Strategic Technological competence
- 1. By Social Business Technologies Consulting July 2011 Identification, Optimisation, Exploitation for the Future
- 2. ’üĮ Defined as: ’üĮ The collective learning in the organisation, especially how to coordinate diverse production skills and integrate multiple streams of technologies. ’üĮ Competences do not diminish with use and are enhanced as they are applied and shared. They need to be nurtured and protected, as they are the glue that binds existing functions within the business and are the engine for new business development (Prahalad and Hamel, 1990). Identification, Optimisation, Exploitation for the Future
- 3. Tests of compliance: ’üĮ Access: ŌŚ” Provide potential access to a wide variety of markets ’üĮ Value: ŌŚ” Should make a significant contribution to the perceived customer benefits of the end product ’üĮ Imitate: ŌŚ” Difficult for competitors to imitate Identification, Optimisation, Exploitation for the Future
- 4. ’üĮ Core competences: ’üĮ Set the direction and trend of the organisations competitiveness ’üĮ Technological competences: ’üĮ Set the direction and trend of technologies needed to support the achievement of the organisations objectives Identification, Optimisation, Exploitation for the Future
- 5. ’üĮ Defined as: ’üĮ The ability of a firm to exploit its resources to dominate particular technologies relevant to the needs of the enterprise. ’üĮ (Estades & Ramani 1998, Rhodes & Wield 1994) Identification, Optimisation, Exploitation for the Future
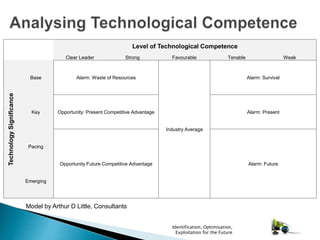
- 6. Tests of Compliance: ’üĮ Attributes (must be able to describe competence in terms of): ŌŚ” Technology, people, structure, culture. ’üĮ Typology (it will be either): ŌŚ” Simple, middle complex, complex ’üĮ Organisational Dimension (it will have): ŌŚ” Physical Aspects / Intellectual Components ’üĮ Competitive Barrier (at least one of these must apply): ŌŚ” Value, Access, Imitate ’üĮ Level of Technology Competence (Of the firm in this area): ŌŚ” Clear leader, Strong, Favourable, Tenable, Weak ’üĮ Technology Significance (To the firm of the competence): Base, Key, Pacing, Emerging Identification, Optimisation, Exploitation for the Future
- 7. Model by Arthur D Little, Consultants Level of Technological Competence Clear Leader Strong Favourable Tenable Weak TechnologySignificance Base Alarm: Waste of Resources Industry Average Alarm: Survival Key Opportunity: Present Competitive Advantage Alarm: Present Pacing Opportunity Future Competitive Advantage Alarm: Future Emerging Identification, Optimisation, Exploitation for the Future
- 8. ’üĮ Develop a Focus or Vision ŌŚ” These are Strategic Technology Competencies ’üĮ Understand the Technological Trajectory ŌŚ” Know what you want to specialise in ’üĮ Create a Technology Strategy ŌŚ” Roadmap to the future ŌĆō know where you want to be Identification, Optimisation, Exploitation for the Future
- 9. ’üĮ Thank you for your time. ’üĮ steventuitt@sbtconsulting.co.uk ’üĮ info@sbtconsulting.co.uk ’üĮ Tel: 0116 2997831 ’üĮ Mob: 07816 416595 Identification, Optimisation, Exploitation for the Future