Stack - Data structures - Dr. Shaukat Wasi
- 1. Stack Dr. Shaukat Wasi and Dr. Syed Imran Jami
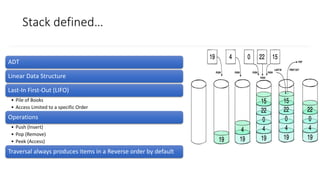
- 2. Stack defined… ADT Linear Data Structure Last-In First-Out (LIFO) • Pile of Books • Access Limited to a specific Order Operations • Push (Insert) • Pop (Remove) • Peek (Access) Traversal always produces items in a Reverse order by default
- 3. Stack Applications • Breadth First Search Algorithms • Python/Java – Function Call Handling • Compilers – Expression Parsing • Balanced Parenthesis Checking • Back Tracking Algorithms • Web Browsers – Back and Next Mechanism • Applications – UNDO/REDO operations
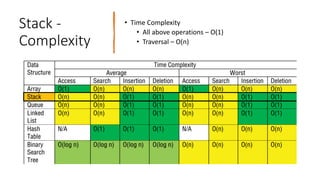
- 4. Stack - Complexity • Time Complexity • All above operations – O(1) • Traversal – O(n)
- 5. Stack Implementations • Random Access Restricted – Is it really needed? • Push and Pop Complexity reaches to O(n) – WHY? If first index is set as Top of the stack. • Else if last pointer is used to consider the current filled slot as the top, complexity will remain O(1). • Search Complexity? Array Implementation • Push – Insert at Top/Head • Pop – Delete from Top/Head • Complexity remains same as expected Linked List Implementation
- 6. Stack Problems ☺ • Convert one form of expression to another form • Infix to Postfix • Arithmetic Expression Evaluation • Postfix Expression Evaluation • Check for balanced parentheses in an expression • Iterative Tower of Hanoi • The Tower of Hanoi is a mathematical puzzle. • It consists of three poles and a number of disks of different sizes which can slide onto any pole. • The puzzle starts with the disk in a neat stack in ascending order of size in one pole, the smallest at the top thus making a conical shape. • The objective of the puzzle is to move all the disks from one pole (say ‘source pole’) to another pole (say ‘destination pole’) with the help of the third pole (say auxiliary pole). • The puzzle has the following two rules. • You can’t place a larger disk onto a smaller disk • Only one disk can be moved at a time
- 7. Stack Problems ☺ • Convert one form of expression to another form • Infix to Postfix • Arithmetic Expression Evaluation • Postfix Expression Evaluation • Check for balanced parentheses in an expression • Iterative Tower of Hanoi • The Tower of Hanoi is a mathematical puzzle. • It consists of three poles and a number of disks of different sizes which can slide onto any pole. • The puzzle starts with the disk in a neat stack in ascending order of size in one pole, the smallest at the top thus making a conical shape. • The objective of the puzzle is to move all the disks from one pole (say ‘source pole’) to another pole (say ‘destination pole’) with the help of the third pole (say auxiliary pole). • The puzzle has the following two rules. • You can’t place a larger disk onto a smaller disk • Only one disk can be moved at a time
- 8. Stack Problems ☺ • Convert one form of expression to another form • Infix to Postfix • Arithmetic Expression Evaluation • Postfix Expression Evaluation • Check for balanced parentheses in an expression • Iterative Tower of Hanoi • The Tower of Hanoi is a mathematical puzzle. • It consists of three poles and a number of disks of different sizes which can slide onto any pole. • The puzzle starts with the disk in a neat stack in ascending order of size in one pole, the smallest at the top thus making a conical shape. • The objective of the puzzle is to move all the disks from one pole (say ‘source pole’) to another pole (say ‘destination pole’) with the help of the third pole (say auxiliary pole). • The puzzle has the following two rules. • You can’t place a larger disk onto a smaller disk • Only one disk can be moved at a time
- 9. Stack Problems ☺ • Convert one form of expression to another form • Infix to Postfix • Arithmetic Expression Evaluation • Postfix Expression Evaluation • Check for balanced parentheses in an expression • Iterative Tower of Hanoi (Iterative) • The Tower of Hanoi is a mathematical puzzle. • It consists of three poles and several disks of different sizes which can slide onto any pole. • The puzzle starts with the disk in a neat stack in ascending order of size in one pole, the smallest at the top thus making a conical shape. • The objective of the puzzle is to move all the disks from one pole (say ‘source pole’) to another pole (say ‘destination pole’) with the help of the third pole (say auxiliary pole). • The puzzle has the following two rules. • You can’t place a larger disk onto a smaller disk • Only one disk can be moved at a time
- 10. Questions !!!