аҙӘаҙҡаөҚаҙҡаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙұаҙҝ аҙңаөҲаҙө аҙ•аөғаҙ·аҙҝаҙ°аөҖаҙӨаҙҝаҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚ
- 1. ORGANIC VEGETABLE CULTIVATION HAPPY MATHEW.K AGRICULTURAL OFFICER KRISHI BHAVAN, MEENADOM KOTTAYAM DISTRICT
- 4. пӮ— аҙӘаҙҡаөҚаҙҡаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙұаҙҝаҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚ аҙ’аҙ°аөҒ аҙёаҙӮаҙ°аҙ•аөҚаҙ·аҙҝаҙӨ аҙҶаҙ№аҙҫаҙ°аҙ®аҙҫаҙЈ пӮ— аҙ•аҙҫаҙІаөҚвҖҚаҙёаҙҜаҙӮ,аҙҮаҙ°аөҒаҙ®аөҚаҙӘаөҚ,аҙ«аҙ«аҙҫаҙёаөҚаҙ«аҙҫаҙұаҙё аҙҺаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаөҖ аҙ§аҙҫаҙӨаөҒаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙі аҙӮ аөҲаөҖаҙөаҙ•аҙҷаөҚаҙҷаҙіаөҚвҖҚ аҙҶаҙҜ A,B,C аҙҺаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаҙҝаҙөаҙҜаөҒаҙӮ аҙ…аҙҹаҙҷаөҚаҙҷаҙҝаҙҜ аҙөаҙҝаҙіаҙҜаҙҫаҙЈ аҙӘаҙҡаөҚаҙҡаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙұаҙҝаҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚ аҙ•аөӮаҙҹаҙҫаөҚаҙӨ аҙ«аөҚаҙӘаҙҫаҙҹаөҖаҙЁаөҚвҖҚ ,аҙ•аҙҫаҙ°аөҚаҙ«аҙ¬аҙҫаҙңаҙ№аҙ«аөҚаҙҹаҙұаөҚаҙұаөҚ,аҙЁаҙҫаҙ°аөҒаҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚ аҙҺаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаҙҝаҙөаҙҜаөҒаҙӮ аҙ…аҙҹаҙҷаөҚаҙҷаҙҝаҙҜаҙҝаҙҹаөҚаҙҹ аҙЈаөҚаҙҹаөҚ
- 5. пӮ— аөҚаҙӘаҙҫаҙҜаҙӘаөӮаҙ°аөҚаҙӨаҙҝ аҙҶаҙҜ аҙ’аҙ°аҙҫаҙіаөҚвҖҚ аҙ’аҙ°аөҒ аҙҰаҙҝаҙөаҙёаҙӮ 300аөҚаөҚаҙҫаҙӮ аҙӘаҙҡаөҚаҙҡаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙұаҙҝаҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚ аҙҺаҙҷаөҚаҙ•аҙҝаҙІаөҒаҙӮ аҙ•аҙҙаҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙЈаҙӮ. пӮ— аҙ…аҙӨаҙҝаҙІаөҚвҖҚ 120 аөҚаөҚаҙҫаҙӮ аҙҮаҙІаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙұаҙҝаҙ•аҙі аҙӮ,90 аөҚаөҚаҙҫаҙӮ аҙөаөҖаҙӨаҙӮ аҙ•аҙҝаҙҙаҙҷаөҚаҙҷаөҒаҙөаҙ°аөҚаҙ—аҙҷаөҚаҙҷаҙі аҙӮ,аҙӘаҙҙаҙөаҙ°аөҚаөҚ аҙӘаҙҡаөҚаҙҡаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙұаҙҝаҙ•аҙі аҙӮ аҙ…аҙҹаҙҷаөҚаҙҷаҙҝаҙҜаҙҝаҙ°аҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙЈаҙӮ. пӮ— аҙ’аҙ°аөҒ аҙөаөҖаҙҹаөҚаҙҹаҙҝаҙ«аҙІаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҚ аҙҶаҙөаҙ¶аөҚаҙҜаҙ®аҙҫаҙҜ аҙӘаҙҡаөҚаҙҡаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙұаҙҝаҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚ аҙүаҙІаөҚвҖҚаҙӘаҙҫаҙҰаҙҝаҙӘаөҚаҙӘаҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙҫаҙЁаөҚвҖҚ аҙ«аҙөаҙЈаөҚаҙҹаҙҝ аҙ’аҙ°аҙҫаҙіаөҚвҖҚаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҚ аҙ’аҙ°аөҒ аөҚаҙёаҙЁаөҚвҖҚаҙұаөҚ (40 m2) аҙёаөҚаҙҘаҙІаҙӮ аҙҶаҙөаҙ¶аөҚаҙҜаҙ®аҙҫаҙЈ
- 6. пӮ— аҙёаөҚаҙҘаҙІаҙӨаҙҝаҙЁаөҚ аҙҡаөҒаҙұаөҚаҙұ аҙӮ аҙ«аҙөаҙІаҙҝ аөҚаҙ•аҙҹаөҚаҙҹаҙЈаҙӮ. пӮ— аҙ’аҙ°аөҒ аҙөаҙ¶аөҚаөҚаҙӨ аҙ«аҙөаҙІаҙҝ аҙҡаҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙ°аөҚаҙ®аҙҫаҙЁаҙҝаҙё аөҚаҙ•аҙҫаҙЈаөҚаҙҹаөҚ аҙүаҙЈаөҚаҙҹаҙҫаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙҫаҙӮ. пӮ— аҙ®аҙұаөҚаҙұ аҙ®аөӮаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаөҒ аҙөаҙ¶аөҚаҙҷаөҚаҙҷаҙіаҙҝаҙІаөҒаҙӮ аҙ«аҙөаҙІаҙҝаҙҜаҙҝаҙІаөҚвҖҚ аҙ«аҙ•аҙҫаҙөаҙІаөҚвҖҚ ,аҙ…аҙ®аҙ°аҙӘаөҚаҙӘаҙҜаҙ°аөҚ , аҙҡаҙӨаөҒаҙ°аҙӘаөҚаҙӘаҙҜаҙ°аөҚ аҙҺаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаҙҝаҙө аҙӘаҙҹаҙ°аөҚаҙӨаҙҝ аҙөаҙіаҙ°аөҚаҙӨаҙҫаҙӮ. пӮ— аҙүаҙіаөҚаҙіаҙҝаҙІаҙҫаҙҜаҙҝ аҙ®аҙұаөҚаҙұ аҙӘаҙҡаөҚаҙҡаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙұаҙҝаҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚ аҙ•аөғаҙ·аҙҝ аөҚаҙҡаҙҜаөҚаҙҫаҙӮ.
- 11. TOMATO
- 12. BRINJAL
- 13. BHINDI
- 14. CHILLI
- 15. CABBAGE
- 16. CAULIFLOWER
- 17. аҙҡаҙҫаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙҝаҙІаөҚвҖҚ/аҙҡаҙҹаөҚаҙҹаҙҝаҙҜаҙҝаҙІаөҚвҖҚ аҙ•аөғаҙ·аҙҝ аөҚаҙҡаҙҜаөҚ аҙЁаөҚаҙЁ аҙөаҙҝаҙ§аҙӮ пӮ— аҙңаөҲаҙө аҙөаҙіаҙӮ(10kg),аҙ®аҙЈаөҚаҙЈаөҚ(70kg),аҙ®аҙЈаҙІаөҚвҖҚ (10kg), аҙ«аҙұаҙҫаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҚ аҙ«аҙ«аҙҫаҙёаҙ«аҙ«аҙұаөҚаҙұаөҚ(10kg), аҙөаҙҫаҙӮ (1kg),аҙ…аҙ«аҙёаҙҫаҙёаҙӘаҙҝаҙ°аҙҝаҙІаҙІаҙӮ (1kg) аҙҺаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаҙҝаҙө аҙЁаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаҙҫаҙҜаҙҝ аҙ•аөӮаҙҹаөҚаҙҹаҙҝ аҙ•аҙІаҙ°аөҚаҙӨаөҒаҙ•. пӮ— аҙҲ аҙөаҙіаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөӮаҙҹаөҚаҙҹаөҚ аҙҡаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙҝаҙ«аҙІаҙҫ /аҙҡаҙҹаөҚаҙҹаҙҝаҙҜаҙҝаҙ«аҙІаҙҫ аҙ®аөҒаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙҫаҙІаөҚвҖҚ аҙӯаҙҫаөҚаҙӮ аҙЁаҙҝаҙұаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙ•. аҙӨаҙөаҙҫаҙ°аҙЈаҙҜаҙҝаҙІаөҚвҖҚ аҙүаҙЈаөҚаҙҹаҙҫаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙҝаҙҜ аҙңаҙӨаҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚ аҙӘаҙұаҙҝаҙҡаөҚаҙҡ аҙЁаҙҹаөҒаҙ•аҙ«аҙҜаҙҫ /аҙөаҙҝаҙӨаҙҝаҙҹаөҚаҙҹаөҚ аҙ•аҙҝаҙіаҙҝаҙ°аөҚаҙӘаөҚаҙӘаҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙ•аҙ«аҙҜаҙҫ аөҚаҙҡаҙҜаөҚ аҙ•. пӮ— аҙҲ аҙҡаҙҫаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚ /аҙҡаҙҹаөҚаҙҹаҙҝаҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚ аөҚаҙҹаҙұаҙёаҙҝаҙ«аҙІаҙҫ/аҙЁаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаҙҫаҙҜаҙҝ аөҚаҙөаҙҜаҙҝаҙІаөҚвҖҚ аҙ•аҙҝаҙҹаөҚаҙҹ аҙЁаөҚаҙЁ аҙёаөҚаҙҘаҙІаҙҷаөҚаҙҷаҙіаҙҝаҙ«аҙІаҙҫ аҙңаҙөаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙҫаҙӮ. пӮ— аҙ°аҙЈаөҚаҙҹаҙҫаҙҙаөҚаҙҡаҙҜаҙҝаҙІаөҚвҖҚ аҙ’аҙЁаөҚаҙЁаөҒ аҙөаөҖаҙӨаҙӮ аҙҡаҙҫаҙЈаҙ•аөҚаҙөаҙіаөҚаҙіаҙӮ аҙ«аҙЁаҙ°аөҚаҙӘаҙҝаҙҡаөҚаҙҡаөҚ аөҚаҙҡаҙҹаҙҝаҙ•аҙі аөҚаҙҹ аҙҡаөҒаҙөаҙҹаөҚаҙҹаҙҝаҙІаөҚвҖҚ аҙ’аҙҙаҙҝаҙҡаөҚаҙҡ аөҚаҙ•аҙҫаҙҹаөҒаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙҫаҙӮ. пӮ— аҙҶаҙөаҙ¶аөҚаҙҜаҙҫаҙЁаөҒаҙёаҙ°аҙЈаҙӮ аҙЁаҙЁаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙ•. аҙҡаөҒаҙөаҙҹаөҚаҙҹаҙҝаҙІаөҚвҖҚ аөҚаҙөаҙіаөҚаҙіаҙӮ аөҚаҙ•аҙҹаөҚаҙҹаҙҝ аҙЁаҙҝаҙІаөҚвҖҚаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙ°аөҒаҙӨаөҚ. пӮ— аҙ®аҙҫаҙёаҙӨаҙҝаҙІаөҚвҖҚ аҙ’аҙЁаөҚаҙЁаөҒ аҙөаөҖаҙӨаҙӮ 250 g аҙ¬аҙ«аҙҜаҙҫ-аҙ“аҙ°аөҚаөҚаҙҫаҙЁаҙҝаҙ•аөҚ аҙөаҙіаҙӮ аҙҡаөҒаҙөаҙҹаөҚаҙҹаҙҝаҙІаөҚвҖҚ аҙҮаҙҹаөҚаҙҹ аөҚаҙ•аҙҫаҙҹаөҒаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙЈаҙӮ.
- 21. Two-in-one
- 22. Excellent for field planting No tillage and no weed competition Simple farming !!
- 23. Field planting with drip irrigation
- 24. Planting beds
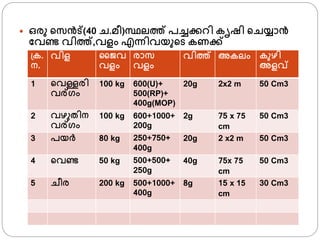
- 26. пӮ— аҙ’аҙ°аөҒ аөҚаҙёаҙЁаөҚвҖҚаөҚ(40 аҙҡ.аҙ®аөҖ)аҙёаөҚаҙҘаҙІаҙӨаөҚ аҙӘаҙҡаөҚаҙҡаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙұаҙҝ аҙ•аөғаҙ·аҙҝ аөҚаҙҡаҙҜаөҚаҙҫаҙЁаөҚвҖҚ аҙ«аҙөаҙЈаөҚаҙҹ аҙөаҙҝаҙӨаөҚ,аҙөаҙіаҙӮ аҙҺаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаҙҝаҙөаҙҜаөҒаөҚаҙҹ аҙ•аҙЈаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҚ аөҚаҙ•. аҙЁ. аҙөаҙҝаҙі аҙңаөҲаҙө аҙөаҙіаҙӮ аҙ°аҙҫаҙё аҙөаҙіаҙӮ аҙөаҙҝаҙӨаөҚ аҙ…аҙ•аҙІаҙӮ аҙ•аөҒаҙҙаҙҝ аҙ…аҙіаҙөаөҚ 1 аөҚаҙөаҙіаөҚаҙіаҙ°аҙҝ аҙөаҙ°аөҚаөҚаҙӮ 100 kg 600(U)+ 500(RP)+ 400g(MOP) 20g 2x2 m 50 Cm3 2 аҙөаҙҙаөҒаҙӨаҙҝаҙЁ аҙөаҙ°аөҚаөҚаҙӮ 100 kg 600+1000+ 200g 2g 75 x 75 cm 50 Cm3 3 аҙӘаҙҜаҙ°аөҚ 80 kg 250+750+ 400g 20g 2 x2 m 50 Cm3 4 аөҚаҙөаҙЈаөҚаҙҹ 50 kg 500+500+ 250g 40g 75x 75 cm 50 Cm3 5 аҙҡаөҖаҙ° 200 kg 500+1000+ 400g 8g 15 x 15 cm 30 Cm3
- 27. аҙҮаҙІаҙ•аҙіаҙҝаҙІаөҚвҖҚ аҙӨаҙіаҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙЁаөҚаҙЁ аҙ°аҙҫаҙё аҙөаҙіаҙҷаөҚаҙҷаҙіаөҚвҖҚ 19:19:19(аөҚаҙӘаҙҫаҙіаҙҝаҙ«аөҖаҙЎаөҚ ),аҙ®аҙіаөҚвҖҚаҙҹаҙҝ аөҚаҙ• вҖ“аҙ°аҙЈаөҚаҙҹаөҒ аҙөаҙіаҙөаөҒаҙӮ 2 аөҚаөҚаҙҫаҙӮ аҙөаөҖаҙӨаҙӮ аҙ’аҙ°аөҒ аҙІаҙҝ. аөҚаҙөаҙіаөҚаҙіаҙӨаҙҝаҙІаөҚвҖҚ аҙ•аҙІаҙ°аөҚаҙӨаҙҝ аҙңаҙөаҙ•аөҒаҙ«аҙЁаөҚаҙЁаҙ°аҙҷаөҚаҙҷаҙіаҙҝаҙІаөҚвҖҚ аҙӨаҙіаҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙ• аҙңаөҲаҙө аҙөаҙіаҙҷаөҚаҙҷаҙіаөҚвҖҚ 1.аҙ«аҙөаҙ°аөҚаҙ®аҙҝ аҙөаҙҫаҙ·аөҚвҖҢ 6-10 аҙҮаҙ°аҙҹаөҚаҙҹаҙҝ аөҚаҙөаҙіаөҚаҙіаҙӮ аҙ«аҙҡаҙ°аөҚаҙӨаөҚ аҙӨаҙіаҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙҫаҙӮ 2.аҙёаҙҜаөҒаҙ«аҙҹаҙҫаҙ«аҙ®аҙҫаҙЈаҙҫаҙё аҙІаҙҫаҙҜаҙЁаҙҝ 2% аҙөаөҖаҙ°аҙҜаҙӨаҙҝаҙІаөҚвҖҚ аҙӨаҙіаҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙҫаҙӮ 3.аҙҡаҙҫаҙЈаҙ•аҙөаөҒаҙӮ,аҙӘаҙҝаҙЈаөҚаҙЈаҙҫаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙӮ аҙ•аөӮаҙҹаҙҝ аҙӘаөҒаҙіаҙҝаҙӘаөҚаҙӘаҙҝаҙҡаөҚаҙҡаөҚ 10 аҙҮаҙ°аҙҹаөҚаҙҹаҙҝ аөҚаҙөаҙіаөҚаҙіаҙӮ аҙ«аҙҡаҙ°аөҚаҙӨаөҚ аҙӨаҙіаҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙҫаҙӮ.
- 28. аҙ…аҙҹаөҒаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙіаҙ«аҙӨаҙҫаҙҹаөҚаҙҹаҙӨаҙҝаҙІаөҚвҖҚ аҙ•аөғаҙ·аҙҝ аөҚаҙҡаҙҜаөҚаҙҫаҙЁаөҚвҖҚ аҙӘаҙұаөҚаҙұаҙҝаҙҜ аҙӘаҙҡаөҚаҙҡаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙұаҙҝаҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚ пӮ— аҙӘаҙҹаҙөаҙІ аҙөаҙ°аөҚаҙ— аҙөаҙҝаҙіаҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚ - аҙӘаҙҫаҙөаҙІаөҚвҖҚ,аҙӘаҙҹаҙөаҙІаҙӮ,аҙ«аҙ•аҙҫаҙөаҙІаөҚвҖҚ,аҙ•аөҒаҙ®аөҚаҙӘаҙіаҙӮ,аҙӘаөҖаҙҡаөҚаҙҡаҙҝ аҙҷаөҚаҙҷ пӮ— аҙӘаҙҫаҙөаҙІаөҚвҖҚ-аөҚаҙӘаҙҝаҙҜ,аөҚаҙӘаөҖаҙӨаҙҝ,аөҚаҙӘаҙҝаҙҜаҙҷаөҚаҙ• пӮ— аҙӘаҙҹаҙөаҙІаҙӮ-аөҚаҙ•аөҢаҙ®аөҒаҙҰаҙҝ,аҙ«аҙ¬аҙ¬аҙҝ,аҙҹаҙҝ.аҙҺ.19 пӮ— аөҚаҙөаҙіаөҚаҙіаҙ°аҙҝвҖ“аҙ®аөҒаҙҹаҙҝаҙ«аҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙҫаөҚ аҙ«аҙІаҙҫаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙІаөҚвҖҚ
- 29. аҙӨаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙҫаҙіаҙҝ аҙөаҙ°аөҚаҙ— аҙөаҙҝаҙіаҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚ пӮ— аҙ®аөҒаҙіаҙ•аөҚ-аҙ®аҙһаөҚаөҲаҙ°аҙҝ,аҙүаөҲаҙөаҙІ,аҙ…аҙЁаөҒаөҚаөҚаҙ№,аҙӘаҙҫаҙЁаөҚаҙӨаөҚ- аҙёаҙҝ.1,аөҲаҙөаҙҫаҙІаҙҫаҙ®аөҒаҙ–аҙҝ пӮ— аҙӨаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙҫаҙіаҙҝ-аҙ¶аөҚаҙ•аөҚаҙӨаҙҝ,аҙ®аөҒаҙ–аөҚаҙӨаҙҝ,аҙ…аҙЁаҙ– пӮ— аҙөаҙҙаөҒаҙӨаҙҝаҙЁ-аҙёаөӮаҙ°аҙҜ,аҙ«аҙ¶аөҚаҙөаҙӨ,аҙ№аҙ°аҙҝаҙӨ ,аҙЁаөҖаҙІаҙҝаҙ®,аҙӘаөӮаҙё аҙӘаҙ°аөҚаҙӘаөҚаҙӘаҙҝаҙіаөҚвҖҚ аҙ•аөҚаҙІаҙёаҙҹаҙ°аөҚ
- 30. аҙӘаҙҜаҙұаөҒаҙөаҙ°аөҚаҙ— аҙөаҙҝаҙіаҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚ пӮ— аҙ•аөҒаҙұаөҚаҙұаҙҝаҙӘаөҚаҙӘаҙҜаҙ°аөҚ- аҙ…аҙЁаҙ¶аөҚаҙөаҙ°,аҙӯаҙҫаөҚаҙҜаҙІаҙ•аөҚаҙ·аөҚаҙ®аҙҝ,аҙңаҙ•аҙ°аҙіаҙҝ,аҙ•аҙЁаҙ•аҙ®аҙЈаҙҝ пӮ— аҙөаҙіаөҚаҙіаҙҝаҙӘаөҚаҙӘаҙҜаҙ°аөҚ- аҙ¶аөҚаҙҫаҙ°аҙҝаҙ•,аҙ®аҙҫаҙІаҙҝаҙ•,аөҚаҙ•.аҙҺаҙӮ.аҙөаҙҝ.1,аҙ«аҙІаҙҫаҙІ,,аҙңаҙөаөҲаҙҜаҙЁаөҚаҙӨаҙҝ
- 31. аҙҮаҙІаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙұаҙҝ аҙөаҙҝаҙіаҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚ пӮ— аҙҡаөҒаҙөаҙӘаөҚаҙӘаөҚ аҙҮаҙЁаҙҷаөҚаҙҷаҙіаөҚвҖҚ -аҙ…аҙ°аөҒаҙЈаөҚвҖҚ,аҙ•аҙЈаөҚаҙЈаҙҫаҙұ аҙ«аҙІаҙҫаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙІаөҚвҖҚ аҙӘаҙҡаөҚаҙҡ аҙҡаөҖаҙ° вҖ“аҙёаҙҝ.аҙ“.1,2,3; аҙ«аҙ®аҙҫаҙ№аҙҝаҙЁаҙҝ аҙёаҙҫаҙ®аөҚаҙӘаҙҫаҙ°аөҚ аҙҡаөҖаҙ°, аҙ…аөҚаҙӨаҙҝ аҙҡаөҖаҙ°,аҙҡаҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙ°аөҚаҙ®аҙҫаҙЁаҙҝаҙё аҙ®аөҒаҙ°аҙҝаҙҷаөҚаҙҷ аөҚаҙөаҙЈаөҚаҙҹ- аҙӘаҙҡаөҚаҙҡ аҙ•аҙҫаҙҜаөҚаҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚ -аҙ…аҙ°аөҚаҙ•аөҚаҙ• аҙ…аҙЁаҙҫаҙ®аҙҝаҙ•,аҙ…аҙ°аөҚаҙ•аөҚаҙ• аҙ…аҙӯаҙҜаөҚ,аҙёаөҒаҙёаөҚаҙҘаҙҝаҙ° аҙҡаөҒаҙөаҙӘаөҚаҙӘаөҚ аҙ•аҙҫаҙҜаөҚаҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚ -аҙ…аҙ°аөҒаҙЈ,аҙёаҙҝ.аҙ“.-1
- 32. аҙңаөҲаҙөаҙөаҙіаҙҷаөҚаҙҷаҙіаөҚвҖҚ пӮ— аҙӘаҙҡаөҚаҙҡаҙҝаҙІ аҙөаҙіаҙҷаөҚаҙҷаҙіаөҚвҖҚ пӮ— аҙҡаҙҫаҙЈаҙ•аҙӮ ,аҙ•аҙ«аҙ®аөҚаҙӘаҙҫаҙёаөҚаҙұаөҚаөҚ , пӮ— аҙҡаҙҫаҙ°аҙӮ,аҙ«аөҚаҙҫаҙ¬аҙ°аөҚ аөҚаҙҜаҙҫаҙё аҙёаөҚаҙІаҙұаҙҝ ,аҙ®аҙЈаөҚаҙЈаҙҝаҙ°аҙ•аҙ«аҙ®аөҚаҙӘаҙҫаҙёаөҚаҙұаөҚаөҚ пӮ— аҙ«аҙөаҙ°аөҚаҙ®аҙҝаҙөаҙҫаҙ·аөҚвҖҢ, аҙҺаҙІаҙІ аөҚаҙӘаҙҫаҙҹаҙҝ пӮ— аҙҶаҙҹаөҚаҙҹаҙҝаҙЁаөҚвҖҚ аҙ•аҙҫаҙ·аөҚаҙҹаҙӮ, пӮ— аҙ«аҙ•аҙҫаҙҙаҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙҫаҙ·аөҚаҙҹаҙӮ , пӮ— аҙҡаҙ•аҙҝаҙ°аҙҝаҙ«аҙҡаөҚаҙҡаҙҫаҙ°аөҚ аҙңаөҲаҙөаҙөаҙіаҙӮ , пӮ— аҙ®аҙ·аөҚвҖҢаҙұаөӮаҙӮ аҙ•аҙ«аҙ®аөҚаҙӘаҙҫаҙёаөҚаҙұаөҚаөҚ, пӮ— аҙӘаҙҝаҙЈаөҚаҙЈаҙҫаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚ , пӮ— аҙҡаҙҫаҙЈаҙ•аҙӮ-аҙӘаҙҝаҙЈаөҚаҙЈаҙҫаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҚ аҙёаөҚаҙІаҙұаҙҝ
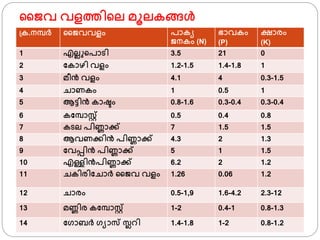
- 33. аҙңаөҲаҙө аҙөаҙіаҙӨаҙҝаөҚаҙІ аҙ®аөӮаҙІаҙ•аҙҷаөҚаҙҷаҙіаөҚвҖҚ аөҚаҙ•.аҙЁаҙ®аөҚаҙӘаҙ°аөҚ аҙңаөҲаҙөаҙөаҙіаҙӮ аҙӘаҙҫаҙ•аҙҜ аөҲаҙЁаҙ•аҙӮ (N) аҙӯаҙҫаҙөаҙ•аҙӮ (P) аҙ•аөҚаҙ·аҙҫаҙ°аҙӮ (K) 1 аҙҺаҙІаҙІ аөҚаҙӘаҙҫаҙҹаҙҝ 3.5 21 0 2 аҙ«аҙ•аҙҫаҙҙаҙҝ аҙөаҙіаҙӮ 1.2-1.5 1.4-1.8 1 3 аҙ®аөҖаҙЁаөҚвҖҚ аҙөаҙіаҙӮ 4.1 4 0.3-1.5 4 аҙҡаҙҫаҙЈаҙ•аҙӮ 1 0.5 1 5 аҙҶаҙҹаөҚаҙҹаҙҝаҙЁаөҚвҖҚ аҙ•аҙҫаҙ·аөҚаҙҹаҙӮ 0.8-1.6 0.3-0.4 0.3-0.4 6 аҙ•аҙ«аҙ®аөҚаҙӘаҙҫаҙёаөҚаҙұаөҚаөҚ 0.5 0.4 0.8 7 аҙ•аҙҹаҙІ аҙӘаҙҝаҙЈаөҚаҙЈаҙҫаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҚ 7 1.5 1.5 8 аҙҶаҙөаҙЈаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙҝаҙЁаөҚвҖҚ аҙӘаҙҝаҙЈаөҚаҙЈаҙҫаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҚ 4.3 2 1.3 9 аҙ«аҙөаҙӘаөҚаҙӘаҙҝаҙЁаөҚвҖҚ аҙӘаҙҝаҙЈаөҚаҙЈаҙҫаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҚ 5 1 1.5 10 аҙҺаҙіаөҚаҙіаҙҝаҙЁаөҚвҖҚаҙӘаҙҝаҙЈаөҚаҙЈаҙҫаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҚ 6.2 2 1.2 11 аҙҡаҙ•аҙҝаҙ°аҙҝаҙ«аҙҡаҙҫаҙ°аөҚ аҙңаөҲаҙө аҙөаҙіаҙӮ 1.26 0.06 1.2 12 аҙҡаҙҫаҙ°аҙӮ 0.5-1,9 1.6-4.2 2.3-12 13 аҙ®аҙЈаөҚаҙЈаҙҝаҙ° аҙ•аҙ«аҙ®аөҚаҙӘаҙҫаҙёаөҚаҙұаөҚаөҚ 1-2 0.4-1 0.8-1.3 14 аҙ«аөҚаҙҫаҙ¬аҙ°аөҚ аөҚаҙҜаҙҫаҙё аҙёаөҚаҙІаҙұаҙҝ 1.4-1.8 1-2 0.8-1.2
- 34. 1000 аҙ•аҙҝ.аөҚаөҚаҙҫаҙӮ аҙүаҙЈаҙҷаөҚаҙҷаҙҝаҙҜ аҙ«аҙ•аҙҫаҙҙаҙҝ аҙөаҙіаҙӮ = пӮ— 100 kg Urea пӮ— 150 kg Super phosphate пӮ— 50 kg MOP пӮ— 750 kg Organic matter пӮ— 125 kg Calcium carbonate пӮ— 30 kg Sulphur пӮ— 12 kg Sodium chloride пӮ— 10 kg Magnesium sulphate пӮ— 5 kg Ferrous sulphate пӮ— 1kg Manganese sulphate пӮ— 1kg Zinc sulphate пӮ— 1 kg Other trace elements
- 35. аҙёаҙӮаҙ«аҙҜаҙҫаөҲаҙҝаҙӨ аҙ•аөҖаҙҹ аҙЁаҙҝаҙҜаөҚаҙЁаөҚаҙӨаҙЈаҙӮ аҙӘаҙҡаөҚаҙҡаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙұаҙҝ аҙөаҙҝаҙіаҙ•аҙіаҙҝаҙІаөҚвҖҚ
- 36. аҙёаҙӮаҙ«аҙҜаҙҫаөҲаҙҝаҙӨ аҙ•аөҖаҙҹаҙЁаҙҝаҙҜаөҚаҙЁаөҚаҙӨаҙЈаҙӨаҙҝаҙІаөҚвҖҚ аҙҠаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаҙІаөҚвҖҚ аөҚаҙ•аҙҫаҙҹаөҒаҙ«аҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙЈаөҚаҙҹ аҙ•аҙҫаҙ°аҙҜаҙҷаөҚаҙҷаҙіаөҚвҖҚ пӮ— аҙ°аҙҫаҙё аҙ•аөҖаҙҹаҙЁаҙҫаҙ¶аөҚаҙҝаҙЁаҙҝ аөҚаҙӘаҙ«аҙҜаҙҫаөҚаҙӮ аҙ…аҙөаҙёаҙҫаҙЁаөҚаҙӨ аҙ®аҙҫаҙ°аөҚаөҚаҙӮ пӮ— аҙ®аҙҝаөҚаҙӨаөҚаҙӘаҙҫаҙЈаҙҝаҙ•аҙі аөҚаҙҹ аҙёаҙӮаҙ°аҙ•аөҚаҙ·аҙЈаҙӮ аҙүаҙұаҙӘаөҚаҙӘ аҙөаҙ°аөҒаҙӨаөҒаҙ• пӮ— аҙӘаҙ°аҙ®аҙҫаҙөаҙ§аҙҝ аҙңаөҲаҙө аҙөаҙіаөҚаҙӘаҙ«аҙҜаҙҫаөҚаҙӮ аҙЁаҙҹаҙӨаөҒаҙ• пӮ— аҙ°аҙҫаҙёаҙөаҙіаҙӮ аҙҶаҙөаҙ¶аөҚаҙҜаҙӨаҙҝаҙЁаөҒаҙ®аҙҫаөҚаҙӨаҙӮ пӮ— аҙӘаҙ®аҙҫаҙөаҙ§аҙҝ аҙңаөҲаҙөаҙ•аөҖаҙҹаҙЁаҙҫаҙ¶аөҚаҙҝаҙЁаҙҝаҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚ аҙүаҙӘаҙ«аҙҜаҙҫаөҚаҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙ• пӮ— аҙ…аҙЁаөҒаҙ«аҙҜаҙҫаөҲаҙҜаҙ®аҙҫаҙҜ аҙёаҙ®аҙҜаҙӨаөҒ аҙ•аөғаҙ·аҙҝаҙҜаҙҝаҙұаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙ• пӮ— аҙ•аҙіаҙЁаҙҝаҙҜаөҚаҙЁаөҚаҙӨаҙЈаҙӮ аҙүаҙұаҙӘаөҚаҙӘ аҙөаҙ°аөҒаҙӨаөҒаҙ• пӮ— аҙ®аҙҝаөҚаҙ¶аөҚ аҙөаҙҝаҙі аҙёаөҚаҙ®аөҚаҙӘаҙҰаҙҫаҙҜаҙӮ аҙЁаҙҹаҙӘаөҚаҙӘаҙҝаҙІаҙҫаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙ• пӮ— аҙ•аөғаҙ·аҙҝаҙҜаҙҝаҙҹаҙҷаөҚаҙҷаҙіаҙҝаҙІаөҚвҖҚ аҙ•аөғаҙӨаҙҜаҙ®аҙҫаҙҜаҙҝ аҙЁаҙҝаҙ°аөҖаҙ•аөҚаҙ·аҙЈаҙӮ аҙЁаҙҹаҙӨаөҒаҙ•,аҙҜаҙҘаҙҫаҙёаҙ®аҙҜаҙӮ аөҚаҙӘаҙөаҙ°аөҚаҙӨаҙЁаҙҷаөҚаҙҷаҙіаөҚвҖҚаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҚ аҙ°аөӮаҙӘаҙӮ аөҚаҙ•аҙҫаҙҹаөҒаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙ•
- 37. аҙ…аҙЁаҙҝаҙҜаөҚаҙЁаөҚаҙӨаҙҝаҙӨаҙ®аҙҫаҙҜ аҙ•аөҖаҙҹаҙЁаҙҫаҙ¶аөҚаҙҝаҙЁаҙҝаөҚаҙӘаҙ«аҙҜаҙҫаөҚаҙӮ аҙ®аөӮаҙІаҙӮ аҙёаҙӮаҙӯаҙөаҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаҙӨаөҚ пӮ— аҙ®аҙҝаөҚаҙӨаҙ•аөҖаҙҹаҙҷаөҚаҙҷаҙіаөҚвҖҚ аҙҡаҙӨаөҒ аҙөаөҖаҙҙаөҒаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаөҒ. пӮ— аҙ¶аөҚаөҚаҙӨаөҒ аҙ•аөҖаҙҹаҙҷаөҚаҙҷаҙіаөҚвҖҚ аөҚаҙӘаҙұаөҚаҙұаөҚ аөҚаҙӘаҙ°аөҒаҙ•аөҒаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаөҒ. пӮ— аҙ…аөҚаҙӘаҙ§аҙҫаҙЁ аҙ•аөҖаҙҹаҙҷаөҚаҙҷаҙіаөҚвҖҚ аөҚаҙӘаҙ§аҙҫаҙЁ аҙ•аөҖаҙҹаҙҷаөҚаҙҷаҙіаҙҫаҙ•аөҒаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаөҒ. пӮ— аҙ•аөҖаҙҹаҙҷаөҚаҙҷаҙіаөҚвҖҚ аҙ•аөҖаҙҹаҙЁаҙҫаҙ¶аөҚаҙҝаҙЁаҙҝаҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚаөҚаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙӨаҙҝаөҚаҙ° аөҚаҙӘаҙӨаҙҝаҙ«аҙ°аҙҫаҙ§ аҙ¶аөҚаҙ•аөҚаҙӨаҙҝ аҙҶаҙ°аөҚаөҲаҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаөҒ. пӮ— аҙ«аҙІаҙҷаөҚаҙҷаҙіаҙҝаҙІаөҚвҖҚ аҙ…аҙөаҙ¶аөҚаҙҝаҙ·аөҚаҙҹ аҙөаҙҝаҙ·аҙӮ аҙӨаҙҷаөҚаҙҷаҙҝ аҙЁаҙҝаҙІаөҚвҖҚаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаөҒ. пӮ— аҙӘаҙ°аҙёаҙ° аҙ®аҙІаҙҝаҙЁаөҖаҙ•аҙ°аҙЈаҙӮ аөҚаҙӘаҙ§аҙҫаҙЁ аөҚаҙӘаҙ¶аөҚаҙЁаҙ®аҙҫаҙ•аөҒаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаөҒ.
- 38. аҙ°аҙҫаҙёаҙ•аөҖаҙҹаҙЁаҙҫаҙ¶аөҚаҙҝаҙЁаҙҝаҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚ аҙүаҙӘаҙ«аҙҜаҙҫаөҚаҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙ«аҙ®аөҚаҙӘаҙҫаҙіаөҚвҖҚ пӮ— аҙҶаҙөаҙ¶аөҚаҙҜаҙӮ аҙ…аҙұаҙҝаҙһаөҚаҙһаөҚ аҙ•аөғаҙӨаҙҜаҙ®аҙҫаҙҜ аҙөаҙҝаҙ·аҙӮ аҙӨаҙҝаҙ°аөҚаҙһаөҚаҙһаҙҹаөҒаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙЈаҙӮ . пӮ— аҙ®аҙҝаөҚаҙӨаөҚаҙӘаҙҫаҙЈаҙҝаҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҚ аҙөаҙІаҙҝаҙҜ аҙЁаҙҫаҙ¶аөҚаҙӮ аҙөаҙ°аөҒаҙӨаҙҫаҙӨ аҙ•аөҖаҙҹаҙЁаҙҫаҙ¶аөҚаҙҝаҙЁаҙҝаҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚ аҙүаҙӘаҙ«аҙҜаҙҫаөҚаҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙЈаҙӮ. пӮ— аҙ…аҙөаҙ¶аөҚаҙҝаҙ·аөҚаҙҹ аҙөаөҖаҙ°аҙҜаҙӮ аҙ•аөҒаҙұаҙһаөҚаҙһ аҙ•аөҖаҙҹаҙЁаҙҫаҙ¶аөҚаҙҝаҙЁаҙҝаҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚ аҙӨаҙҝаҙ°аөҚаҙһаөҚаҙһаҙҹаөҒаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙЈаҙӮ. пӮ— аҙӘаҙ°аҙҝаҙёаҙ° аҙ®аҙІаҙҝаҙЁаөҖаҙ•аҙ°аҙЈаҙӮ аҙ•аөҒаҙұаҙһаөҚаҙһаҙө аҙҶаҙҜаҙҝаҙ°аҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙЈаҙӮ пӮ— аҙ•аөғаҙӨаҙҜаҙ®аҙҫаҙҜ аҙ…аҙіаҙөаҙҝаҙІаөҚвҖҚ аҙ®аҙҫаөҚаҙӨаҙӮ аҙүаҙӘаҙ«аҙҜаҙҫаөҚаҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙЈаҙӮ. пӮ— аҙ•аҙҙаҙҝаҙөаҙӨаөҒаҙӮ аҙңаҙөаҙ•аөҒаҙ«аҙЁаөҚаҙЁаҙ°аҙҷаөҚаҙҷаҙіаҙҝаҙІаөҚвҖҚ аҙ•аөҖаҙҹаҙЁаҙҫаҙ¶аөҚаҙҝаҙЁаҙҝаҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚ аҙӨаҙіаҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙ•.
- 39. аҙӘаҙҹаҙөаҙІ аҙөаҙ°аөҚаҙ— аҙӘаҙҡаөҚаҙҡаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙұаҙҝаҙ•аҙі аөҚаҙҹ аҙ•аөҖаҙҹаҙЁаҙҝаҙҜаөҚаҙЁаөҚаҙӨаҙЈаҙӮ пӮ— аҙ•аөҖаҙҹаҙҷаөҚаҙҷаҙіаөҚвҖҚ пӮ— аҙӘаҙҡаөҚаҙҡаҙӨаөҒаҙіаөҚаҙіаҙЁаөҚвҖҚ (GLH) пӮ— аөҚаҙөаҙіаөҚаҙіаөҖаҙҡаөҚаҙҡаҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚ (WHITE FLIES) пӮ— аҙ®аөҒаҙһаөҚаҙһаҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚ (APHIDS) пӮ— аҙҶаҙ® аҙөаҙЈаөҚаҙҹаөҒаҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚ (EPPILACHNA BEETLES) пӮ— аҙ®аҙӨаҙЁаөҚвҖҚ аҙөаҙЈаөҚаҙҹаөҒаҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚ (PUMPKIN BEETLES) пӮ— аҙ®аҙЈаөҚаҙҹаҙ°аҙҝаҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚ(MITES) пӮ— аҙөаҙ°аҙҜаҙЁаөҚвҖҚ аҙӘаөҒаҙҙаөҒ пӮ— аҙ•аөӮаҙЁаҙЁаөҚвҖҚ аҙӘаөҒаҙҙаөҒ пӮ— аҙӨаҙЈаөҚаҙҹаөҒаҙӨаөҒаҙ°аҙӘаөҚаҙӘаҙЁаөҚвҖҚ аҙӘаөҒаҙҙаөҒ пӮ— аҙ•аҙҫаҙҜаөҖаҙҡаөҚаҙҡаҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚ (FRUIT FLIES) пӮ— аҙЁаҙҝаҙ®аҙҫаҙөаҙҝаҙ°аҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚ (NEMATODES) пӮ— аҙҡаҙҝаөҚаҙӨаҙ•аөҖаҙҹаҙӮ(LEAF MINOR) пӮ— аҙ¶аөҚаҙІаөҚаҙ•аҙ•аөҖаҙҹаҙӮ (SCALE INSECT) пӮ— аҙ®аөҖаҙІаҙҝаҙ®аөӮаҙҹаөҚаҙҹ(MEALY BUGS)
- 40. аҙ°аҙҫаҙё аҙ•аөҖаҙҹаҙЁаҙҫаҙ¶аөҚаҙҝаҙЁаҙҝаҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚ пӮ— аҙҮаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙҫаҙІаҙ•аөҚаҙё пӮ— аҙЁаөҒаҙөаҙҫаҙЁаөҚвҖҚ пӮ— аҙ®аҙҫаҙІаҙӨаҙҝаҙ«аҙҜаҙҫаҙЈаөҚвҖҚ пӮ— аҙ«аҙұаҙҫаөҚаҙ°аөҚ пӮ— аҙңаҙ«аҙҜаҙҝаҙӮ/аҙҹаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙ®аҙҝ
- 41. аҙ«аҙ•аҙҫаҙөаҙІаөҚвҖҚ аҙӨаҙЈаөҚаҙҹаҙҝаҙІаөҚвҖҚ аҙүаҙЈаөҚаҙҹаҙҫаҙ•аөҒаҙЁаөҚаҙЁ аҙ®аөҒаҙҙаҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚ (Stem fly)
- 42. аҙңаөҲаҙөаҙ•аөҖаҙҹаҙЁаҙҫаҙ¶аөҚаҙҝаҙЁаҙҝаҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚ 1. аҙ®аөҚаҙЈаөҚаҙЈаҙЈаөҚаҙЈ-аҙ«аҙёаҙҫаҙӘаөҚаҙӘаөҚ аҙҮаҙ®аҙІаөҚвҖҚаҙ·аҙЁаөҚвҖҚ-500 аөҚаөҚаҙҫаҙӮ аҙёаҙҫаҙ§аҙҫаҙ°аҙЈ аҙ¬аҙҫаҙ°аөҚ аҙ«аҙёаҙҫаҙӘаөҚаҙӘаөҚ 4.5 аҙІаҙҝ.аөҚаҙөаҙіаөҚаҙіаҙӨаҙҝаҙІаөҚвҖҚ аҙӨаҙҝаҙіаҙӘаөҚаҙӘаҙҝаҙҡаөҚаҙҡаөҚ аҙІаҙҜаҙҝаҙӘаөҚаҙӘаҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙ•.аҙӨаҙЈаөҒаҙӨаөҒ аҙ•аҙҙаҙҝаҙҜаөҒаҙ«аҙ®аөҚаҙӘаҙҫаҙіаөҚвҖҚ 1 аҙІаҙҝ.аҙ®аөҚаҙЈаөҚаҙЈаҙЈаөҚаҙЈ аҙ«аҙҡаҙ°аөҚаҙӨаөҚ аҙЁаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаҙҫаҙҜаҙҝ аҙҮаҙіаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙҝ аҙ«аҙҡаҙ°аөҚаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙ•.20 аҙҮаҙ°аҙҹаөҚаҙҹаҙҝ аөҚаҙөаҙіаөҚаҙіаҙӮ аҙ«аҙҡаҙ°аөҚаҙӨаөҚ аҙӨаҙіаҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙҫаҙӮ.(аҙЁаөҖаҙ°аөҚ аҙөаҙІаҙҝаҙҡаөҚаҙҡаөҚ аҙ•аөҒаҙҹаҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙЁаөҚаҙЁ аҙ•аөҖаҙҹаҙҷаөҚаҙҷаҙіаөҚвҖҚаөҚаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙӨаҙҝаөҚаҙ°) 2. аҙӘаөҒаҙ•аҙҜаҙҝаҙІаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙ·аҙҫаҙҜаҙӮ-500аөҚаөҚаҙҫаҙӮ аҙӘаөҒаҙ•аҙҜаҙҝаҙІ/аҙ«аҙөаҙёаөҚаҙұаөҚаөҚ 4.5аҙІаҙҝ аөҚаҙөаҙіаөҚаҙіаҙӨаҙҝаҙІаөҚвҖҚ 24 аҙ®аҙЈаҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөӮаҙ°аөҚ аҙ•аөҒаҙӨаҙҝаҙ°аөҚаҙӨаөҒ аҙөаҙҡаөҚаҙҡаөҚ аөҚаөҶаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙҝ аҙӘаҙҝаҙҙаҙҝаҙһаөҚаҙһаөҚ аҙҡаҙҫаөҚаҙұаҙҹаөҒаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙ• .120аөҚаөҚаҙҫаҙӮ аҙ¬аҙҫаҙ°аөҚ аҙ«аҙёаҙҫаҙӘаөҚаҙӘаөҚ аҙҶаҙөаҙ¶аөҚаҙҜаҙӨаҙҝаҙЁаөҚ аөҚаҙөаҙіаөҚаҙіаҙӨаҙҝаҙІаөҚвҖҚ аҙІаҙҫаҙҜаҙЁаҙҝ аҙҶаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙ•.аҙ«аҙёаҙҫаҙӘаөҚаҙӘаөҚ аҙІаҙҫаҙҜаҙЁаҙҝ аҙӘаөҒаҙ•аҙҜаҙҝаҙІ аҙҡаҙҫаҙұаҙҝаөҚаҙІаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҚ аҙ«аҙҡаҙ°аөҚаҙӨаөҚ аҙЁаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаҙҫаҙҜаҙҝ аҙҮаҙіаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙ•. 7 аҙҮаҙ°аҙҹаөҚаҙҹаҙҝ аөҚаҙөаҙіаөҚаҙіаҙӮ аҙ«аҙҡаҙ°аөҚаҙӨаөҚ аҙӨаҙіаҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙҫаҙӮ.(аҙ®аөҒаҙһаөҚаҙһ аҙ«аҙӘаҙҫаҙІаөҒаҙіаөҚаҙі аҙ•аөҖаҙҹаҙҷаөҚаҙҷаҙіаөҚвҖҚаөҚаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙӨаҙҝаөҚаҙ° )
- 43. 3.аҙ«аҙөаҙӘаөҚаҙӘаҙҝаҙЁаөҚвҖҚ аҙ•аөҒаҙ°аөҒ аҙёаҙӨаөҚ -300 аөҚаөҚаҙҫаҙӮ аҙ«аҙөаҙӘаөҚаҙӘаҙҝаҙЁаөҚвҖҚ аҙ•аөҒаҙ°аөҒ аөҚаҙӨаҙҫаҙІаҙҝ аҙ•аҙіаҙһаөҚаҙһаөҚаҙЁаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаҙҫаҙҜаҙҝ аөҚаҙӘаҙҫаҙҹаҙҝаөҚаҙҡаөҚаҙҡаҙҹаөҒаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙ•.аҙҲ аөҚаҙӘаҙҫаҙҹаҙҝ аҙ’аҙ°аөҒ аҙ®аҙёаөҚаҙІаҙҝаҙЁаөҚвҖҚ аҙӨаөҒаҙЈаҙҝаҙҜаҙҝаҙІаөҚвҖҚ аҙ•аҙҝаҙҙаҙҝ аөҚаҙ•аҙҹаөҚаҙҹаҙҝ 12 аҙ®аҙЈаҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөӮаҙ°аөҚ аөҚаҙөаҙіаөҚаҙіаҙӨаҙҝаҙІаөҚвҖҚ аҙ•аөҒаҙӨаҙҝаҙ°аөҚаҙӨаөҒ аҙөаҙҜаөҚаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙ•.аҙӘаҙҝаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаөҖаөҚ аҙЁаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаҙҫаҙҜаҙҝ аөҚаөҶаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙҝаҙӘаөҚаҙӘаҙҝаҙҙаҙҝаҙһаөҚаҙһаөҒ аҙҡаҙҫаҙ°аөҚ аҙҺаҙҹаөҒаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙ•.(3% NSKE)-аҙҮаҙІ аҙӨаөҖаҙЁаҙҝаҙӘаөҚаҙӘ аҙҙаөҒаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚ,аҙ®аҙұаөҚаҙұ аҙ•аөҖаҙҹаҙҷаөҚаҙҷаҙіаөҚвҖҚ аҙҺаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаҙҝаҙөаҙҜаөҚаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҚ аҙҺаҙӨаҙҝаөҚаҙ° 4.аөҚаҙөаҙі аҙӨаөҒаҙіаөҚаҙіаҙҝ-аҙ«аҙөаөҚаҙӘаөҚаҙӘаҙЈаөҚаҙЈ аҙ®аҙҝаөҚаҙ¶аөҚаҙҝаҙӨаҙӮ(2%)- 50аөҚаөҚаҙҫаҙӮ аҙ¬аҙҫаҙ°аөҚ аҙ«аҙёаҙҫаҙӘаөҚаҙӘаөҚ 500 аҙ®аҙҝаҙІаҙІаҙҝ.аөҚаҙөаҙіаөҚаҙіаҙӨаҙҝаҙІаөҚвҖҚ аҙІаҙҜаҙҝаҙӘаөҚаҙӘаҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙ•. 200 аөҚаөҚаҙҫаҙӮ аөҚаҙөаҙі аҙӨаөҒаҙіаөҚаҙіаҙҝ аҙЁаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаҙҫаҙҜаҙҝ аҙ…аҙ°аөҚаҙҡаөҚаҙҡаҙҹаөҒаҙӨаөҚ 300 аҙ®аҙҝаҙІаҙІаҙҝ. аөҚаҙөаҙіаөҚаҙіаҙӨаҙҝаҙІаөҚвҖҚ аҙ•аҙІаҙ°аөҚаҙӨаҙҝ аҙЁаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаҙҫаҙҜаҙҝ аҙҮаҙіаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙҝ аҙҡаҙҫаҙ°аөҚ аҙ…аҙ°аҙҝаөҚаҙҡаөҚаҙҡаҙҹаөҒаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙ•. 500 аҙ®аҙҝаҙІаҙІаҙҝ аҙ«аҙёаҙҫаҙӘаөҚаҙӘаөҚ аҙІаҙҫаҙҜаҙЁаҙҝ 200 аҙ®аҙҝаҙІаҙІаҙҝ.аҙ«аҙөаөҚаҙӘаөҚаҙӘаҙЈаөҚаҙЈаҙҜаөҒаҙ®аҙҫаҙҜаҙҝ аҙЁаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаҙҫаҙҜаҙҝ аҙҮаҙіаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙҝаҙ«аҙҡаҙ°аөҚаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙ•.300 аҙ®аҙҝаҙІаҙІаҙҝ.аөҚаҙөаҙі аҙӨаөҒаҙіаөҚаҙіаҙҝ аҙҡаҙҫаҙ°аөҚ аҙ•аөӮаҙҹаҙҝ аҙ«аҙҡаҙ°аөҚаҙӨаөҚ аҙЁаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаҙҫаҙҜаҙҝ аҙҮаҙіаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙҝ аҙ•аөҒаҙӘаөҚаҙӘаҙҝаҙҜаҙҝаҙІаөҚвҖҚ аҙҶаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙҝ аҙёаөӮаҙ•аөҚаҙ·аҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙҫаҙӮ.аҙҮаҙӨаҙҝаҙІаөҚвҖҚ аҙ’аҙ°аөҒ аҙӯаҙҫаөҚаҙӮ 9 аҙҮаҙ°аҙҹаөҚаҙҹаҙҝ аөҚаҙөаҙіаөҚаҙіаҙөаөҒаҙ®аҙҫаҙҜаҙҝ аҙ«аҙҡаҙ°аөҚаҙӨаөҚ аҙӨаҙіаҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙҫаҙӮ.(2%)-аөҚаҙӘаҙ§аҙҫаҙЁаҙ®аҙҫаҙҜаөҒаҙӮ аҙ®аҙЈаөҚаҙҹаҙ°аҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҚ аҙҺаҙӨаҙҝаөҚаҙ°
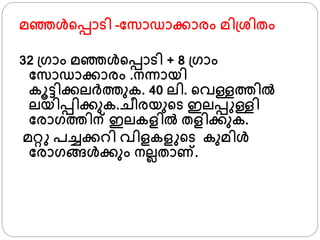
- 44. аҙ®аҙһаөҚаҙһаҙіаөҚвҖҚаөҚаҙӘаөҚаҙӘаҙҫаҙҹаҙҝ вҖ“аҙ«аҙёаҙҫаҙЎаҙҫаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙҫаҙ°аҙӮ аҙ®аҙҝаөҚаҙ¶аөҚаҙҝаҙӨаҙӮ 32 аөҚаөҚаҙҫаҙӮ аҙ®аҙһаөҚаҙһаҙіаөҚвҖҚаөҚаҙӘаөҚаҙӘаҙҫаҙҹаҙҝ + 8 аөҚаөҚаҙҫаҙӮ аҙ«аҙёаҙҫаҙЎаҙҫаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙҫаҙ°аҙӮ .аҙЁаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаҙҫаҙҜаҙҝ аҙ•аөӮаҙҹаөҚаҙҹаҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙІаҙ°аөҚаҙӨаөҒаҙ•. 40 аҙІаҙҝ. аөҚаҙөаҙіаөҚаҙіаҙӨаҙҝаҙІаөҚвҖҚ аҙІаҙҜаҙҝаҙӘаөҚаҙӘаҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙ•.аҙҡаөҖаҙ°аҙҜаөҒаөҚаҙҹ аҙҮаҙІаҙӘаөҚаҙӘ аҙіаөҚаҙіаҙҝ аҙ«аҙ°аҙҫаөҚаҙӨаҙҝаҙЁаөҚ аҙҮаҙІаҙ•аҙіаҙҝаҙІаөҚвҖҚ аҙӨаҙіаҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙ•. аҙ®аҙұаөҚаҙұ аҙӘаҙҡаөҚаҙҡаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙұаҙҝ аҙөаҙҝаҙіаҙ•аҙі аөҚаҙҹ аҙ•аөҒаҙ®аҙҝаҙіаөҚвҖҚ аҙ«аҙ°аҙҫаөҚаҙҷаөҚаҙҷаҙіаөҚвҖҚаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙӮ аҙЁаҙІаҙІаҙӨаҙҫаҙЈ.
- 45. аөҚаҙ•аҙЈаҙҝаҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚ пӮ— аҙ«аҙҝаҙ«аҙұаҙҫаҙ«аҙ®аҙҫаҙЈаөҚвҖҚ аөҚаҙ•аҙЈаҙҝаҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚ пӮ— аҙӘаҙҙаөҚаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙЈаҙҝ пӮ— аҙ¶аөҚаҙ°аөҚаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙ°аөҚаҙ•аҙЈаҙҝ пӮ— аҙ®аөҖаҙЁаөҚвҖҚ аөҚаҙ•аҙЈаҙҝ пӮ— аҙӨаөҒаҙіаҙёаҙҝаөҚаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙЈаҙҝ пӮ— аҙ•аҙһаөҚаҙһаҙҝаөҚаҙөаҙіаөҚаҙіаөҚаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙЈаҙҝ
- 46. аөҲаөҖаҙөаҙҫаҙЈаөҒ аҙ«аҙ°аҙҫаөҚ аҙЁаҙҫаҙ¶аөҚаҙҝаҙЁаҙҝаҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚ пӮ— аҙңаөҚаҙҹаҙ«аҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙҫаҙЎаҙ°аөҚаҙ® пӮ— аҙёаҙҜаөӮаҙ«аҙЎаҙҫаҙ«аҙ®аҙҫаҙЈаҙҫаҙё пӮ— аҙңаҙ®аҙ«аҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙҫаҙңаҙұаҙё (VAM) пӮ— аҙ¬аҙҫаҙёаҙҝаҙІаҙІаҙё аҙёаҙ¬аөҚаҙҹаҙҝаҙІаҙҝаҙё
- 47. VAM/ MYCORRHIZAE пӮ— аөҚаҙҡаҙҹаҙҝаҙ•аҙі аөҚаҙҹ аҙ«аҙөаҙ°аҙҝаҙЁаөҒаҙіаөҚаҙіаҙҝаҙІаөҚвҖҚ аҙ•аҙҹаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаөҚ аҙ¬аҙҫаҙ№аҙҜаҙөаөҒаҙӮ,аҙҶаҙЁаөҚаҙӨаҙ°аҙҝаҙ•аҙөаөҒаҙ®аҙҫаҙҜ аҙ«аҙ•аҙҫаҙ¶аөҚаҙҷаөҚаҙҷаҙіаҙҝаҙІаөҚвҖҚ аҙӘаҙҹаҙ°аөҚаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаөҚ аҙӘаҙҝаҙҹаҙҝаҙҡаөҚаҙҡаөҚаҙ®аҙЈаөҚаҙЈаҙҝаҙ«аҙІаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҚ аҙөаҙіаҙ°аөҒаҙЁаөҚаҙЁ аҙҡаҙҝаҙІ аҙ•аөҒаҙ®аҙҝаҙі аҙ•аөҚаҙіаҙҜаҙҫаҙЈ VAM аҙҺаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаөҒ аҙөаҙҝаҙіаҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаҙӨаөҚ.аҙҮаҙө аҙ«аҙөаҙ°аҙҝаҙІаөҚвҖҚ аҙөаҙіаҙ°аөҒаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаҙӨаөҒаҙ®аөӮаҙІаҙӮ аөҚаҙҡаҙҹаҙҝаҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙӮ аҙ•аөҒаҙ®аҙҝаҙіаҙҝаҙЁаөҒаҙӮ аөҚаҙӘаҙ«аҙҜаҙҫаөҲаҙЁаҙӮ аҙІаҙӯаҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаөҒ.(Symbiotic relationship) пӮ— Glomus spp.,Acaulospora sp. аҙҺаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаҙҝаҙөаҙҜаҙҫаҙЈ аөҚаҙӘаҙ§аҙҫаҙЁ аҙёаҙӘаөҖаҙ·аөҖаҙёаөҒаҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚ .VAM аҙ®аөӮаҙІаҙ®аөҒаҙіаөҚаҙі аөҚаөҒаҙЈаҙҷаөҚаҙҷаҙіаөҚвҖҚ 1.аҙ•аөӮаҙҹаөҒаҙӨаҙІаөҚвҖҚ аҙ«аҙӘаҙҫаҙ·аҙ•аҙҷаөҚаҙҷаҙіаөҚвҖҚ аҙөаҙІаҙҝаөҚаҙҡаөҚаҙҡаҙҹаөҒаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙҫаҙЁаөҚвҖҚ аҙёаҙ№аҙҫаҙҜаҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаөҒ. (P,N,K,Ca,Mg) 2. аҙөаҙҝаҙіаҙ•аҙі аөҚаҙҹ аҙөаҙіаҙ°аөҚаҙҡаөҚаҙҡаҙҜаөҒаҙӮ,аҙөаҙҝаҙіаҙөаөҒаҙӮ аҙөаҙ°аөҚаҙ§аҙҝаҙӘаөҚаҙӘаҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаөҒ. 3.аҙүаҙЈаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙҝаөҚаҙЁ аөҚаҙӘаҙӨаҙҝаҙ«аҙ°аҙҫаҙ§аҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаөҒ.
- 48. 4.аҙ«аҙҰаҙҫаҙ·аҙ•аҙ°аҙ®аҙҫаҙҜ аҙ®аөӮаҙІаҙ•аҙҷаөҚаҙҷаҙіаҙҝаҙІаөҚвҖҚ аҙЁаҙҝаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаөҒаҙӮ аҙөаҙҝаҙіаҙ•аөҚаҙі аҙёаҙӮаҙ°аҙ•аөҚаҙ·аҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаөҒ.(аөҚаҙҡаҙ®аөҚаҙӘаөҚ,аҙҮаҙ°аөҒаҙ®аөҚаҙӘаөҚ,аҙЁаҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аҙІаөҚвҖҚ, аҙүаҙӘаөҚаҙӘ аҙ°аҙёаҙӮ).аҙҮаҙө аҙ•аөӮаҙҹаөҒаҙӨаҙІаөҒаҙіаөҚаҙі аҙ®аҙЈаөҚаҙЈаҙҝаҙІаөҚвҖҚ аөҚаҙҡаҙҹаҙҝаҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚ аҙЁаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаҙҫаҙҜаҙҝ аҙөаҙіаҙ°аҙҫаҙЁаөҚвҖҚ аҙёаҙ№аҙҫаҙҜаҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаөҒ. 5.аҙ…аҙЁаөҚаҙЁаөҲаҙӮ аҙүаҙІаөҚвҖҚаҙӘаөҚаҙӘаҙҫаҙҰаҙҝаҙӘаөҚаҙӘаҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаҙӨаҙҝаҙЁаөҒаҙіаөҚаҙі аҙ•аҙҙаҙҝаҙөаөҚ аҙөаҙ°аөҚаҙ§аҙҝаҙӘаөҚаҙӘаҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаөҒ, аҙөаҙіаҙ°аөҚаҙҡаөҚаҙҡаҙҫ аҙ«аҙ№аҙҫаҙ°аөҚаҙ«аҙ®аҙҫаҙЈаөҒаҙ•аҙі аөҚаҙҹ аҙүаҙІаөҚаҙӘаҙҫаҙҰаҙЁаҙӮ аҙөаҙҙаҙҝ аҙөаҙҝаҙіаҙ•аҙі аөҚаҙҹ аҙөаҙіаҙ°аөҚаҙҡаөҚаҙҡаҙҜаөҒаҙӮ аҙөаҙҝаҙіаҙөаөҒаҙӮ аҙөаҙ°аөҚаҙ§аҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаөҒ. 6.аҙ®аҙҝаөҚаҙӨ аҙёаөӮаҙ•аөҚаҙ·аөҚаҙ®аҙҫаҙЈаөҒаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҚаҙі аҙёаҙ№аҙҫаҙҜаҙҝаҙ•аөҚаҙ•аөҒаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаөҒ. 7.аҙ®аҙЈаөҚаҙЈаҙҝаөҚаҙЁаөҚвҖҚаҙұ аҙҳаҙҹаҙЁ аөҚаҙ®аҙҡаөҚаҙҡаөҚаҙӘаөҚаҙӘаҙҹаөҒаҙӨаөҒаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаөҒ,аҙ’аҙ°аөҒ аҙӘаҙ°аҙҝаҙ§аҙҝ аҙөаөҚаҙ° аҙ®аөҚаҙЈаөҚаҙЈаҙҫаҙІаҙҝаҙӘаөҚаҙӘаөҚ аҙӨаҙҹаҙҜаөҒаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаөҒ. 8.аҙ«аҙөаҙ°аөҒаҙ«аҙ°аҙҫаөҚаҙҷаөҚаҙҷаҙіаөҚвҖҚ аҙӨаҙҹаҙҜаөҒаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаөҒ. 9.аҙҹаҙҝаҙ·аҙҜаөҒ аҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚаҙҡаөҚаҙҡаҙ°аөҚ аҙңаҙӨаҙ•аҙі аөҚаҙҹ аҙөаҙіаҙ°аөҚаҙҡаөҚаҙҡ аҙӨаҙөаҙ°аҙҝаҙӨаөҚаҙӘаөҚаҙӘаҙҹаөҒаҙӨаөҒаҙЁаөҚаҙЁаөҒ.
- 49. аөҲаөҖаҙөаҙҫаҙЈаөҒ аҙ•аөҖаҙҹаҙЁаҙҫаҙ¶аөҚаҙҝаҙЁаҙҝаҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚ аөҚаҙ®аҙұаөҚаҙұаҙҫаҙұаҙҝаҙёаҙҝаҙҜаҙӮ аҙ¬аҙҜаөҒаҙ«аҙөаҙұаҙҝаҙҜ аөҚаҙөаҙ°аөҚаҙҹаҙҝаҙёаөҖаҙІаҙҝаҙҜаҙӮ аҙӘаөҖаҙёаҙҝаҙ«аҙІаҙҫаҙңаҙ®аҙёаҙё аҙ¬аҙҫаҙёаҙҝаҙІаҙІаҙҫаҙё аҙӨаөҒаҙ°аҙҝаҙЁаөҚаөҲаҙҝаҙҜаҙЁаөҚаҙёаҙҝаҙё (Bt) аҙңаҙөаҙұаҙёаөҒаҙ•аҙіаөҚвҖҚ
- 51. Prepared by : Dr. T.E. George, Professor & Head