SQLGitHub - Access GitHub API with SQL-like syntaxes
- 1. Servo & SQLGitHub A JOURNEY OF TRANSFORMING FAILURES INTO A GOOD IDEA
- 2. Servo ’üĄ A new browser engine written from scratch in Rust by Mozilla ’üĄ Original Project: Write an Android frontend for servo ’üĄ Issues, Issues and issues ’üĄ Zero knowledge about mobile development and Rust ’üĄ Outdated documentation ’üĄ Very poorly supported on Android ’üĄ Tried approaching in various ways, but to no avail ’üĄ Made build and packaging guide and reported issues
- 3. SQLGitHub ŌĆō Motivation (I) ’üĄ Who is stealing all my easy bugs/issues? ’üĄ There are very limited tools for managing GitHub organizations ’üĄ Open-source organizations are usually understaffed ’üĄ The Servo project on GitHub for example, contains 129 repositories managed by practically 1 person.
- 4. SQLGitHub ŌĆō Background ’üĄ Organization: Organizations are shared accounts where businesses and open-source projects can collaborate across many projects at once. ’üĄ Repository: A repository contains all of the project files, and stores each file's revision history. ’üĄ Commit: An individual change to a set of files. ’üĄ Issue: Suggested improvements, tasks or questions ’üĄ Pull Request: Proposed change to a repository. Repository Organization Repository Repository ŌĆó Commits ŌĆó Issues ŌĆó Pull Requests ŌĆó ŌĆ” ŌĆó Commits ŌĆó Issues ŌĆó Pull Requests ŌĆó ŌĆ” ŌĆó Commits ŌĆó Issues ŌĆó Pull Requests ŌĆó ŌĆ”https://help.github.com/articles/github-glossary/
- 5. SQLGitHub ŌĆō Motivation (II) ’üĄ Common questions/problems an organization admin include: ’üĄ Obtain certain metrics of the organization in machine-friendly format for post-processing (eg. KPI report) ’üĄ Get the current list of projects hosted on GitHub ’üĄ List of the most popular repositories in the organization ’üĄ Get the list of issues closed (resolved) for the past 7 days ’üĄ What are the critical issues that are still left open? ’üĄ Who are the top contributors of the past month? ’üĄ ŌĆ” endless possible questions
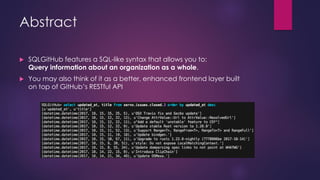
- 6. Abstract ’üĄ SQLGitHub features a SQL-like syntax that allows you to: Query information about an organization as a whole. ’üĄ You may also think of it as a better, enhanced frontend layer built on top of GitHubŌĆÖs RESTful API
- 7. Introduction ŌĆō Supported Schema ’üĄ SELECT select_expr [, select_expr ...] FROM {org_name | org_name.{repos | issues | pulls | commits}} [WHERE where_condition] [GROUP BY {col_name | expr} [ASC | DESC], ...] [HAVING where_condition] [ORDER BY {col_name | expr} [ASC | DESC], ...] [LIMIT row_count]
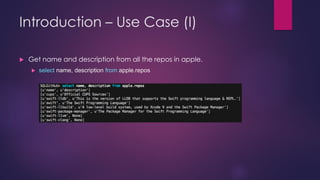
- 8. Introduction ŌĆō Use Case (I) ’üĄ Get name and description from all the repos in apple. ’üĄ select name, description from apple.repos
- 9. Introduction ŌĆō Use Case (II) ’üĄ Get last-updated time and title of the issues closed in the past week (7 days) in servo listed in descending order of last-updated time. ’üĄ select updated_at, title from servo.issues.closed.7 order by updated_at desc
- 10. Introduction ŌĆō Use Case (III) ’üĄ Get top 10 most-starred repositories in servo. ’üĄ select concat(concat("(", stargazers_count, ") ", name), ": ", description) from servo.repos order by stargazers_count desc, name limit 10
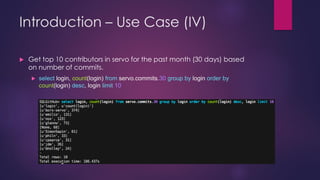
- 11. Introduction ŌĆō Use Case (IV) ’üĄ Get top 10 contributors in servo for the past month (30 days) based on number of commits. ’üĄ select login, count(login) from servo.commits.30 group by login order by count(login) desc, login limit 10
- 12. Introduction ŌĆō Technology Stack ’üĄ Python ’üĄ re & regex, regular expression libraries ’üĄ PyGithub (patched), an unofficial client library for GitHub API ’üĄ prompt_toolkit, a library for building prompts ’üĄ pygments, a library for syntax highlighting
- 13. Introduction ŌĆō (Simplified) Flow Fetch data (from) Filter by where conditions Evaluate partial exprs Group by group exprs Order by order exprs Evaluate select exprs Fetch data with required fields from GitHub API Evaluate where conditions and filter fetched data Evaluate group exprs and other ŌĆ£fieldŌĆØ exprs Generate table groups by values of group exprs Sort within and between tables Evaluate select exprs Filter by having conditions Evaluate having conditions and filter tables
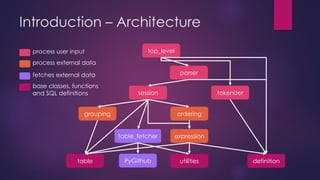
- 14. Introduction ŌĆō Architecture top_level parser tokenizersession grouping ordering table_fetcher expression definitionutilitiestable PyGithub process user input process external data fetches external data base classes, functions and SQL definitions
- 15. Introduction ŌĆō Challenges (I) ’üĄ Algorithm of parsing is almost identical to that of expression evaluation ’āĀ waste of time ’üĄ Lazy Parsing: Only parse clauses (eg. select, from, where) and comma- separated fields ’üĄ Comma-separated fields, strings and escape characters Evaluate this: concat("[)"Stars"(: ", stargazers_count) ’üĄ concat("[)"Stars"(: ", stargazers_count) concat("[)"Stars"(: ", stargazers_count) ’üĄ concat("[)"Stars"(: ", stargazers_count)
- 16. Introduction ŌĆō Challenges (II) ’üĄ Extracting all relevant fields from expressions to fetch at once ’üĄ select concat("[)"-> avg(stargazers_count)"(: ", stargazers_count - avg(stargazers_count), "] ", name) from apple.repos where description like "%library%" order by id ’üĄ Algorithm: for each expression, ’üĄ Remove all literal strings. Use r""(?:[^"]|.)*"" to match. ’üĄ Find all possible tokens with r"([a-zA-Z_]+)(?:[^(a-zA-Z_]|$)". ’üĄ For each token, check if itŌĆÖs a predefined token (ie. part of SQL).
- 17. Introduction ŌĆō Challenges (III) ’üĄ Expression Evaluation is really complicated ’üĄ Regular (eg. concat, floor) and Aggregate functions (eg. max, min) ’üĄ Have to evaluate an entire table at once ’üĄ Nested functions (eg. sum(avg(field_a) + avg(field_b))) ’üĄ Use recursive regex patterns to extract tokens ŌĆō rŌĆØ((?:(?>[^()]+|(?R))*))ŌĆØ ’üĄ Assign special precedence and insert extra logic in place ’üĄ Operator Precedence ’üĄ Modified 2-stack evaluation approach + ’üĄ Finite State Machine + One-token Lookahead
- 18. Introduction ŌĆō Challenges (IV) ’üĄ PythonŌĆÖs built-in sort is not customizable: sorted(iterable, *, key=None, reverse=False) ’üĄ order by requires sorting with multiple keys each with potentially different reverse: order by field_a desc, field_b asc, field_c, desc ’üĄ Wrote custom sort that integrates better with the workflow
- 19. Future Directions ’üĄ Improve SQL, MySQL compatibility ’üĄ Extend to end users not just organizations ’üĄ Migrate to the new GraphQL backend (GitHub API v4) ’üĄ Integrate SQLGitHub directly on the server end (better efficiency and perhaps better security!)
- 20. Acknowledgements ’üĄ We would like to thank: ’üĄ Shing Lyu, former software engineer at Mozilla Taiwan for the mentorship ’üĄ Irvin Chen, Liaison of MozTW (Mozilla Taiwan Community) for coordinating the program ’üĄ Prof. Cheng-Chung Lin for organizing the program





![Introduction ŌĆō Supported Schema
’üĄ SELECT
select_expr [, select_expr ...]
FROM {org_name | org_name.{repos | issues | pulls | commits}}
[WHERE where_condition]
[GROUP BY {col_name | expr}
[ASC | DESC], ...]
[HAVING where_condition]
[ORDER BY {col_name | expr}
[ASC | DESC], ...]
[LIMIT row_count]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sqlgithub-171023085625/85/SQLGitHub-Access-GitHub-API-with-SQL-like-syntaxes-7-320.jpg)





![Introduction ŌĆō Challenges (II)
’üĄ Extracting all relevant fields from expressions to fetch at once
’üĄ select concat("[)"-> avg(stargazers_count)"(: ", stargazers_count -
avg(stargazers_count), "] ", name) from apple.repos where description
like "%library%" order by id
’üĄ Algorithm: for each expression,
’üĄ Remove all literal strings. Use r""(?:[^"]|.)*"" to match.
’üĄ Find all possible tokens with r"([a-zA-Z_]+)(?:[^(a-zA-Z_]|$)".
’üĄ For each token, check if itŌĆÖs a predefined token (ie. part of SQL).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sqlgithub-171023085625/85/SQLGitHub-Access-GitHub-API-with-SQL-like-syntaxes-16-320.jpg)
![Introduction ŌĆō Challenges (III)
’üĄ Expression Evaluation is really complicated
’üĄ Regular (eg. concat, floor) and Aggregate functions (eg. max, min)
’üĄ Have to evaluate an entire table at once
’üĄ Nested functions (eg. sum(avg(field_a) + avg(field_b)))
’üĄ Use recursive regex patterns to extract tokens ŌĆō rŌĆØ((?:(?>[^()]+|(?R))*))ŌĆØ
’üĄ Assign special precedence and insert extra logic in place
’üĄ Operator Precedence
’üĄ Modified 2-stack evaluation approach +
’üĄ Finite State Machine + One-token Lookahead](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sqlgithub-171023085625/85/SQLGitHub-Access-GitHub-API-with-SQL-like-syntaxes-17-320.jpg)


