Strategic planning to attract and retain customers.
- 1. Marketing Unit 1 : Overview of Marketing
- 2. Reference Books ŌĆó Principles of Marketing , Philip Kotler 13th Ed, PHI publications ŌĆó Marketing Management , Rajan Saxena, 3rd Ed, Tata McGraw Hill ŌĆó Marketing Management 3rd Ed, Ramaswamy, Namakumari ŌĆó Marketing Management-A south Asian Perspective ŌĆó Kotler, Keller, Koshy and Jha, Pearson (14 e)
- 3. Concept of Market ŌĆó Market refers to a place where transactions take place between buyers and sellers with respect to exchange of goods and services. ŌĆó Markets are bifurcated on the basis of the type of product. For instance, cotton market, grains market and flower market. Sometimes, they are also bifurcated on the basis of quantity. For example, wholesale market and retail market. ŌĆó The market may be physical entity or may be virtual, it may be local or global ŌĆó However, in modern times, the term market has a wider meaning. It now includes all potential buyers of goods or/and services.
- 4. Concept of Marketing ŌĆó Marketing refers to the process of interaction between buyers and sellers with the objective of exchange of goods and services. ŌĆó Marketing is a much wider concept which comprises various activities involved in the process of exchange of goods and services between buyers and sellers. ŌĆó The activities which are part of marketing are basically the various functions which are performed under marketing such as planning. designing the product, packaging and labelling of the product, standardizing, branding, warehousing, transport, advertising, pricing and distribution. In addition, it includes after sales activities such as customer care and feedback.
- 5. Marketing Management ŌĆó Marketing management means management of all the activities related to marketing or in other words we can say, it refers to planning, organizing, directing and controlling the activities which result in exchange of goods and services. ŌĆó The main focus of marketing is on exchange of goods and services. ŌĆó Philip Kotler defined marketing management as "The art and science of choosing target markets and getting, keeping and growing customers through creating delivering and communicating superior customer values of management".
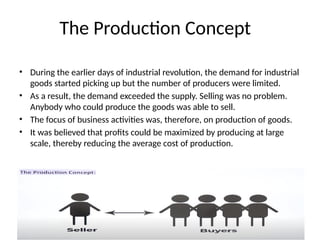
- 7. The Production Concept ŌĆó During the earlier days of industrial revolution, the demand for industrial goods started picking up but the number of producers were limited. ŌĆó As a result, the demand exceeded the supply. Selling was no problem. Anybody who could produce the goods was able to sell. ŌĆó The focus of business activities was, therefore, on production of goods. ŌĆó It was believed that profits could be maximized by producing at large scale, thereby reducing the average cost of production.
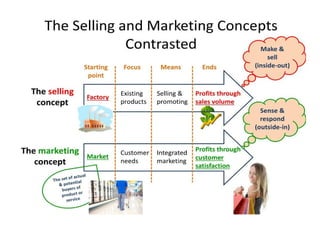
- 9. Selling Concept ŌĆó The product quality and availability did not ensure the survival and growth of firms because of the large number of sellers selling quality products. ŌĆó This led to greater importance to attracting and persuading customers to buy the product. ŌĆó The business philosophy changed. It was assumed that the customers would not buy, or not buy enough, unless they are adequately convinced and motivated to do so ŌĆó Therefore, firms must undertake aggressive selling and promotional efforts to make customers buy their products. The use of promotional techniques such as advertising. personal selling and sales promotion were considered essential for selling of products.
- 10. The Marketing Concept ŌĆó Marketing orientation implies that focus on satisfaction of customer's needs is the key to the success of any organization in the market. ŌĆó It assumes that in the long run an organization can achieve its objective of maximization of profit by identifying the needs of its present and prospective buyers and satisfying them in an effective way. ŌĆó All the decisions in a firm are taken from the point of view of the customers. ŌĆó For example, what product will be produced, with what features and at what price shall it be sold, or where shall it be made available for sale will depend on what do the customers want. If the customers want features like double door in a refrigerator or a separate provision for water cooler in it, the organization would produce a refrigerator with these features. would price it at a level which the customers are willing to pay and so on. ŌĆ£Our goal is to lead customers where they want to go before they know where they want to goŌĆØ
- 12. The Societal Marketing Concept ŌĆó The marketing concept, cannot be considered as adequate if we look at the challenges posed by social problems like environmental pollution, deforestation, shortage of resources, population explosion and inflation. ŌĆó It is so because any activity which satisfies human needs but is detrimental to the interests of the society at large cannot be justified. The business orientation should, therefore, not be short-sighted to serve only consumers' needs. It should also consider large issues of long-term social welfare.
- 13. Marketing Myopia ŌĆó When a company focuses more on sales than on marketing or consumersŌĆÖ needs, thatŌĆÖs when marketing myopia strikes in. ŌĆó A firm might think that product sales will grow without conducting proper research. Sometimes, they donŌĆÖt see that customers behave differently in the digital age. ŌĆó Step-Child Treatment Businesses often treat their product as their own child and customersŌĆÖ needs as a stepchild. This result in spending most of the resources in the development of their product and the remaining (less or no) resources on conducting research and marketing. This backfires on the businesses as the stepchild always turn out to be the Cinderella of the story.
- 14. Marketing Myopia ŌĆó Marketing Myopia is focusing only on existing wants and losing sight of underlying consumer needs
- 15. Examples Of Marketing Myopia ŌĆó Kodak lost much of its share to Sony cameras when digital cameras boomed and Kodak didnŌĆÖt plan for it. ŌĆó Yahoo (worth $100 billion dollars in 2000) lost to Google and was bought by Verizon at approx. $5 billion (2016).---Yahoo could have acquired Google for $1 billion in 2002. But top leaders delayed it. ---It offered $1 billion to Facebook. But after a while, they decreased it to $850 million.----- Microsoft wanted to buy Yahoo in 2008 for $44.6 billion. Yahoo turned it down. ŌĆó Google Glass was launched in 2014. It was exposed to a lot of negative reviews from consumers. They had concerns about privacy and safety. Most people werenŌĆÖt interested in high-tech glasses that gave information at a glance of people or objects.--Google concentrated so much on selling this high-tech device that they overlooked the usefulness of it.
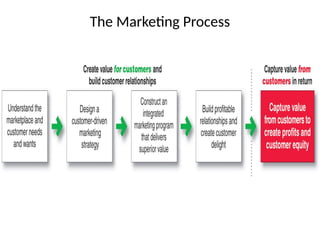
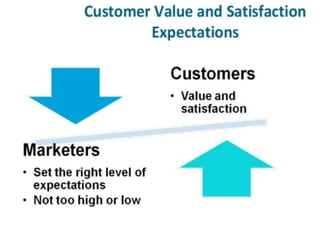
- 17. Step-1-Understanding the Marketplace and Customer Needs ŌĆó Customer needs, wants, and demands ŌĆó Market offerings ŌĆó Value and satisfaction ŌĆó Exchanges and relationships ŌĆó Markets
- 18. Understanding the Marketplace and Customer Needs ŌĆó States of deprivation ŌĆó PhysicalŌĆöfood, clothing, warmth, safety ŌĆó SocialŌĆöbelonging and affection ŌĆó IndividualŌĆöknowledge and self-expression ŌĆó ------Food-------- Needs ŌĆó Form that needs take as they are shaped by culture and individual personality ŌĆó --------what customer prefer-chicken, Burger-------- Wants ŌĆó Wants backed by buying power ŌĆó ------- only burger is within my budget----------- Demands
- 19. In the above example, responding to only stated need ie., ŌĆ£I need a phone or CarŌĆØ doesnŌĆÖt help in arriving at a right product proposition. As a marketer, it is important to dig deeper and uncover not only the real, but also his other needs: unstated need, delight need and secret needs.
- 20. Market Offerings ŌĆó Market offerings are some combination, mixture, or blend of physical products, services, information, ideas, or experiences offered to a market to satisfy a need or a want. ŌĆó Eg: CokeŌĆÖs Open Happiness
- 21. Value and Satisfaction ŌĆó Satisfied customers will buy again and tell others about their good experiences, on the other hand, dissatisfied customers will eventually switch to competitors and surely disparage the product to others. ŌĆó Eg: Pizza Hut Bell
- 22. Exchanges and Relationship ŌĆó Exchange is the act of obtaining a desired object from someone by offering something in return.ŌĆŗ ŌĆó The goal is to retain customers and grow their business and build strong relationship by consistently delivering superior customer value.ŌĆŗ
- 23. Step-2-Designing a Customer-Driven Marketing Strategy To design a winning marketing strategy, the marketing manager must answer two important questions: ŌĆó What customers will we serve ( whatŌĆÖs our target market)? -Dividing the market into segments and selecting which segment it will go ŌĆó How can we serve these customers best ( whatŌĆÖs our value proposition)?--- A companyŌĆÖs value proposition is the set of benefits or values it promises to deliver to consumers to satisfy their needs BMW promises ŌĆ£the ultimate driving machineŌĆØ Apple iPhone ŌĆō The Experience IS the Product Uber ŌĆō The Smartest Way to Get Around Red BullŌĆō Gives you Wiiings ŌĆó It answer the customerŌĆÖs question: Why should I buy your brand rather than a competitor's?
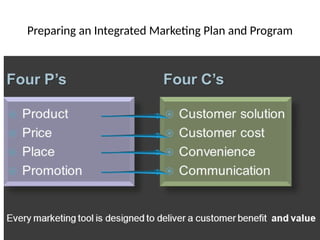
- 24. Step-3-Preparing an Integrated Marketing Plan and Program
- 25. Preparing an Integrated Marketing Plan and Program
- 26. Step-4 Building Customer Relationship The first three steps in the marketing process, leads up to the fourth and most important step: Building profitable Customer Relationship Customer Relationship Management is the overall process of building and maintaining profitable customer relationships by delivering superior customer value( perceived) and satisfaction. It deals with all the aspects of acquiring, keeping, and growing customers ŌĆó Communicate ŌĆó Ask for feedback ŌĆó Show appreciation ŌĆó Delight customers-by delivering more than promise ŌĆó Frequency marketing programs- reward customer who buy frequently-point system
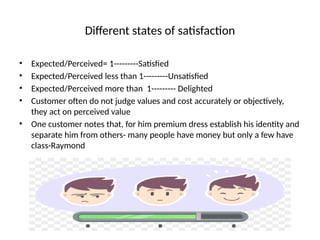
- 27. Different states of satisfaction ŌĆó Expected/Perceived= 1---------Satisfied ŌĆó Expected/Perceived less than 1---------Unsatisfied ŌĆó Expected/Perceived more than 1--------- Delighted ŌĆó Customer often do not judge values and cost accurately or objectively, they act on perceived value ŌĆó One customer notes that, for him premium dress establish his identity and separate him from others- many people have money but only a few have class-Raymond
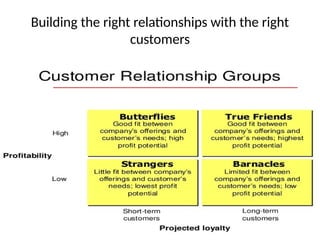
- 30. Step-5 Capturing Customer Value ŌĆó The final step involves capturing value in return- in the form of current and future sales, market share, and profits. ŌĆó Creating Customer Loyalty and Retention-customer life time value ŌĆó Growing Share of Customer ŌĆó Building Customer Equity- The total combined customer life time values of all the companyŌĆÖs customers ŌĆó Building the Right Relationships with the Right Customer
- 31. Building the right relationships with the right customers
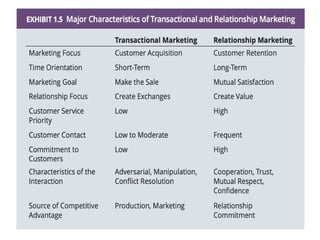
- 32. Relationship Marketing ŌĆó Relationship marketing refers to marketing efforts that focuses on developing long-term relationship with customers. It is a part of Customer relationship management (CRM) which aims to achieve long-term engagement of clients with business for maintaining its profitability. Relationship marketing is distinct from other types of traditional marketing. ŌĆó It carries out activities for achievement of long-term goals like customer loyalty. Whereas, traditional marketing works towards getting short-term goals like customer acquisition and one-time sales. Traditional marketing does not pay any attention on building relationships. Relationship marketing instead of sales transactions emphasizes on customer retention and their satisfaction level.
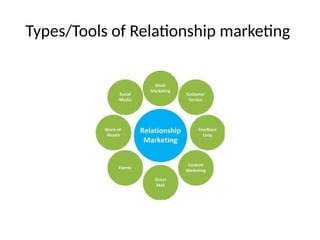
- 34. Types/Tools of Relationship marketing