Storage head works
- 1. STORAGE HEAD WORKS 1 ANIRUDHAN K M LECTURER IN CIVIL ENGINEERING
- 2. DAMS ? Hydraulic structure ? Solid Impervious (or fairly impervious) barrier constructed at a suitable location across a natural stream (river), to store water in its upstream side. ? A reservoir is formed due to its construction ? The water in the reservoir is utilised as and when it is needed 2
- 3. TYPES OF DAM ? Classification according to use ĻC Storage Dam ĻC Diversion Dam ĻC Detention Dam ? Classification by hydraulic design ĻC Overflow Dam ĻC Non Overflow Dam ? Classification by Materials ĻC Rigid Dams ĻC Non ĻC Rigid Dams ? Classification By Mode of Stability ĻC Gravity Dam ĻC Non Gravity Dam 3
- 4. TYPES OF DAM ? Classification according to use ĻCStorage Dam ? Constructed to store water during the rainy season, when water is available in the river. ? Released gradually for intended purposes. ? They may store water for hydroelectric power generation, irrigation or for Water Supply. ĻCDiversion Dam ? Used to raise water level and divert water. ? No Reservoir is formed. ? No or a little Storage. ĻCDetention Dam ? Flood mitigation. ? Stores water in the time of flood and released after flood at safe rate. ? Another type allows water to enter slowly to the ground water. 4
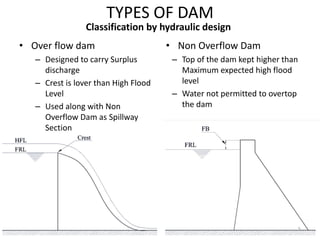
- 5. TYPES OF DAM ? Over flow dam ĻC Designed to carry Surplus discharge ĻC Crest is lover than High Flood Level ĻC Used along with Non Overflow Dam as Spillway Section ? Non Overflow Dam ĻC Top of the dam kept higher than Maximum expected high flood level ĻC Water not permitted to overtop the dam Classification by hydraulic design 5
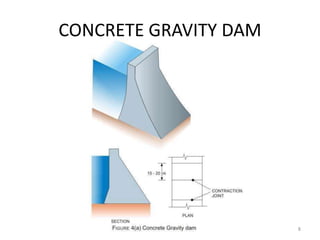
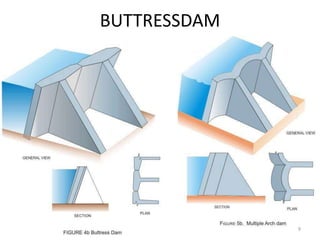
- 6. TYPES OF DAM ? Rigid Dam ĻC Constructed of Rigid Materials ? Solid Masonry or Concrete Gravity Dam ? Arched Masonry or Concrete Dam ? Concrete Buttress Dam ? Steel Dam ? Timber Dam ? Non Rigid Dam ĻC Constructed of Non Rigid Materials ? Earth Dam ? Rockfill Dam ? Combined Earth and Rockfill Classification by Materials 6
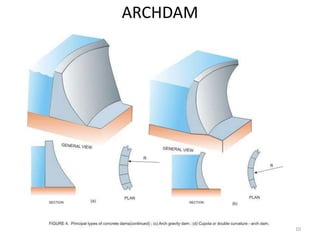
- 7. TYPES OF DAM ? Gravity Dam ĻC Self Weight of the Dam the major Stabilization Force ? Solid Masonry or Concrete Gravity Dam ? Earth Dam ? Rockfill Dam ? Combined Earth and Rockfill ? Non Gravity Dam ĻC Stabilises against mobilising forces using Non Gravity Methods ? Arch Dam ĻC Load Transfer by Arch Action ? Buttress Dam ĻC Load Transferred to Supporting Buttresses. Classification by Mode of Stability 7
- 10. ARCHDAM 10
- 11. SITE SELECTION Factors governing site selection ? Foundation conditions ? Topography ? Site for spillway ? Material availability ? Reservoir capacity ? Communication ? Healthy Locality 11
- 12. SITE INVESTIGATION FOR DAM CONSTRUCTION ? Reconnaissance ? Preliminary Surveys ĻC Engineering Surveys ĻC Geological Surveys ĻC Hydrologic Surveys ? Detailed Investigations 12
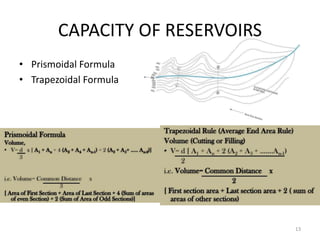
- 13. CAPACITY OF RESERVOIRS ? Prismoidal Formula ? Trapezoidal Formula 13
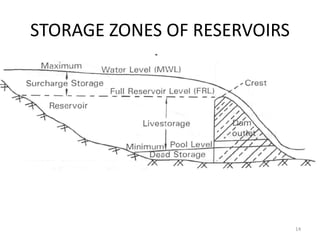
- 14. STORAGE ZONES OF RESERVOIRS 14
- 15. EVAPORATION LOSSES IN RESERVOIRS ? Losses in Reservoirs are mainly due to evaporation and seepage ? The depth of water evaporated per year from the reservoir surface may vary from about 400 mm in cool and humid climate to more than 2500 mm in hot and arid regions. ? Water budget method, Energy budget method etc are used for estimation of Evaporation Losses ? Accurate estimation is done by using data from pan-evaporimeters or pans exposed to atmosphere with or without meshing in or near the reservoir site and suitably adjusted. 15
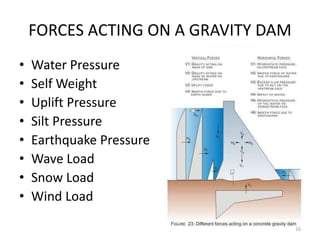
- 16. FORCES ACTING ON A GRAVITY DAM ? Water Pressure ? Self Weight ? Uplift Pressure ? Silt Pressure ? Earthquake Pressure ? Wave Load ? Snow Load ? Wind Load 16
- 17. FAILURES OF GRAVITY DAM ? Due to Overturning ? Due to Development of Tension at the Base ? Due to Sliding ? Due to Crushing or Compression 17
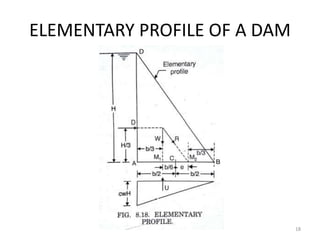
- 18. ELEMENTARY PROFILE OF A DAM 18
- 19. PRACTICAL PROFILE OF A DAM 19
- 20. FREE BOARD AND TOP WIDTH ? Practical Considerations ĻC Roadway at top ĻC Load due to Roadway ĻC Freeboard ? Top width is provided about 14% of the total height of dam ? Free Board ĻC Margin provided Between KFL and Top of dam ĻC Prevent waves, unforeseen floods ĻC Provided equal to 3/2 x Height of Waves 20
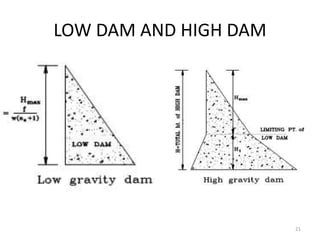
- 21. LOW DAM AND HIGH DAM 21
- 22. DRAINAGE GALLARY ? A gallery is an opening provided in the body of a dam for various purposes ? Drainage gallery is a gallery extends only through the deepest portion of the dam serving purpose of drilling and draining the downstream portion of the foundation. ? Inspection gallery is provided for inspection purpose 22
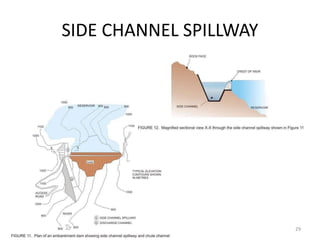
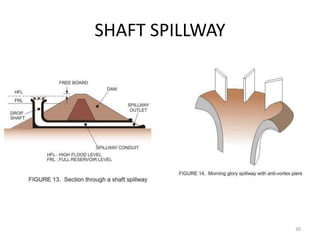
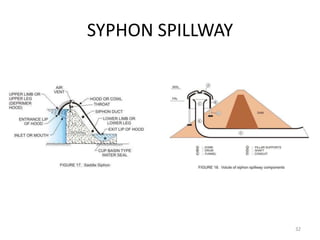
- 23. SPILLWAYS ? Free Overfall (Straight Drop) Spillway ? Overflow (Ogee) Spillway ? Chute (Open Channel/Trough) Spillway ? Side Channel Spillway ? Shaft (Drop Inlet/Morning Glory) spillway ? Tunnel (Conduit) spillway ? Siphon spillway 23
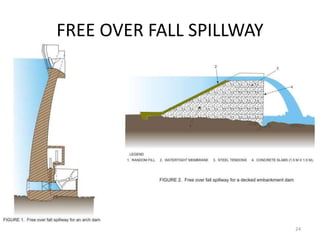
- 24. FREE OVER FALL SPILLWAY 24
- 25. OGEE SPILLWAY 25
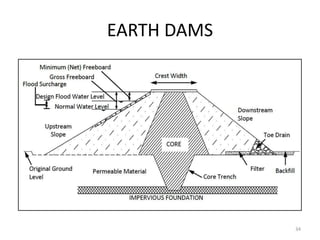
- 33. EARTH DAMS ? Earth dams are the oldest type of dams, as well as the most common ones. ? They are always most economical type that can be constructed on soil foundations. ? Can be constructed using locally available soils. ? No special foundations are required for the construction of these dams. ? Skilled labour is not required. ? Modern earth moving equipments can be used to construct such type ofdams. 33
- 34. EARTH DAMS 34
- 35. SITE SELECTION OF EARTH DAM ? Topography - A wide valley with deep overburden ? Geology and Foundation Conditions ĻC Gravel foundations, if well compacted is suitable for earth dams. ĻC Silt or fine sand foundations can be used for earth dams, the main problems include settlement, prevention of piping, excessive percolation losses. ĻC Clay foundation may be used for each dams but require flat side slopes ? Material availability ? Environmental Considerations ? Economy 35
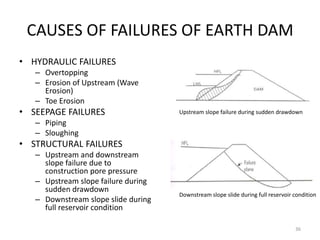
- 36. CAUSES OF FAILURES OF EARTH DAM ? HYDRAULIC FAILURES ĻC Overtopping ĻC Erosion of Upstream (Wave Erosion) ĻC Toe Erosion ? SEEPAGE FAILURES ĻC Piping ĻC Sloughing ? STRUCTURAL FAILURES ĻC Upstream and downstream slope failure due to construction pore pressure ĻC Upstream slope failure during sudden drawdown ĻC Downstream slope slide during full reservoir condition Upstream slope failure during sudden drawdown Downstream slope slide during full reservoir condition 36
- 37. THANK YOU 37