Stress management
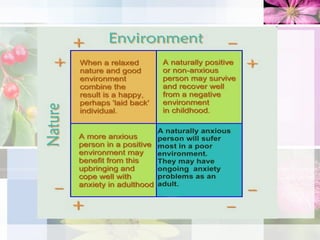
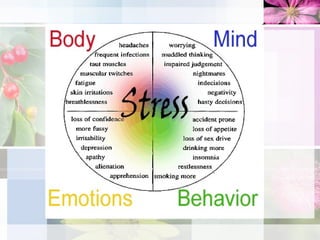
- 2. Stress What is stress? It’s the spice of life or the kiss of death depending on how we cope with it. Stress gives us the means to express our talents and energies and pursue happiness; it can also cause exhaustion and illness, nervous breakdowns, heart attacks, accidents. Strictly speaking, stress is simply the body’s non-specific response to any demand made on it, and is not necessarily synonymous with nervous tension or anxiety….
- 4. Anxiety Anxiety or tension is a feeling of apprehension or fear that lingers. The source for this uneasiness is not always known or recognized which adds to the distress: "Everything stresses me out.“ "I am always worried." Fundamentally, it is not the quality or intensity of the events that counts. What matters is not what happens to us, but the way we take it. Judge how you are taking the stress in your life at any particular moment; if there are too many signs of distress in your feelings or behavior, there are various little tricks to minimize these
- 6. Tips to Reduce Stress Take a break ¨ Breath deeply ¨ Sit back and relax ¨ Do something you love ¨ Read a good book ¨ Change your surroundings ¨ Learn to Play Organize your life: ¨ Manage your time ¨ Make to do lists ¨ Plan ahead ¨ Set mini goals ¨ Learn to Plan Communicate: ¨ Express your emotions ¨ Talk to a friend ¨ Eliminate negative talk ¨ Cry ¨ Laugh Practice Relaxation: ¨ Meditation ¨ Deep Breathing ¨ Get a Massage ¨ Visualization ¨ Take a Bath ¨ Try saying the Serenity Prayer Stretch ¨ Stand up and reach up ¨ Neck stretch: roll your head in a half circle, starting at one side, then dropping your chin to your chest, then to the other side ¨ Watch a cat stretch and do the same
- 8. Other stress management tips: ¨ Learn to live one day at a time ¨ Improve your appearance ¨ Do something for someone else (volunteer work) ¨ Allow yourself private time everyday ¨ Learn to forgive and forget ¨ Watch a good movie ¨ Listen too your favorite music ¨ Eat well ¨ Be a positive person ¨ Avoid unnecessary competition
- 9. Your personal reactions to anxiety: For one full week, record moments when you feel anxiety. Where were you (in class, at work), what was the situation (were you being called on in class, ice breaker during an extracurricular activity, at work), why did you feel anxious, how did you react physically (did your stomach hurt, did you shake, palms sweat)? How does anxiety influence your attitude or behavior? (do you get angry with yourself; do you have an attitude with other people?) What are some techniques for dealing with each situation? Then plan to use some relaxation technique the next time you encounter these situations. With a little planning you will be able to anticipate and, therefore, better manage your anxiety. These two questions should help you get started: 1. I usually feel anxious when: 2. I notice when I am anxious I see these changes in myself:
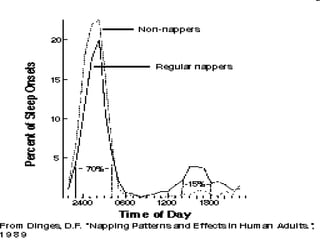
- 10. Better Sleep Guide We all have too much to do, recharge yourself by getting a good night’s sleep. The quality and quantity of your sleep can make all the difference in how productive you’ll be the next day.
- 13. Tips to get a good sleep 1. Give yourself “permission” to go to bed. As hard as it may be to put away your “to do” list, make sleep a “priority,” You’ll thank yourself in the morning. 2. Unwind early in the evening. Try to deal with worries and distractions several hours before bedtime. 3. Develop a sleep ritual. Doing the same things each night just before bed signals your body to settle down for the night. 4. Keep regular hours. Keep your biological clock in check by going to bed around the same time each morning – even on weekends. 5. Make your bedroom a Sleep Haven. Create a restful place to sleep. Sleep in a moderate (temperature not too hot or too cold), dark room that is free from noises that may disturb your sleep. Make sure the mattress and foundation meet your needs for both comfort and support. 6. Sleep on a comfortable, supportive mattress and foundation. It’s difficult to sleep on a bed that’s too small, too soft, too hard, or too old. 7. Exercise regularly. Regular exercise can help relieve daily tension and stress – but don’t exercise too close to bedtime or you may have trouble falling asleep.
- 14. Tips to get a good sleep 8. Cut down on stimulants. Consuming stimulants, such as caffeine, in the evening can make it more difficult to fall asleep. 9. Don’t smoke. Smokers take longer to fall asleep and wake up more often during the night. 10. Reduce alcohol intake. Drinking alcohol shortly before bedtime interrupts and fragments sleep. 11. Exercise. Sometimes exercise an hour or two before bed can relieve you from the stress gained throughout the day. It not only is healthy for you, but can help you rest better. 12. Journal. Keep a journal of the day’s activities, highlighting challenging moments of the day and developing strategies on how to handle such situations in the future. Also discuss the lessons learned from both positive and negative interactions with other people, noting blessings also. 13. Herbal tea. There are several brands of non-caffeine herbal teas available in your local grocers that are natural sleep aids.
- 16. Relaxation Techniques The information below briefly describes several relaxation techniques. To learn more about these relaxation techniques, please visit the LAC Blackboard website, which has links to various websites. 1.Meditation: this technique involves focusing on something unchanging (such as a spot on the wall) or something repetitive (such as repeating a word – a mantra). Then you realize your mind has wandered, merely return to repeating the word. 2. Imagery: Imagery can be guided or unguided. When guided, someone else determines which image you should keep in mind when trying to relax. When unguided, you decide what image would be relaxing. If possible, it is best to choose your own image since you have a better idea of what you find relaxing than does someone else. Some images people generally find relaxing are sunshine warming the body, a day at the beach, a rippling lake, a walk in the woods, the surf rolling on the shore, birds flying through the air, a carpeted room warmed by a fire, and a sailboat floating on the water.
- 17. Relaxation Techniques 3. Autogenic Training: Autogenic training requires you to imagine your arms and legs feel heavy, warm and tingly. By doing this, blood flow increases to these body parts due to a dilation (widening) of blood vessels in the arms and legs. This is part of the relaxation response. After the body is relaxed this way, the mind is calmed by adding images of relaxing scenes. Imagery that is part of autogenic training is called autogenic mediation. 4. Progressive Relaxation: Progressive relaxation teaches the sensation of muscular contraction by focusing attention on the feeling of the muscles as they are tensed throughout the body. It then teaches the sensation to your more tense parts. The relaxed sensation can be imagined to be a warm ball that travels to various bodily locations warming and relaxing them. 5. Diaphragmatic Breathing: Relaxed breathing occurs as a result of the diaphragm expanding, as opposed to stressful breathing that is a function of the chest expanding. Relaxed breathing is called Diaphragmatic Breathing. To try Diaphragmatic Breathing, lie on your back and place your hands on your abdomen. As you breathe you should feel your abdomen riseand your chest remain fairly stable.
- 18. Relaxation Techniques 6. Quieting Reflex: With practice, this technique is said to relax a person in just six seconds. The Quieting Reflex is done as follows: o Think about something that makes you afraid or anxious. o Smile inside. This breaks up the anxious facial muscle tension. o Tell yourself, “I can keep a calm body in an alert mind.” o Let your jaw go loose as you exhale, keeping your lower and upper teeth slightly apart. o Imagine heaviness and warmth moving throughout your body, from head to toe.