Steam power plant
- 1. STEAM POWER PLANT ABSTRACT: ïķ Steam Power Plant is convert Mechanical rotary energy into Electrical energy. A mechanical interface, consisting of a boiler, heater and a suitable coupling transmits the energy to an electrical generator. The output of this generator is connected to the Battery or system grid. The battery is connected to the inverter. The inverter is used to convert DC voltages to AC voltages. The load is drawn current from the inverter. Generator Mains shaft with Leafs Amount of Steam (or) Pressure ïķ The power ratings can be divided into three convenient grouping, small to 1kW, medium to 50 kW and large 200 kW to megawatt frame size. ECWAY TECHNOLOGIES IEEE PROJECTS & SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENTS OUR OFFICES @ CHENNAI / TRICHY / KARUR / ERODE / MADURAI / SALEM / COIMBATORE BANGALORE / HYDRABAD CELL: 9894917187 | 875487 1111/2222/3333 | 8754872111 / 3111 / 4111 / 5111 / 6111 Visit: www.ecwayprojects.com Mail to: ecwaytechnologies@gmail.com
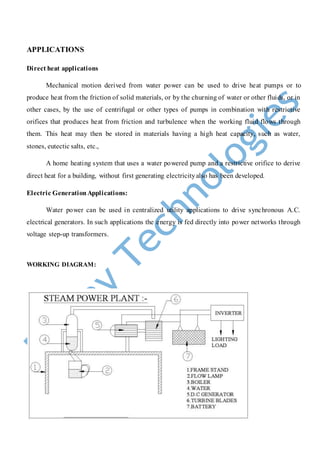
- 2. SCOPE OF THE PROJECT: MAN AND ENERGY: Man has needed and used energy at an increasing rate for its sustenance and well being ever since he came on the earth a few million years ago. Primitive man required energy primarily in the form of food. He derived this by eating plants or animals, whic h he hunted. Subsequently he discovered fire and his energy needs increased as he started to make use of wood and other bio mass to supply the energy needs for cooking as well as agriculture. He added a mew dimension to the use of energy by domesticating and training animals to work for him. With further demand for energy, man began to use the wind for sailing ships and for driving windmills, and the force of failing water to turn water wheels. Till this time, it would not be wrong to say that the sun was supplying all the energy needs of man either directly or indirectly and that man was using only renewable sources of energy WORKING PRINCIPLE The block diagram of steam power plant is shown in figure, it consist of a boiler unit, 12 voltage battery, an inverter and a florescent lamp. As we studied from the generator gives a D.C. output of 12V this D.C. output is not always constant there is some variation in this D.C. output this cannot be given to the battery storage it may weaken the life of the battery. So in order to get constant D.C. output and also to avoid the reverse flow of current to the panel in the case of no load a charge controller have been used this help us to allow only the constant voltage of 12V D.C. to the battery and also it act as an blocking diode and protect the motor principle. By this way the battery gets charged then this D.C. storage is given to an inverter this inverter inverts 12V D.C. to input in to AC output, step upped in to 230V.The 230V AC supply is given to the supply to the lamp. The lamp used for street lighting is 230V, 50 Hz, single-phase supply.
- 3. LAMP ADVANTAGES ïž Steam is produced by the simply the flow lamp ïž This is a Non-conventional system ïž Battery is used to store the generated power ïž High pressure steam produced DISADVANTAGES ïž Only applicable for the particular place. ïž Initial cost of this arrangement is high. ïž Input Fuel supply needed BOILER UNIT D.C GENERATOR BATTERY INVERTOR
- 4. APPLICATIONS Direct heat applications Mechanical motion derived from water power can be used to drive heat pumps or to produce heat from the friction of solid materials, or by the churning of water or other fluids, or in other cases, by the use of centrifugal or other types of pumps in combination with restrictive orifices that produces heat from friction and turbulence when the working fluid flows through them. This heat may then be stored in materials having a high heat capacity, such as water, stones, eutectic salts, etc., A home heating system that uses a water powered pump and a restrictive orifice to derive direct heat for a building, without first generating electricityalso has been developed. Electric GenerationApplications: Water power can be used in centralized utility applications to drive synchronous A.C. electrical generators. In such applications the energy is fed directly into power networks through voltage step-up transformers. WORKING DIAGRAM: