Stimulant Drugs & the Brain
- 1. What we know about Dopamine, Methylphenidate & the Brain Activation of OFC and mPFC by Methylphenidate in Cocaine Addicted Subjects But Not in Controls: Relevance to Addiction (Volkow et al., J Neuroscience, 2005).
- 2. Methylphenidate (MP) ÔÇóÔÇ» Stimulant used to treat ADHD ÔÇóÔÇ» Oral dose: 10-60mg; peak brain levels 1-2 hours ÔÇóÔÇ» Mechanism: Blocks Dopamine Transporter (DAT)
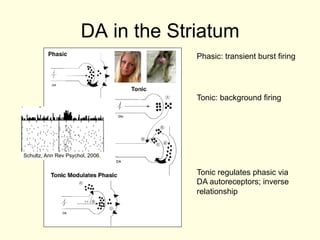
- 3. DA in the Striatum Phasic: transient burst firing Tonic: background firing Schultz, Ann Rev Psychol, 2006. Tonic regulates phasic via DA autoreceptors; inverse relationship
- 4. DA Circuitry ÔÇóÔÇ» Ôåæ PFC (corticostriatal) - inhibit VP - disinhibit VTA + + - Ôåæ phasic DA - Ôåæ novelty response, flexibility, SNR + - ÔÇóÔÇ» Tonic DA - Ôåô phasic DA - Ôåô mesocortical DA - - Ôåæ perseveration ÔÇóÔÇ» ÔÇ£permissive gateÔÇØ Grace et al. TINS (2007).
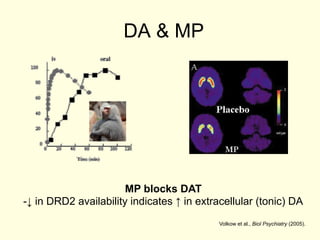
- 5. DA & MP MP blocks DAT -Ôåô in DRD2 availability indicates Ôåæ in extracellular (tonic) DA Volkow et al., Biol Psychiatry (2005).
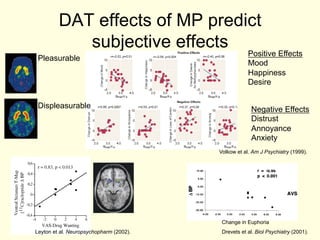
- 6. DAT effects of MP predict subjective effects Positive Effects Pleasurable Mood Happiness Desire Displeasurable Negative Effects Distrust Annoyance Anxiety Volkow et al. Am J Psychiatry (1999). Change in Euphoria Leyton et al. Neuropsychopharm (2002). Drevets et al. Biol Psychiatry (2001).
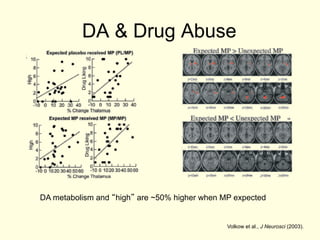
- 7. DA & Drug Abuse DA metabolism and ÔÇ£highÔÇØ are ~50% higher when MP expected Volkow et al., J Neurosci (2003).
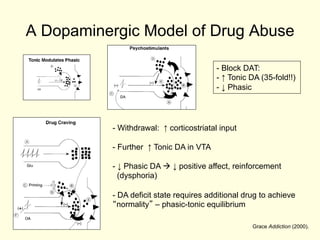
- 8. A Dopaminergic Model of Drug Abuse -ÔÇ» Block DAT: - Ôåæ Tonic DA (35-fold!!) - Ôåô Phasic -ÔÇ» Withdrawal: Ôåæ corticostriatal input -ÔÇ» Further Ôåæ Tonic DA in VTA -ÔÇ» Ôåô Phasic DA ├á´âá Ôåô positive affect, reinforcement (dysphoria) - DA deficit state requires additional drug to achieve ÔÇ£normalityÔÇØ ÔÇô phasic-tonic equilibrium Grace Addiction (2000).
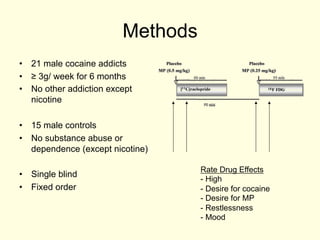
- 9. Methods ÔÇóÔÇ» 21 male cocaine addicts ÔÇóÔÇ» ÔëÑ 3g/ week for 6 months ÔÇóÔÇ» No other addiction except nicotine ÔÇóÔÇ» 15 male controls ÔÇóÔÇ» No substance abuse or dependence (except nicotine) Rate Drug Effects ÔÇóÔÇ» Single blind -ÔÇ» High ÔÇóÔÇ» Fixed order -ÔÇ» Desire for cocaine -ÔÇ» Desire for MP -ÔÇ» Restlessness -ÔÇ» Mood
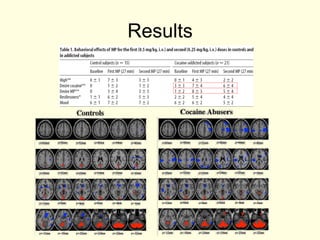
- 10. Results
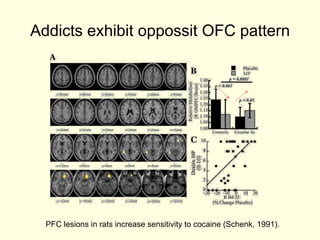
- 11. Addicts exhibit oppossit OFC pattern PFC lesions in rats increase sensitivity to cocaine (Schenk, 1991).
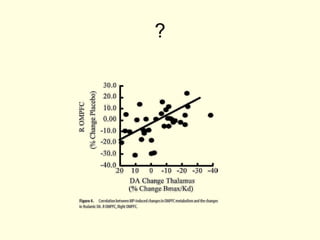
- 12. ?
- 13. Discussion ÔÇóÔÇ» OFC/ ACC abnormalities in cocaine, meth, heroine, marijauna & alcohol addiction ÔÇóÔÇ» Conditioned stimuli activate OFC/ ACC in addicts; blunted response to other rewards ÔÇóÔÇ» Discrepancy: Ôåô in NAcc and INS contrasts with cocaine ÔÇô induced Ôåæ (subjects, drugs, methods . . .) ÔÇóÔÇ» BA 25 ÔÇô emotional reactivity; BA11 ÔÇô motivational salience ÔÇôÔÇ» Maybe common substrates for compulsive disorders