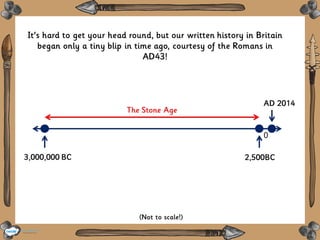
Stone Age Timeline
Download as ppt, pdf4 likes12,887 views
Take a look at the Stone Age timeline
1 of 11
Downloaded 210 times










Ad
Recommended
Bronze age lesson 5
Bronze age lesson 5mkwoods77
╠²
Bronze was a superior material to stone for making tools and weapons during the Bronze Age. Bronze is an alloy of copper and tin that is harder than pure copper. Bronze held its shape after forming and could be cast into molds, allowing for standardized tools and weapons to be produced in large quantities.History of Stone Age
History of Stone AgePinecrest Academy Nevada
╠²
The Mesolithic Age occurred between 10,000-8,000 BCE. During this time, humans moved out of caves and began building huts. They invented new stone tools like bows and arrows for hunting and boats for fishing. Humans also began domesticating wolves, which eventually became dogs. Societies grew larger and people started making pottery and jewelry. However, humans still maintained a nomadic lifestyle, hunting and gathering food and then migrating to new areas once resources were depleted.The Early Human History Pack
The Early Human History PackTeaching Ideas
╠²
The document provides an overview of early human history, focusing on the Stone Age, Bronze Age, and Iron Age, highlighting the tools, hunting practices, and burial customs of prehistoric peoples in Britain. It describes the transition from simple stone tools to more advanced metalworking, as well as cultural aspects such as cave art and significant archaeological finds like the Amesbury Archer and Lindow Man. It emphasizes human adaptation and social practices, including the importance of teamwork in hunting and the spiritual beliefs surrounding funerary practices.Stone age palaeolithic period
Stone age palaeolithic periodnaa692
╠²
The document discusses the three periods of the Stone Age:
1. The Paleolithic period was the earliest period when the first stone tools were invented. Humans during this time were hunter-gatherers who did not practice agriculture.
2. During the Mesolithic period, tools like bows and arrows were developed to help hunt deer.
3. The Neolithic period marked the beginning of farming.The stone age
The stone ageHST130mcc
╠²
1) Early humans like Homo sapiens emerged 100,000-400,000 years ago in Africa and were nomadic hunter-gatherers who used simple stone tools to find food and shelter.
2) Starting around 10,000 BC, humans began farming and domesticating plants and animals, leading to the Neolithic Revolution. Villages like Catal Huyuk in Turkey grew to house thousands as people specialized in jobs like farming, weaving, and pottery-making.
3) The Neolithic Age from around 8000 BC to 3000 BC saw further agricultural advances as people engaged in practices like slash-and-burn farming and raising livestock. Permanent settlements replaced nomadic lifestyles.Neolithic age
Neolithic ageARYAN GUPTA
╠²
This document provides information about the Neolithic village of Skara Brae located in Scotland. It is considered Europe's most complete Neolithic village dating back to around 3100 BC. The village was uncovered in 1850 after a severe coastal storm and provides insight into the daily lives of people who lived during the Neolithic period in northern Europe.Stonehenge
StonehengeHome
╠²
The document discusses several mysteries and theories about the origins and purpose of Stonehenge. Archaeologists have uncovered clues but many secrets remain. Some theories suggest it was used for ancient funerary practices or had astronomical alignments. Recent discoveries found people were buried there as early as 3000 BC, showing it was used as a cemetery from the start.Powerpoint stone age
Powerpoint stone agehome based
╠²
The document outlines the timeline of world history from prehistory to modern times. It divides world history into two periods: prehistory, before writing was invented; and history, after writing allowed events to be recorded. Prehistory is further divided into the Stone Age, Bronze Age, and Iron Age. The Stone Age includes the Paleolithic Age (Old Stone Age), Mesolithic Age, and Neolithic Age (New Stone Age). The Paleolithic Age saw early humans' absolute dependence on nature and use of stone tools. Agriculture and animal domestication began in the Neolithic Age.49. stone age
49. stone ageDiana Paola Garz├│n D├Łaz
╠²
The document summarizes the Stone Age period of human history. It was called the Stone Age because it was the period when early humans first started using stone tools, which helped them hunt and build shelter. Archaeologists divide the Stone Age into three periods based on tool sophistication: the Paleolithic Age (Old Stone Age), Mesolithic Age (Middle Stone Age), and Neolithic Age (New Stone Age). During the Neolithic Age, humans transitioned to farming and domesticated animals like cows and sheep.Neolithic Period
Neolithic PeriodReine Marie Arrojado
╠²
The document discusses the Neolithic period, highlighting the social organization of small tribes and the emergence of complex societies with the advent of metallurgy. It describes the transition from nomadic lifestyles to permanent agriculture, the development of housing, and advancements in technology, including tools and food preservation methods. Additionally, it addresses the challenges faced by early agrarian communities, such as famine and disease resulting from increased population density.Pre-History
Pre-Historysjbstudents
╠²
The document discusses life during the Paleolithic period of pre-history. During this time, which began around 2.5 million years ago:
- Humans lived in small nomadic bands and relied on hunting, gathering, and scavenging for food. They made tools from stone to aid in hunting and daily tasks.
- Around 30,000 years ago, early humans began painting images of animals on cave walls, indicating the beginning of artistic expression. They also learned to control fire.
- By the end of the Paleolithic period around 10,000 years ago, tools had advanced and included specialized tools made from stone, bone, and horn. Humans began burying their dead.Old stone age
Old stone ageARYAN GUPTA
╠²
The Paleolithic era, or Old Stone Age, is characterized by the first use of stone tools and lasted until about 12,000 to 70,000 years ago. During this period, early humans survived by hunting and gathering, forming groups for activities such as hunting, and utilizing materials like stone, wood, and bone for tools and clothing. The discovery of fire was also a significant development during this time.Mesolithic Age
Mesolithic AgeARYAN GUPTA
╠²
The document provides an overview of the prehistoric age, focusing on the Mesolithic era, characterized by advancements in technology such as the introduction of microliths and bone tools. It describes the transition from the Paleolithic's hunting and gathering lifestyle to more complex societies that began domestication of plants and animals, with various settlement types emerging. The Mesolithic period varies in duration and geographic significance, indicating an evolution in human development during this time.The differences between paleolithic and neolithic ages
The differences between paleolithic and neolithic agesjessieleininger
╠²
The document summarizes the key differences between the Paleolithic and Neolithic Ages in 3 main areas: food, shelter, and tools. In the Paleolithic Age, people hunted and gathered food without farming, lived in temporary shelters as they followed food sources, and used simple stone tools. In contrast, the Neolithic Age was characterized by farming, domestication of animals, permanent homes made of timber or bricks, and more advanced tools such as bows, arrows, and spear tips.Mesolithic age
Mesolithic ageQaiser Nadeem
╠²
The Mesolithic Age was a period of transition between the Old and New Stone Ages from 11,000-6,000 BCE. During this time, early humans began controlling fire, developing language, and moving from hunter-gatherer to more settled lifestyles. They began domesticating animals and plants, developing tools like bows and arrows and pottery, and forming early social structures and religious beliefs.Bronze age
Bronze agelogicrules12
╠²
The Bronze Age was a period of human history between the Stone Age and the Iron Age defined by the widespread use of bronze. Bronze is an alloy of copper and tin that was harder than copper alone, allowing it to be used for weapons and tools. The Bronze Age occurred at different times in different regions, ranging from around 3300 BC to 1200 BC in Egypt and 3000 BC to 700 BC in China. This period saw advances in agriculture, trade, and specialized labor.Holocene Period
Holocene PeriodSue Quirante
╠²
This document provides an overview of the geologic time scale and the Pleistocene epoch. It discusses how during the Pleistocene, between 2.6 million and 11,700 years ago, humanity evolved and survived dramatic climate swings through increased intelligence and adaptability. As ice ages occurred, humans developed new cultural technologies to deal with cold environments, such as controlling fire and wearing clothing. The document then outlines the Holocene interglacial period, from 11,700 years ago to present, when glaciers retreated and forests and agriculture spread across Asia and Europe.Paleolithic times
Paleolithic timesIndiana Council for the Social Studies
╠²
The document summarizes key developments from the Paleolithic period including the emergence of stone tool technology, the movement of humans from caves to villages, and early forms of shelter, art, and symbolic communication. Stone tools allowed humans to cut, shape, and work wood, enabling the creation of projectile weapons, shelters, and other technologies. Cave paintings provided early expressions of beliefs and perspectives on life. Archaeological artifacts and remains like the Skara Brae houses in Orkney, Scotland provide clues about Paleolithic life and how societies were organized.Early Humans
Early HumansSD Paul
╠²
The document outlines the lifestyles, tools, and societal changes of Paleolithic and Neolithic people, highlighting their adaptations to environments, and the shift from nomadic hunting-gathering to settled farming communities. It discusses the roles of historians, archaeologists, and anthropologists in studying human history, as well as technological advancements such as tool-making and the domestication of plants and animals. Key examples of early communities such as Jericho and Catal H├╝y├╝k are presented, alongside comparisons of Paleolithic and Neolithic societies.Prehistory
PrehistoryNombre Apellidos
╠²
This document summarizes prehistory from the Paleolithic era to the Metal Age. It describes how early humans evolved from hunter-gatherers to settling in agricultural communities. Key developments included controlling fire, crafting sophisticated stone tools, domesticating animals, inventing pottery, and beginning to trade. During the Neolithic, humans established permanent villages and constructed megalithic monuments like menhirs, dolmens, and stone circles. The Metal Age saw the rise of copper, bronze, and iron tools and technologies, enabling early cities to form with hundreds of inhabitants.Prehistory for 4th grade
Prehistory for 4th gradeNeus Vi├▒allonga
╠²
This document summarizes the three main periods of prehistory: the Paleolithic Age, Neolithic Age, and Metal Age. The Paleolithic Age began 3 million years ago and ended around 10,000 BCE when humans transitioned from hunting and gathering to agriculture. During the Neolithic Age from 10,000 BCE to 5,000 BCE, humans developed farming and domesticated animals. The Metal Age started around 5,000 BCE when humans began working with metals to create tools and weapons.Origin of humans
Origin of humansDexvor tex
╠²
1. The document discusses the evolution of early humans from 4 million years ago to the development of civilizations. It outlines 4 stages of early human development and the key species at each stage.
2. During the Paleolithic Age between 2.5 million to 10,000 years ago, early humans like Homo habilis and Homo erectus lived nomadic lifestyles, hunting and gathering food. They began using tools and fire.
3. From 200,000 to 10,000 years ago in Stage 3, Neanderthals and Cro-Magnons inhabited Europe and Asia. Cro-Magnons eventually replaced Neanderthals. The last Ice Age occurred from 70,000 toStone age
Stone ageSadaf Walliyani
╠²
The document summarizes differences between the Old Stone Age (Paleolithic Age) and New Stone Age (Neolithic Age). During the Paleolithic Age, people hunted and gathered food, lived nomadically in temporary shelters, and wore clothing made of animal furs. In contrast, the Neolithic Age saw the development of agriculture and domestication of animals, with people settling in permanent homes near crops and herding animals. Clothing incorporated wool from domesticated sheep.Living stone age
Living stone ageRachel Collishaw
╠²
The document discusses life during the Stone Age period of prehistory. It describes some of the key human species that lived during this time, including Homo habilis who used stone tools, Homo erectus who were the first to control fire and travel out of Africa, and Homo sapiens. Neanderthals are also mentioned as a variety of early modern humans. During the Paleolithic period, humans lived in small nomadic groups and relied on hunting and gathering, while the Neolithic period saw the beginning of agriculture, domestication of animals, and more complex social structures. Many innovations occurred during the Stone Age, including the earliest known art, religion and spiritual practices, and developments that eventually led to the emergencestone henge
stone hengesiddharth patel
╠²
Stonehenge is an ancient stone circle located in Wiltshire, England. It was constructed in multiple phases beginning around 2950 BCE, when a timber circle and ring of 56 pits were built. Around 2550 BCE, construction began on the stone circle, using large sarsen stones weighing up to 60 tons brought from nearby and smaller bluestones transported from Wales. The site and stones were carefully constructed and oriented using geometric proportions and the golden ratio, with the number three incorporated throughout the design. Stonehenge was likely used for rituals connected to astronomy and as a burial ground.Living and non living things powerpoint 1
Living and non living things powerpoint 1Mari Carmen Ocete, C.E.I.P. Francisco Giner de los R├Łos
╠²
The document compares and contrasts living and non-living things. It lists various objects and asks the reader to identify them as living or non-living. It then discusses whether certain items are natural or man-made. Finally, it prompts the reader to draw a picture of a plant and animal, provide reasons they are living, and share their answers with a partner.Wild Animals
Wild AnimalsPrashant Mahajan
╠²
This document lists the names of various wild animals under the category "Wild Animals". It includes mammals such as lions, tigers, leopards, elephants, giraffes and camels. It also includes other animals like kangaroos, hyenas, foxes, wolves, jackals, bears, rhinoceros, hippopotamus, crocodiles, gorillas and pandas. The document was created by Prashant Mahajan to share information about different wild animals that may be helpful for students and their parents.Neolithic age
Neolithic ageibrahimjade
╠²
In the Neolithic Period, people in the Near East began developing agriculture, taming animals, and establishing villages as they transitioned to a farming way of life. This included gathering seeds and domesticating plants. Notable sites from this period included Jericho, considered the earliest walled city and town, and Catal Huyuk, which served as a center for trade and home to Neolithic farmer villages. Trade developed through bartering goods and the emergence of specialized artisans.Fiver Challenge Adverting
Fiver Challenge Adverting hpy6
╠²
This document discusses key aspects of creating advertisements, including what advertisements are used for, where they can be seen/heard, and which media channels are best based on the target audience. It emphasizes including important details like the business/product/service being advertised, contact information, and making the ad memorable. The document also contains sample questions to test recall of real advertisements and their key elements to demonstrate memorable advertising.The magic box
The magic boxhpy6
╠²
The poem describes a magic box that can hold anything imaginable, from sensations like the swish of silk to fantastical creatures like a snowman with a rumbling belly. The box itself is made of ice, gold and steel, with stars on the lid and dinosaur toe joints for hinges. The speaker plans to surf on the wild Atlantic waves inside the box before emerging on a sunny yellow beach. In the end, the reader is invited to consider what they would place in their own magic box.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
49. stone age
49. stone ageDiana Paola Garz├│n D├Łaz
╠²
The document summarizes the Stone Age period of human history. It was called the Stone Age because it was the period when early humans first started using stone tools, which helped them hunt and build shelter. Archaeologists divide the Stone Age into three periods based on tool sophistication: the Paleolithic Age (Old Stone Age), Mesolithic Age (Middle Stone Age), and Neolithic Age (New Stone Age). During the Neolithic Age, humans transitioned to farming and domesticated animals like cows and sheep.Neolithic Period
Neolithic PeriodReine Marie Arrojado
╠²
The document discusses the Neolithic period, highlighting the social organization of small tribes and the emergence of complex societies with the advent of metallurgy. It describes the transition from nomadic lifestyles to permanent agriculture, the development of housing, and advancements in technology, including tools and food preservation methods. Additionally, it addresses the challenges faced by early agrarian communities, such as famine and disease resulting from increased population density.Pre-History
Pre-Historysjbstudents
╠²
The document discusses life during the Paleolithic period of pre-history. During this time, which began around 2.5 million years ago:
- Humans lived in small nomadic bands and relied on hunting, gathering, and scavenging for food. They made tools from stone to aid in hunting and daily tasks.
- Around 30,000 years ago, early humans began painting images of animals on cave walls, indicating the beginning of artistic expression. They also learned to control fire.
- By the end of the Paleolithic period around 10,000 years ago, tools had advanced and included specialized tools made from stone, bone, and horn. Humans began burying their dead.Old stone age
Old stone ageARYAN GUPTA
╠²
The Paleolithic era, or Old Stone Age, is characterized by the first use of stone tools and lasted until about 12,000 to 70,000 years ago. During this period, early humans survived by hunting and gathering, forming groups for activities such as hunting, and utilizing materials like stone, wood, and bone for tools and clothing. The discovery of fire was also a significant development during this time.Mesolithic Age
Mesolithic AgeARYAN GUPTA
╠²
The document provides an overview of the prehistoric age, focusing on the Mesolithic era, characterized by advancements in technology such as the introduction of microliths and bone tools. It describes the transition from the Paleolithic's hunting and gathering lifestyle to more complex societies that began domestication of plants and animals, with various settlement types emerging. The Mesolithic period varies in duration and geographic significance, indicating an evolution in human development during this time.The differences between paleolithic and neolithic ages
The differences between paleolithic and neolithic agesjessieleininger
╠²
The document summarizes the key differences between the Paleolithic and Neolithic Ages in 3 main areas: food, shelter, and tools. In the Paleolithic Age, people hunted and gathered food without farming, lived in temporary shelters as they followed food sources, and used simple stone tools. In contrast, the Neolithic Age was characterized by farming, domestication of animals, permanent homes made of timber or bricks, and more advanced tools such as bows, arrows, and spear tips.Mesolithic age
Mesolithic ageQaiser Nadeem
╠²
The Mesolithic Age was a period of transition between the Old and New Stone Ages from 11,000-6,000 BCE. During this time, early humans began controlling fire, developing language, and moving from hunter-gatherer to more settled lifestyles. They began domesticating animals and plants, developing tools like bows and arrows and pottery, and forming early social structures and religious beliefs.Bronze age
Bronze agelogicrules12
╠²
The Bronze Age was a period of human history between the Stone Age and the Iron Age defined by the widespread use of bronze. Bronze is an alloy of copper and tin that was harder than copper alone, allowing it to be used for weapons and tools. The Bronze Age occurred at different times in different regions, ranging from around 3300 BC to 1200 BC in Egypt and 3000 BC to 700 BC in China. This period saw advances in agriculture, trade, and specialized labor.Holocene Period
Holocene PeriodSue Quirante
╠²
This document provides an overview of the geologic time scale and the Pleistocene epoch. It discusses how during the Pleistocene, between 2.6 million and 11,700 years ago, humanity evolved and survived dramatic climate swings through increased intelligence and adaptability. As ice ages occurred, humans developed new cultural technologies to deal with cold environments, such as controlling fire and wearing clothing. The document then outlines the Holocene interglacial period, from 11,700 years ago to present, when glaciers retreated and forests and agriculture spread across Asia and Europe.Paleolithic times
Paleolithic timesIndiana Council for the Social Studies
╠²
The document summarizes key developments from the Paleolithic period including the emergence of stone tool technology, the movement of humans from caves to villages, and early forms of shelter, art, and symbolic communication. Stone tools allowed humans to cut, shape, and work wood, enabling the creation of projectile weapons, shelters, and other technologies. Cave paintings provided early expressions of beliefs and perspectives on life. Archaeological artifacts and remains like the Skara Brae houses in Orkney, Scotland provide clues about Paleolithic life and how societies were organized.Early Humans
Early HumansSD Paul
╠²
The document outlines the lifestyles, tools, and societal changes of Paleolithic and Neolithic people, highlighting their adaptations to environments, and the shift from nomadic hunting-gathering to settled farming communities. It discusses the roles of historians, archaeologists, and anthropologists in studying human history, as well as technological advancements such as tool-making and the domestication of plants and animals. Key examples of early communities such as Jericho and Catal H├╝y├╝k are presented, alongside comparisons of Paleolithic and Neolithic societies.Prehistory
PrehistoryNombre Apellidos
╠²
This document summarizes prehistory from the Paleolithic era to the Metal Age. It describes how early humans evolved from hunter-gatherers to settling in agricultural communities. Key developments included controlling fire, crafting sophisticated stone tools, domesticating animals, inventing pottery, and beginning to trade. During the Neolithic, humans established permanent villages and constructed megalithic monuments like menhirs, dolmens, and stone circles. The Metal Age saw the rise of copper, bronze, and iron tools and technologies, enabling early cities to form with hundreds of inhabitants.Prehistory for 4th grade
Prehistory for 4th gradeNeus Vi├▒allonga
╠²
This document summarizes the three main periods of prehistory: the Paleolithic Age, Neolithic Age, and Metal Age. The Paleolithic Age began 3 million years ago and ended around 10,000 BCE when humans transitioned from hunting and gathering to agriculture. During the Neolithic Age from 10,000 BCE to 5,000 BCE, humans developed farming and domesticated animals. The Metal Age started around 5,000 BCE when humans began working with metals to create tools and weapons.Origin of humans
Origin of humansDexvor tex
╠²
1. The document discusses the evolution of early humans from 4 million years ago to the development of civilizations. It outlines 4 stages of early human development and the key species at each stage.
2. During the Paleolithic Age between 2.5 million to 10,000 years ago, early humans like Homo habilis and Homo erectus lived nomadic lifestyles, hunting and gathering food. They began using tools and fire.
3. From 200,000 to 10,000 years ago in Stage 3, Neanderthals and Cro-Magnons inhabited Europe and Asia. Cro-Magnons eventually replaced Neanderthals. The last Ice Age occurred from 70,000 toStone age
Stone ageSadaf Walliyani
╠²
The document summarizes differences between the Old Stone Age (Paleolithic Age) and New Stone Age (Neolithic Age). During the Paleolithic Age, people hunted and gathered food, lived nomadically in temporary shelters, and wore clothing made of animal furs. In contrast, the Neolithic Age saw the development of agriculture and domestication of animals, with people settling in permanent homes near crops and herding animals. Clothing incorporated wool from domesticated sheep.Living stone age
Living stone ageRachel Collishaw
╠²
The document discusses life during the Stone Age period of prehistory. It describes some of the key human species that lived during this time, including Homo habilis who used stone tools, Homo erectus who were the first to control fire and travel out of Africa, and Homo sapiens. Neanderthals are also mentioned as a variety of early modern humans. During the Paleolithic period, humans lived in small nomadic groups and relied on hunting and gathering, while the Neolithic period saw the beginning of agriculture, domestication of animals, and more complex social structures. Many innovations occurred during the Stone Age, including the earliest known art, religion and spiritual practices, and developments that eventually led to the emergencestone henge
stone hengesiddharth patel
╠²
Stonehenge is an ancient stone circle located in Wiltshire, England. It was constructed in multiple phases beginning around 2950 BCE, when a timber circle and ring of 56 pits were built. Around 2550 BCE, construction began on the stone circle, using large sarsen stones weighing up to 60 tons brought from nearby and smaller bluestones transported from Wales. The site and stones were carefully constructed and oriented using geometric proportions and the golden ratio, with the number three incorporated throughout the design. Stonehenge was likely used for rituals connected to astronomy and as a burial ground.Living and non living things powerpoint 1
Living and non living things powerpoint 1Mari Carmen Ocete, C.E.I.P. Francisco Giner de los R├Łos
╠²
The document compares and contrasts living and non-living things. It lists various objects and asks the reader to identify them as living or non-living. It then discusses whether certain items are natural or man-made. Finally, it prompts the reader to draw a picture of a plant and animal, provide reasons they are living, and share their answers with a partner.Wild Animals
Wild AnimalsPrashant Mahajan
╠²
This document lists the names of various wild animals under the category "Wild Animals". It includes mammals such as lions, tigers, leopards, elephants, giraffes and camels. It also includes other animals like kangaroos, hyenas, foxes, wolves, jackals, bears, rhinoceros, hippopotamus, crocodiles, gorillas and pandas. The document was created by Prashant Mahajan to share information about different wild animals that may be helpful for students and their parents.Neolithic age
Neolithic ageibrahimjade
╠²
In the Neolithic Period, people in the Near East began developing agriculture, taming animals, and establishing villages as they transitioned to a farming way of life. This included gathering seeds and domesticating plants. Notable sites from this period included Jericho, considered the earliest walled city and town, and Catal Huyuk, which served as a center for trade and home to Neolithic farmer villages. Trade developed through bartering goods and the emergence of specialized artisans.More from hpy6 (7)
Fiver Challenge Adverting
Fiver Challenge Adverting hpy6
╠²
This document discusses key aspects of creating advertisements, including what advertisements are used for, where they can be seen/heard, and which media channels are best based on the target audience. It emphasizes including important details like the business/product/service being advertised, contact information, and making the ad memorable. The document also contains sample questions to test recall of real advertisements and their key elements to demonstrate memorable advertising.The magic box
The magic boxhpy6
╠²
The poem describes a magic box that can hold anything imaginable, from sensations like the swish of silk to fantastical creatures like a snowman with a rumbling belly. The box itself is made of ice, gold and steel, with stars on the lid and dinosaur toe joints for hinges. The speaker plans to surf on the wild Atlantic waves inside the box before emerging on a sunny yellow beach. In the end, the reader is invited to consider what they would place in their own magic box.Sa ts meeting 2014a
Sa ts meeting 2014ahpy6
╠²
The document outlines the schedule for SATs tests that will take place from May 12-15. It details the subjects and timings of tests for both level 3-5 and level 6 students. The afternoons will involve revision and exercises. Results from previous years show the school outperforming national averages in reading, writing, and maths for levels 4-5. The document also addresses common questions about measuring progress, support for students, and how results will be reported.Eve 1950's Topic Homework
Eve 1950's Topic Homeworkhpy6
╠²
False. Seat belts in the 1950s served the same purpose as they do now - to restrain occupants in vehicles during accidents or sudden stops to prevent injury.Year 6 Question Creation
Year 6 Question Creationhpy6
╠²
The document contains questions created by students in Year 6 on various maths topics. There are 14 questions in total covering calculations involving weights, money, areas, percentages, sales and time. The questions range in complexity from single-step calculations to multi-step word problems.Adverbial clauses
Adverbial clauseshpy6
╠²
The document discusses using adverbial clauses to change the meaning of sentences in speech. It provides 6 sentences with blanks that can be filled in with adverbial clauses drawn from a list of 6 options. The adverbial clauses provide context about the actions or situations of the characters, altering the meaning of the core sentences. It then asks the reader to consider what actions the characters might be doing and what situation they could be in to prompt different speech.Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
How to Manage Multi Language for Invoice in Odoo 18
How to Manage Multi Language for Invoice in Odoo 18Celine George
╠²
Odoo supports multi-language functionality for invoices, allowing you to generate invoices in your customersŌĆÖ preferred languages. Multi-language support for invoices is crucial for businesses operating in global markets or dealing with customers from different linguistic backgrounds. Birnagar High School Platinum Jubilee Quiz.pptx
Birnagar High School Platinum Jubilee Quiz.pptxSourav Kr Podder
╠²
Birnagar High School Platinum Jubilee Celebration QuizThis is why students from these 44 institutions have not received National Se...
This is why students from these 44 institutions have not received National Se...Kweku Zurek
╠²
This is why students from these 44 institutions have not received National Service PIN codes (LIST)Q1_ENGLISH_PPT_WEEK 1 power point grade 3 Quarter 1 week 1
Q1_ENGLISH_PPT_WEEK 1 power point grade 3 Quarter 1 week 1jutaydeonne
╠²
Grade 3 Quarter 1 Week 1 English part 2Introduction to Generative AI and Copilot.pdf
Introduction to Generative AI and Copilot.pdfTechSoup
╠²
In this engaging and insightful two-part webinar series, where we will dive into the essentials of generative AI, address key AI concerns, and demonstrate how nonprofits can benefit from using MicrosoftŌĆÖs AI assistant, Copilot, to achieve their goals.
This event series to help nonprofits obtain Copilot skills is made possible by generous support from Microsoft.ABCs of Bookkeeping for Nonprofits TechSoup.pdf
ABCs of Bookkeeping for Nonprofits TechSoup.pdfTechSoup
╠²
Accounting can be hard enough if you havenŌĆÖt studied it in school. Nonprofit accounting is actually very different and more challenging still.
Need help? Join Nonprofit CPA and QuickBooks expert Gregg Bossen in this first-time webinar and learn the ABCs of keeping books for a nonprofit organization.
Key takeaways
* What accounting is and how it works
* How to read a financial statement
* What financial statements should be given to the board each month
* What three things nonprofits are required to track
What features to use in QuickBooks to track programs and grantsUniversity of Ghana Cracks Down on Misconduct: Over 100 Students Sanctioned
University of Ghana Cracks Down on Misconduct: Over 100 Students SanctionedKweku Zurek
╠²
University of Ghana Cracks Down on Misconduct: Over 100 Students Sanctioned
LDM Recording Presents Yogi Goddess by LDMMIA
LDM Recording Presents Yogi Goddess by LDMMIALDM & Mia eStudios
╠²
A bonus dept update. Happy Summer 25 almost. Do Welcome or Welcome back. Our 10th Free workshop will be released the end of this week, June 20th Weekend. All Materials/updates/Workshops are timeless for future students.
6/17/25: ŌĆ£My now Grads, YouŌĆÖre doing well. I applaud your efforts to continue. We all are shifting to new paradigm realities. Its rough, thereŌĆÖs good and bad days/weeks. However, Reiki with Yoga assistance, does work.ŌĆØ
6/18/25: "For those planning the Training Program Do Welcome. Happy Summer 2k25. You are not ignored and much appreciated. Our updates are ongoing and weekly since Spring. I Hope you Enjoy the Practitioner Grad Level. There's more to come. We will also be wrapping up Level One. So I can work on Levels 2 topics. Please see documents for any news updates. Also visit our websites. Every decade I release a Campus eMap. I will work on that for summer 25. We have 2 old libraries online thats open. https://ldmchapels.weebly.com "
A Safe House,
sanctuary of virtual relaxation and rejuvenation.
By ┬®YogiGoddess of ┬®LDMMIA, ┬®LDMYoga.
ŌÖźTeacher Dept: (Rev Dr) Leslie Moore, ND Yoga (Aide/LPN Trained), Metaphysician,
Using Reiki Practitioner/Master Level Trained.
#yogigoddess @YogiGoddessVEVO
ŌÖźLDMMIA & Depts: are fusing the fan clubs so do welcome.
We are timeless and a safe haven / Cyber Space. ThatŌĆÖs the design of our Fan/Reader/Loyal Blog.ŌÖź
LDM HQ Est. in Ann Arbor, MI 2005.
- Moved to Detroit in 2006,
- Expanded online 2007-2024+
- Became a Beatz Studio in 2009 as Yogi Goddess. After our Apple Podcast
- Relocated to Mount Pleasant MI for College The Pandemic Ending.
- Endemic - Present; Moved back to assist Family in Metro Detroit.
Practitioner Student. Level/Session 2
* The Review & Topics:
* All virtual, adult, education students must be over 18 years to attend LDMMIA eClasses and vStudio Thx.
* Please refer to our Free Workshops anytime for review/notes.
*Tech: Products Sold Separately are for Uploading Size Reasons, THX.
MIA TECH: Videos under Copyright including our Music Video for Yogi Goddess, Can only be picked up vs shop downloaded. We are under vydia.com
Pickup will be our Youtube, for unlisted Playlist.
We do have another Vod for Session 2, Level 1.
After that we move on to Session 3.
Levels 1-3 should be done by August to Sept.
LDM Recording, Yogi Goddess Bio (ReverbNation)
Organization functions as a Studio 1st. We are a Media Co, Private Sector, and Global Listed.
Imagine we are 2 different studios. One for Yoga, the Other for Music Beatz. We are also Vevo TV for Smart TV and Youtube, 2 platforms. The audience differs.
Our Biz income are Media monetization within The Entertainment genre. This includes the category of Yoga, Reiki, ASMR, and Music Beatz. Any other tips, donations, B2C sales/Student Tuition are extra. The Biz gifts are appreciated. (We have been given a few $K for random emergencies.)
Battle of Bookworms 2025 - U25 Literature Quiz by Pragya
Battle of Bookworms 2025 - U25 Literature Quiz by Pragya Pragya - UEM Kolkata Quiz Club
╠²
Battle of Bookworms is a literature quiz organized by Pragya, UEM Kolkata, as part of their cultural fest Ecstasia. Curated by quizmasters Drisana Bhattacharyya, Argha Saha, and Aniket Adhikari, the quiz was a dynamic mix of classical literature, modern writing, mythology, regional texts, and experimental literary forms. It began with a 20-question prelim round where ŌĆśstar questionsŌĆÖ played a key tie-breaking role. The top 8 teams moved into advanced rounds, where they faced audio-visual challenges, pounce/bounce formats, immunity tokens, and theme-based risk-reward questions. From Orwell and Hemingway to Tagore and Sarala Das, the quiz traversed a global and Indian literary landscape. Unique rounds explored slipstream fiction, constrained writing, adaptations, and true crime literature. It included signature IDs, character identifications, and open-pounce selections. Questions were crafted to test contextual understanding, narrative knowledge, and authorial intent, making the quiz both intellectually rewarding and culturally rich. Battle of Bookworms proved literature quizzes can be insightful, creative, and deeply enjoyable for all.Assisting Individuals and Families to Promote and Maintain Health ŌĆō Unit 7 | ...
Assisting Individuals and Families to Promote and Maintain Health ŌĆō Unit 7 | ...RAKESH SAJJAN
╠²
This PowerPoint presentation is based on Unit 7 ŌĆō Assisting Individuals and Families to Promote and Maintain Their Health, a core topic in Community Health Nursing ŌĆō I for 5th Semester B.Sc Nursing students, as per the Indian Nursing Council (INC) guidelines.
The unit emphasizes the nurseŌĆÖs role in family-centered care, early detection of health problems, health promotion, and appropriate referrals, especially in the context of home visits and community outreach. It also strengthens the studentŌĆÖs understanding of nursing responsibilities in real-life community settings.
¤ōś Key Topics Covered in the Presentation:
Introduction to family health care: needs, principles, and objectives
Assessment of health needs of individuals, families, and groups
Observation and documentation during home visits and field assessments
Identifying risk factors: environmental, behavioral, genetic, and social
Conducting growth and development monitoring in infants and children
Recording and observing:
Milestones of development
Menstrual health and reproductive cycle
Temperature, blood pressure, and vital signs
General physical appearance and personal hygiene
Social assessment: understanding family dynamics, occupation, income, living conditions
Health education and counseling for individuals and families
Guidelines for early detection and referral of communicable and non-communicable diseases
Maintenance of family health records and individual health cards
Assisting families with:
Maternal and child care
Elderly and chronic disease management
Hygiene and nutrition guidance
Utilization of community resources ŌĆō referral linkages, support services, and local health programs
Role of nurse in coordinating care, advocating for vulnerable individuals, and empowering families
Promoting self-care and family participation in disease prevention and health maintenance
This presentation is highly useful for:
Nursing students preparing for internal exams, university theory papers, or community postings
Health educators conducting family teaching sessions
Students conducting fieldwork and project work during community postings
Public health nurses and outreach workers dealing with preventive, promotive, and rehabilitative care
ItŌĆÖs structured in a step-by-step format, featuring tables, case examples, and simplified explanations tailored for easy understanding and classroom delivery.Environmental Science, Environmental Health, and Sanitation ŌĆō Unit 3 | B.Sc N...
Environmental Science, Environmental Health, and Sanitation ŌĆō Unit 3 | B.Sc N...RAKESH SAJJAN
╠²
This PowerPoint presentation covers Unit 3 ŌĆō Environmental Science, Environmental Health, and Sanitation from the 5th Semester B.Sc Nursing syllabus prescribed by the Indian Nursing Council (INC). It is carefully designed to support nursing students, educators, and community health professionals in understanding the environmental components that influence health and disease prevention.
The unit emphasizes the interrelationship between the environment and human health, highlighting various environmental factors, hazards, and strategies for disease prevention through sanitation and public health initiatives.
Ō£│’ĖÅ Topics Covered in the PPT:
Definition and scope of environmental science and environmental health
Importance of a safe environment for public health
Types of environmental pollution ŌĆō air, water, soil, noise, and radiation
Sources, effects, and prevention of different types of pollution
Concept of ecosystem and its components
Water safety and purification methods at household and community levels
Disposal of waste and excreta ŌĆō types, methods, health risks
Introduction to environmental sanitation
Vector control measures: Mosquitoes, houseflies, rodents, etc.
Biological and non-biological health hazards in the environment
National programs related to environmental health and sanitation
Health education for safe water, hygiene, and sanitation behavior change
Role of a community health nurse in promoting environmental health
Use of community bags and home visit kits to educate rural families
Practical methods for solid waste management and waste segregation
This presentation supports:
Class lectures and revision
Health teaching in field visits
Community awareness campaigns
Internal assessments and final exam preparation
It ensures that all essential environmental health concepts are simplified and well-structured for easy understanding and application in nursing practice.Pests of Maize: An comprehensive overview.pptx
Pests of Maize: An comprehensive overview.pptxArshad Shaikh
╠²
Maize is susceptible to various pests that can significantly impact yields. Key pests include the fall armyworm, stem borers, cob earworms, shoot fly. These pests can cause extensive damage, from leaf feeding and stalk tunneling to grain destruction. Effective management strategies, such as integrated pest management (IPM), resistant varieties, biological control, and judicious use of chemicals, are essential to mitigate losses and ensure sustainable maize production.GEOGRAPHY-Study Material [ Class 10th] .pdf
GEOGRAPHY-Study Material [ Class 10th] .pdfSHERAZ AHMAD LONE
╠²
"Geography Study Material for Class 10th" provides a comprehensive and easy-to-understand resource for key topics like Resources & Development, Water Resources, Agriculture, Minerals & Energy, Manufacturing Industries, and Lifelines of the National Economy. Designed as per the latest NCERT/JKBOSE syllabus, it includes notes, maps, diagrams, and MODEL question Paper to help students excel in exams. Whether revising for exams or strengthening conceptual clarity, this material ensures effective learning and high scores. Perfect for last-minute revisions and structured study sessions.Chalukyas of Gujrat, Solanki Dynasty NEP.pptx
Chalukyas of Gujrat, Solanki Dynasty NEP.pptxDr. Ravi Shankar Arya Mahila P. G. College, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India.
╠²
This presentation has been made keeping in mind the students of undergraduate and postgraduate level. In this slide try to present the brief history of Chaulukyas of Gujrat up to Kumarpala To keep the facts in a natural form and to display the material in more detail, the help of various books, websites and online medium has been taken. Whatever medium the material or facts have been taken from, an attempt has been made by the presenter to give their reference at the end.
Chaulukya or Solanki was one of the Rajputs born from Agnikul. In the Vadnagar inscription, the origin of this dynasty is told from Brahma's Chauluk or Kamandalu. They ruled in Gujarat from the latter half of the tenth century to the beginning of the thirteenth century. Their capital was in Anahilwad. It is not certain whether it had any relation with the Chalukya dynasty of the south or not. It is worth mentioning that the name of the dynasty of the south was 'Chaluky' while the dynasty of Gujarat has been called 'Chaulukya'. The rulers of this dynasty were the supporters and patrons of Jainism.Paper 108 | ThoreauŌĆÖs Influence on Gandhi: The Evolution of Civil Disobedience
Paper 108 | ThoreauŌĆÖs Influence on Gandhi: The Evolution of Civil DisobedienceRajdeep Bavaliya
╠²
Dive into the powerful journey from ThoreauŌĆÖs 19thŌĆæcentury essay to GandhiŌĆÖs mass movement, and discover how one manŌĆÖs moral stand became the backbone of nonviolent resistance worldwide. Learn how conscience met strategy to spark revolutions, and why their legacy still inspires todayŌĆÖs social justice warriors. Uncover the evolution of civil disobedience. DonŌĆÖt forget to like, share, and follow for more deep dives into the ideas that changed the world.
M.A. Sem - 2 | Presentation
Presentation Season - 2
Paper - 108: The American Literature
Submitted Date: April 2, 2025
Paper Name: The American Literature
Topic: ThoreauŌĆÖs Influence on Gandhi: The Evolution of Civil Disobedience
[Please copy the link and paste it into any web browser to access the content.]
Video Link: https://youtu.be/HXeq6utg7iQ
For a more in-depth discussion of this presentation, please visit the full blog post at the following link: https://rajdeepbavaliya2.blogspot.com/2025/04/thoreau-s-influence-on-gandhi-the-evolution-of-civil-disobedience.html
Please visit this blog to explore additional presentations from this season:
Hashtags:
#CivilDisobedience #ThoreauToGandhi #NonviolentResistance #Satyagraha #Transcendentalism #SocialJustice #HistoryUncovered #GandhiLegacy #ThoreauInfluence #PeacefulProtest
Keyword Tags:
civil disobedience, Thoreau, Gandhi, Satyagraha, nonviolent protest, transcendentalism, moral resistance, Gandhi Thoreau connection, social change, political philosophyROLE PLAY: FIRST AID -CPR & RECOVERY POSITION.pptx
ROLE PLAY: FIRST AID -CPR & RECOVERY POSITION.pptxBelicia R.S
╠²
Role play : First Aid- CPR, Recovery position and Hand hygiene.
Scene 1: Three friends are shopping in a mall
Scene 2: One of the friend becomes victim to electric shock.
Scene 3: Arrival of a first aider
Steps:
Safety First
Evaluate the victimŌĆśs condition
Call for help
Perform CPR- Secure an open airway, Chest compression, Recuse breaths.
Put the victim in Recovery position if unconscious and breathing normally.
LAZY SUNDAY QUIZ "A GENERAL QUIZ" JUNE 2025 SMC QUIZ CLUB, SILCHAR MEDICAL CO...
LAZY SUNDAY QUIZ "A GENERAL QUIZ" JUNE 2025 SMC QUIZ CLUB, SILCHAR MEDICAL CO...Ultimatewinner0342
╠²
¤¦Ā Lazy Sunday Quiz | General Knowledge Trivia by SMC Quiz Club ŌĆō Silchar Medical College
Presenting the Lazy Sunday Quiz, a fun and thought-provoking general knowledge quiz created by the SMC Quiz Club of Silchar Medical College & Hospital (SMCH). This quiz is designed for casual learners, quiz enthusiasts, and competitive teams looking for a diverse, engaging set of questions with clean visuals and smart clues.
¤Ä» What is the Lazy Sunday Quiz?
The Lazy Sunday Quiz is a light-hearted yet intellectually rewarding quiz session held under the SMC Quiz Club banner. ItŌĆÖs a general quiz covering a mix of current affairs, pop culture, history, India, sports, medicine, science, and more.
Whether youŌĆÖre hosting a quiz event, preparing a session for students, or just looking for quality trivia to enjoy with friends, this PowerPoint deck is perfect for you.
¤ōŗ Quiz Format & Structure
Total Questions: ~50
Types: MCQs, one-liners, image-based, visual connects, lateral thinking
Rounds: Warm-up, Main Quiz, Visual Round, Connects (optional bonus)
Design: Simple, clear slides with answer explanations included
Tools Needed: Just a projector or screen ŌĆō ready to use!
¤¦Ā Who Is It For?
College quiz clubs
School or medical students
Teachers or faculty for classroom engagement
Event organizers needing quiz content
Quizzers preparing for competitions
Freelancers building quiz portfolios
¤ÆĪ Why Use This Quiz?
Ready-made, high-quality content
Curated with lateral thinking and storytelling in mind
Covers both academic and pop culture topics
Designed by a quizzer with real event experience
Usable in inter-college fests, informal quizzes, or Sunday brain workouts
¤ōÜ About the Creators
This quiz has been created by Rana Mayank Pratap, an MBBS student and quizmaster at SMC Quiz Club, Silchar Medical College. The club aims to promote a culture of curiosity and smart thinking through weekly and monthly quiz events.
¤öŹ SEO Tags:
quiz, general knowledge quiz, trivia quiz, ║▌║▌▀ŻShare quiz, college quiz, fun quiz, medical college quiz, India quiz, pop culture quiz, visual quiz, MCQ quiz, connect quiz, science quiz, current affairs quiz, SMC Quiz Club, Silchar Medical College
¤ōŻ Reuse & Credit
YouŌĆÖre free to use or adapt this quiz for your own events or sessions with credit to:
SMC Quiz Club ŌĆō Silchar Medical College & Hospital
Curated by: Rana Mayank PratapChalukyas of Gujrat, Solanki Dynasty NEP.pptx
Chalukyas of Gujrat, Solanki Dynasty NEP.pptxDr. Ravi Shankar Arya Mahila P. G. College, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India.
╠²
LAZY SUNDAY QUIZ "A GENERAL QUIZ" JUNE 2025 SMC QUIZ CLUB, SILCHAR MEDICAL CO...
LAZY SUNDAY QUIZ "A GENERAL QUIZ" JUNE 2025 SMC QUIZ CLUB, SILCHAR MEDICAL CO...Ultimatewinner0342
╠²
Ad
Stone Age Timeline
- 1. A task setting PowerPoint about events in the Stone Age