Starbucks Analysis
- 1. Foundations of Business Strategy Darden School of Business ŌĆō University of Virginia Irene Cl├Īudia Mendes Martins 1 To: Howard Schultz, chairman, president and executive officer From: Subject: Executive Summary: Starbucks Competitive Position Analysis Introduction Starbucks Corporation engages in the purchase, roasting, and sale of whole bean coffees, along with handcrafted coffee and tea beverages and various fresh food items, through its company-operated retail stores. The company has three segments: United States (US), International, and Global Consumer Products Group (CPG). The United States and International segments both include company- operated retail stores and certain components of specialty operations. The CPG segment includes packaged coffee and tea, Starbucks VIA Ready Brew, and other branded products sold worldwide through channels, such as grocery stores, warehouse clubs, convenience stores, and US foodservice accounts. CPG operates a portion of its business through licensing arrangements and a joint venture with a consumer products business partner. Starbucks is standing as one of the most recognized and respected brands in the world. To achieve this goal, they are continuing the disciplined expansion of their global store base. In addition, by leveraging the experience gained through their traditional store model, they continue to offer consumers new coffee products in a variety of forms, across new categories, and through diverse channels. Starbucks Global Responsibility strategy and commitments related to coffee and the communities they do business in, as well as their focus on being an employer of choice, are also key complements to their business strategies. Competitors Analysis Due to its vertical integration, diversification and success, Starbucks now has many competitors. Direct Competition: Starbucks has had to face many competitors in the image of Seattle's Best Coffee or Pasqua, but many other brands appeared in the meantime. However, his biggest competitor is Peet's, introduced himself on the stock exchange in 2001 and now distributed in supermarkets. United States: Starbucks must deal with regional chains like Peet's or The Coffee Bean & Tea Leaf. In Canada: Tim Hortons and Second Cup.
- 2. Foundations of Business Strategy Darden School of Business ŌĆō University of Virginia Irene Cl├Īudia Mendes Martins 2 In France, the only direct competitor is Starbucks Coffee Colombus. Created in 1994, the first French channel "espresso bars" which has thirty stores in France and very little abroad Non-direct competition: First, the regional chains like Dunkin 'Donuts, and most recently, Burger King and McDonald's, the latter wishing to engage in different types mocha coffee, cappuccino, latte, and cold drinks, fruit juices, smoothies, all these products offered at lower prices. These stores were repositioned by providing specialty coffee and espresso-based drinks at competitive prices, often playing on an image more accessible and down-to-earth than that of Starbucks. "Within an industry, strategic groups together organizations with similar strategic characteristics, following similar strategies or rely on the same competitive factors." There are 2 different strategic groups: internationally and regionally:
- 3. Foundations of Business Strategy Darden School of Business ŌĆō University of Virginia Irene Cl├Īudia Mendes Martins 3 SWOT Analysis PESTLE (Environment) Analysis: The PESTLE analysis will be used to identify and understand the important factors Starbucks must consider in all areas of the business.
- 4. Foundations of Business Strategy Darden School of Business ŌĆō University of Virginia Irene Cl├Īudia Mendes Martins 4
- 5. Foundations of Business Strategy Darden School of Business ŌĆō University of Virginia Irene Cl├Īudia Mendes Martins 5 Michael PorterŌĆÖs five forces Competition ŌĆó TullyŌĆÖs Coffee, Gloria JeanŌĆÖs, Caribou Coffee etc.
- 6. Foundations of Business Strategy Darden School of Business ŌĆō University of Virginia Irene Cl├Īudia Mendes Martins 6 ŌĆó Competition nowhere in terms of volume of operations ŌĆó Competitors selling similar products, incl. specialty coffees & high quality food Threat of new entrants ŌĆó Controlled access of distribution channels ŌĆó Innovation & product differentiation Bargaining power of buyers ŌĆó More options due to no. of competitors ŌĆó Large variety of products Bargaining power of suppliers ŌĆó Over crowding of market ŌĆó Rise in prices of coffee beans ŌĆó Choose suppliers based on quality, social, environmental & economic issues Threat from substitutes ŌĆó Tea ŌĆó Soft drinks ŌĆó Juices StarbucksŌĆÖ Corporate Capabilities Starbucks has numerous capabilities but the ones that allow them to stand apart from the other specialty coffee companies are their market leadership, superior real estate locations, and their supply chain operations. Their superior retail locations give them powerful capabilities over their competitors. They have stores that are exposed to areas with much higher foot traffic and better local demographic compositions. However, StarbucksŌĆÖ strongest capabilities are in their supply chain operations.
- 7. Foundations of Business Strategy Darden School of Business ŌĆō University of Virginia Irene Cl├Īudia Mendes Martins 7 These operations are superior to competitors in the specialty coffee industry for a few primary reasons: ŌĆó Starbucks transportation rates are the best in the industry; ŌĆó Both their bakery distribution model, coupled with their sophisticated forecasting process, enable them to accurately identify where coffee is needed and when. This allows them to make appropriate and on-time deliveries; ŌĆó Their complex manufacturing and distribution process allows them to maintain strong inventory turns as compared to competitors in the specialty coffee industry; ŌĆó Their ability to protect the integrity of their coffee beans from the detrimental effects of oxygen and time through a closed loop system of packaging. Key Competences The global strategy of Starbucks is to provide costumers with more than a cup of coffee: Core competences help to provide firms with a ŌĆścompetitive advantage'. They are used to achieve a strategic advantage through activities, skills or know-how, and basically a general expertise in the development of the product. This advantage will provide value to customers. For Starbucks, these competences include the knowledge of where the finest coffee beans are grown, the knowledge of how best to prepare them in order to make the best
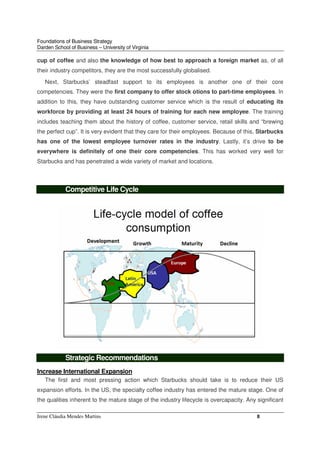
- 8. Foundations of Business Strategy Darden School of Business ŌĆō University of Virginia Irene Cl├Īudia Mendes Martins 8 cup of coffee and also the knowledge of how best to approach a foreign market as, of all their industry competitors, they are the most successfully globalised. Next, StarbucksŌĆÖ steadfast support to its employees is another one of their core competencies. They were the first company to offer stock otions to part-time employees. In addition to this, they have outstanding customer service which is the result of educating its workforce by providing at least 24 hours of training for each new employee. The training includes teaching them about the history of coffee, customer service, retail skills and ŌĆ£brewing the perfect cupŌĆØ. It is very evident that they care for their employees. Because of this, Starbucks has one of the lowest employee turnover rates in the industry. Lastly, itŌĆÖs drive to be everywhere is definitely of one their core competencies. This has worked very well for Starbucks and has penetrated a wide variety of market and locations. Competitive Life Cycle Strategic Recommendations Increase International Expansion The first and most pressing action which Starbucks should take is to reduce their US expansion efforts. In the US, the specialty coffee industry has entered the mature stage. One of the qualities inherent to the mature stage of the industry lifecycle is overcapacity. Any significant
- 9. Foundations of Business Strategy Darden School of Business ŌĆō University of Virginia Irene Cl├Īudia Mendes Martins 9 expansion efforts in an environment where overcapacity is present will be met with failure. By reducing their expansion efforts in the US, Starbucks can redirect the capital saved into their international expansion efforts. For example, Starbucks currently operates roughly 16,000 stores with 10,000 in the US and 6000 internationally. Rewards Program Howard Shultz has referred to a strategy he calls ŌĆ£segmentation,ŌĆØ as being one of the initiatives he will use to reach new consumer segments. However, if Starbucks pursues their ŌĆ£segmentationŌĆØ strategy they risk degrading the most significant competitive advantage they possess: their brand image. By selling a discounted specialty coffee at StarbucksŌĆÖ locations, the overall brand's image could be degraded and an un-winnable price war with McDonalds and Dunkin' Donuts becomes more likely. Starbucks should concentrate on creating more elaborate discounting techniques to employ with their most frequent customers. This both eliminates the potential degradation of the StarbucksŌĆÖ brand and increases the bond customers will experience with Starbucks. Additionally, a rewards program will encourage customers to visit Starbucks more often and will dissuade them from visiting competitor stores, such as McDonald's and Dunkin' Donuts, which seem unlikely to offer reward programs. Rent Out Meeting Space and Install Free Wireless Internet Next, Starbucks should create a more business and technology friendly atmosphere in its stores. With the advent of the Internet and the ever increasing array of electronic products capable of accessing it, there has been an increasing shift in consumer's work locations from office buildings to home offices. These meeting spaces should be accompanied with the addition of free wireless Internet access throughout every Starbucks store and printers accessible to the customers, which are color capable and reasonably priced. The meeting space should be offered at a per hour rate while the printers should charge per copy. CD Burning In addition to free wireless Internet access, Starbucks could equip stores with a CD burning device to allow customers to burn copies of the online albums they purchase within Starbucks at a small fee. Increase Connection with Customer One way in which Starbucks has always differentiated itself from its competition has been through the emotional connection formed with its customers. Starbucks could implement digital picture frames in all store locations and upload local customer photos and perhaps even customer supplied family photos, which are appropriate in nature, upon request. Currently, the majority of Starbucks stores have latte machines that are positioned in such a way as to block
- 10. Foundations of Business Strategy Darden School of Business ŌĆō University of Virginia Irene Cl├Īudia Mendes Martins 10 the baristas from viewing the customers and vice versa when the barista is in the act of making the latte. These latte machines should be lowered so as to give the baristas a demonstration kitchen of sorts. Continually Improve the Coffee Given the specialty coffee marketŌĆÖs transition into the mature stage of the industry lifecycle, it is important to maintain a reputation for the highest quality coffee in the industry. To ensure the quality of their coffee, Starbucks should continually analyze their brewing systems and practices and consider renovations. Becoming More Environmentally Friendly Although many efforts are being made at Starbucks to enhance their image as being environmentally friendly, as is true for all modern corporations, they still have much room to improve, thus, further differentiating themselves.
- 11. Foundations of Business Strategy Darden School of Business ŌĆō University of Virginia Irene Cl├Īudia Mendes Martins 11 BIBLIOGRAPHY www.starbucks.com http://investor.starbucks.com/phoenix.zhtml?c=99518&p=irol-reportsannual http://www.cimaglobal.com/Documents/ImportedDocuments/cid_tg_strategic_analysis_tools_nov07.pdf.pdf http://www.slideshare.net/ezendu/strategic-analysis-6365371 http://www.slideshare.net/avinav2712/starbucks-1085483 http://www.academicmind.com/unpublishedpapers/business/marketing/2002-04-000aag-catching-the-starbucks- fever.html