6]; EXEC SQL END DECLARE SECTION; printf ("Enter order number: "); scanf ("%d", &OrderID); EXEC SQL SELECT CustID, SalesPerson, Status FROM Orders WHERE OrderID = :OrderID INTO :CustID, :SalesPerson, :Status; printf ("Customer number: %d n", CustID); printf ("Salesperson: %s n", SalesPerson); printf ("Status: %s n", Status); }
- 9. Embedded SQL Connecting to Database using embedded sql EXEC SQL CONNECT :userid IDENTIFIED BY :passwd; EXEC SQL CREATE TABLE Test (a int); EXEC SQL INSERT INTO Test VALUES (1); EXEC SQL SELECT MAX (a) INTO :value from R; printf (ŌĆ£Max value=%dnŌĆØ,value);
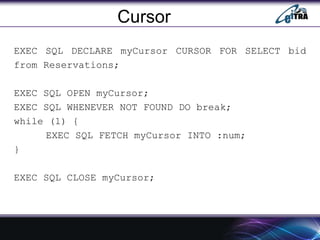
- 10. Cursor ŌĆó Can declare a cursor on a query statement which generates a relation. ŌĆó Can open a cursor, repeatedly fetch a tuple, move the cursor, until all tuples have been retrieved. ŌĆó Control order: ORDER BY, in queries that are accessed through a cursor ŌĆó Can also modify/delete tuple pointed to by cursor. ŌĆó Must close cursor at end.
- 11. Cursor EXEC SQL DECLARE myCursor CURSOR FOR SELECT bid from Reservations; EXEC SQL OPEN myCursor; EXEC SQL WHENEVER NOT FOUND DO break; while (1) { EXEC SQL FETCH myCursor INTO :num; } EXEC SQL CLOSE myCursor;
- 12. Dynamic SQL ŌĆó Dynamic SQL means composing and executing new (not previously compiled) SQL statements at run-time. ŌĆó Although static SQL statements are relatively easy to incorporate, Dynamic SQL statements are much more flexible as they can be constructed at run time. ŌĆó Dynamic queries can be complex because the type and number of retrieved attributes are unknown at compile time. INSERT INTO EMPLOYEES VALUES (?, ?) DELETE FROM DEPARTMENT WHERE DEPTID = ?
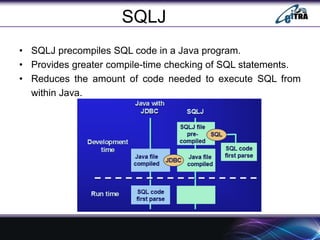
- 13. SQLJ ŌĆó SQLJ ŌĆō Standard for embedding SQL in Java ŌĆó Similar to existing SQL extensions provided for C, FORTRAN, and other programming languages. ŌĆó IBM, Oracle, and several other companies proposed SQLJ as a standard and as a simpler and easier-to-use alternative to JDBC. ŌĆó An SQLJ translator converts SQL statements into Java ŌĆó These are executed through the JDBC interface ŌĆó Certain classes have to be imported E.g., java.sql
- 14. SQLJ ŌĆó SQLJ precompiles SQL code in a Java program. ŌĆó Provides greater compile-time checking of SQL statements. ŌĆó Reduces the amount of code needed to execute SQL from within Java.
- 15. SQLJ v/s JDBC // SQLJ int n; #sql { INSERT INTO emp VALUES (:n)}; // JDBC int n; Statement stmt = conn.prepareStatement (ŌĆ£INSERT INTO emp VALUES (?)ŌĆØ); stmt.setInt(1,n); stmt.execute (); stmt.close();
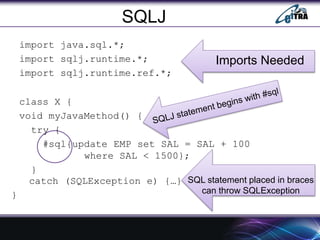
- 16. class X { void myJavaMethod() { try { #sql{update EMP set SAL = SAL + 100 where SAL < 1500}; } SQLJ import java.sql.*; import sqlj.runtime.*; import sqlj.runtime.ref.*; Imports Needed SQL statement placed in braces can throw SQLException catch (SQLException e) {ŌĆ”} }
- 17. SQLJ Loading the JDBC Driver SQLJ requires that the JDBC driver class is loaded. This can be performed in the same way as for JDBC try { Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver"); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { System.out.println("Could not load driver"); }
- 18. SQLJ Specifying a Connection Context ŌĆó All SQLJ statements execute in a ŌĆ£connection contextŌĆØ ŌĆó Plays similar role as a Connection object does in JDBC. ŌĆó Establishes the database we are connecting to, the user name, and the password. try { Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver"); DefaultContext.setDefaultContext(new DefaultContext( "jdbc:oracle:thin:@HOSTID:1521:ORCL", "theUser", "thePassword") ); }
- 19. SQLJ Passing Host Variables into a SQLJ Statement ŌĆó Prefix the java variable name with a colon (:) #sql {delete from EMP where SAL >= :amt};
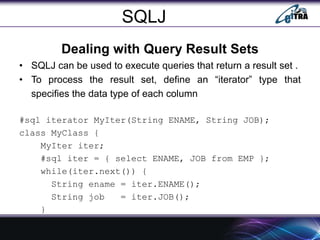
- 20. SQLJ Dealing with Query Result Sets ŌĆó SQLJ can be used to execute queries that return a result set . ŌĆó To process the result set, define an ŌĆ£iteratorŌĆØ type that specifies the data type of each column #sql iterator MyIter(String ENAME, String JOB); class MyClass { MyIter iter; #sql iter = { select ENAME, JOB from EMP }; while(iter.next()) { String ename = iter.ENAME(); String job = iter.JOB(); }
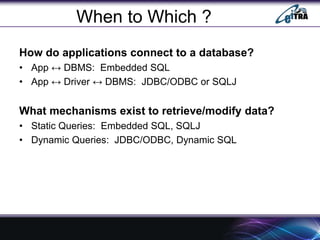
- 21. When to Which ? How do applications connect to a database? ŌĆó App Ōåö DBMS: Embedded SQL ŌĆó App Ōåö Driver Ōåö DBMS: JDBC/ODBC or SQLJ What mechanisms exist to retrieve/modify data? ŌĆó Static Queries: Embedded SQL, SQLJ ŌĆó Dynamic Queries: JDBC/ODBC, Dynamic SQL
- 22. Thank you
Editor's Notes
- #2: 1
- #4: Structured Query Language (SQL) is a standardized language used to manipulate database objects and the data they contain. SQL is comprised of several different statements that are used to define, alter, and destroy database objects, as well as add, update, delete, and retrieve data values. However, SQL is nonprocedural, and therefore is not a general-purpose programming language. (SQL statements are executed by the DB2 Database Manager, not by the operating system.) As a result, database applications are usually developed by combining the decision and sequence control of a high-level programming language with the data storage, manipulation, and retrieval capabilities of SQL. Several methods are available for merging SQL with a high-level programming language, but the simplest approach is to embed SQL statements directly into the source code file(s) that will be used to create an application. This technique is referred to as embedded SQL programming.
- #6: When the preprocessor (a special tool known as the SQL precompiler) encounters these keywords, it replaces the text that follows (until a semicolon (;) or the keywords END-EXEC is found) with a DB2 UDB-specific function call that forwards the specified SQL statement to the DB2 Database Manager for processing.
- #7: Host variables that transfer data to a database are known as input host variables, while host variables that receive data from a database are known as output host variables. Regardless of whether a host variable is used for input or output, its attributes must be appropriate for the context in which it is used. Therefore, you must define host variables in such a way that their data types and lengths are compatible with the data types and lengths of the columns they are intended to work with
- #8: A declare section can be coded anywhere high-level programming language variable declarations can be coded in a source code file. Although a source code file typically contains only one declare section, multiple declare sections are allowed.
- #13: a program accepts SQL statements from the keyboard at run-time. Generally, dynamic SQL statements are well suited for applications that interact with a rapidly changing database or that allow users to define and execute ad-hoc queries.
- #14: JDBC is an API that enables database access from Java programs
- #15: SQLJ is passed through a precompiler Checks SQL against the database Generates Java code with JDBC calls
- #16: JDBC needs: explicit statement handles explicit setXxx binds explicit connection
- #18: JDBC is an API that enables database access from Java programs
- #19: JDBC is an API that enables database access from Java programs
- #20: JDBC is an API that enables database access from Java programs
- #21: JDBC is an API that enables database access from Java programs



![Embedded SQL
ŌĆó Host variables are ordinary programming language variables.
ŌĆó To be set apart, they must be defined within a special section
known as a declare section.
EXEC SQL BEGIN DECLARE SECTION
char EmployeeID[7];
double Salary;
EXEC SQL END DECLARE SECTION
ŌĆó Each host variable must be assigned a unique name
even though declared in different declaration section.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sqldynamicembeddedj-150906153120-lva1-app6891/85/SQL-Embedded-SQL-Dynamic-SQL-and-SQLJ-7-320.jpg)
![Embedded SQL
main() {
EXEC SQL BEGIN DECLARE SECTION;
int OrderID, CustID;
char SalesPerson[10], Status[6];
EXEC SQL END DECLARE SECTION;
printf ("Enter order number: ");
scanf ("%d", &OrderID);
EXEC SQL SELECT CustID, SalesPerson, Status FROM
Orders WHERE OrderID = :OrderID INTO :CustID,
:SalesPerson, :Status;
printf ("Customer number: %d n", CustID);
printf ("Salesperson: %s n", SalesPerson);
printf ("Status: %s n", Status);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sqldynamicembeddedj-150906153120-lva1-app6891/85/SQL-Embedded-SQL-Dynamic-SQL-and-SQLJ-8-320.jpg)