Java String
- 1. Wrapper Classes And String Satyam Shrivastav
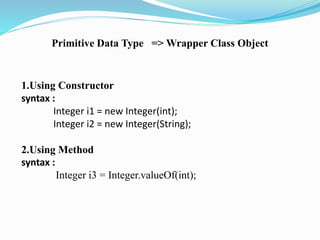
- 3. Primitive Data Type => Wrapper Class Object 1.Using Constructor syntax : Integer i1 = new Integer(int); Integer i2 = new Integer(String); 2.Using Method syntax : Integer i3 = Integer.valueOf(int);
- 4. Wrapper Class Object => Primitive Data Type 1.Using method xxxValue() syntax : Integer io=Integer.valueOf(254) int i=io.xxxValue();
- 5. Primitive String Object => Wrapper Class Object 1.Using Constructor syntax : Integer i1 = new Integer(âprimitiveTypeâ); 2.using method syntax : Integer i1=Integer.valueOf(âprimitiveTypeâ);
- 6. Primitive String Object => Primitive Data Type //1.Primitive String Object =>Primitive String Object => Primitive Data Type //2Primitive String Object => Primitive Data Type Using method parseInt(âprimitive typeâ); syntax : String s1=Integer.parseInt(â100â)
- 7. Wrapper Class Object => String Object 1.using method toString() syntax : Integer io=new Integer(254); String s=io.toString()
- 8. Primitive Data Type => Non String Object 1.using method toString(primitive type) syntax : String s=Integer.toString(10);
- 9. String
- 10. String ï String is a sequence of characters placed in double quote(â â). ï Strings are constant , their values cannot be changed in the same memory after they are created.
- 11. How to create String object ï There are two ways to create String object: 1)By string literal. 2)By new keyword. ï 1)By string literal: For Example: String s1=âwelcome"; String s2=âwelcomeâ; //no new object will be created
- 12. 2) By new keyword:- For Example: String s=new String(âSachin"); String s=new String(âSachinTendulkar");//create two objects and one reference variable.
- 13. Immutability âĒ In java, string objects are immutable. Immutable simply means unmodifiable or unchangeable. âĒ Once string object is created its data or state can't be changed but a new string object is created.
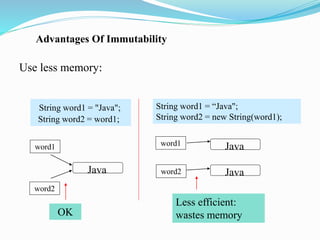
- 14. Advantages Of Immutability Use less memory: String word1 = "Java"; String word2 = word1; String word1 = âJava"; String word2 = new String(word1); word1 OK Less efficient: wastes memory Java Java Java word2 word1 word2
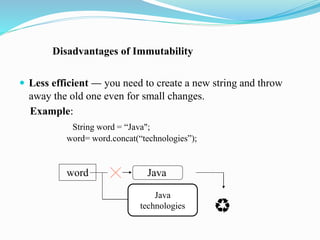
- 15. Disadvantages of Immutability ï Less efficient â you need to create a new string and throw away the old one even for small changes. Example: String word = âJava"; word= word.concat(âtechnologiesâ); word Java Java technologies
- 16. Constructors ï No Argument Constructors: No-argument constructor creates an empty String. Rarely used. Example: String empty=new String(); ï Copy Constructors: Copy constructor creates a copy of an existing String . Also rarely used. Example: String word = new String(âJavaâ); String word2 = new String(word); ï Other Constructors: Most other constructors take an array as a parameter to create a String. Example: char[] letters = {âJâ, âaâ, âvâ, âaâ}; String word = new String(letters);//âJavaâ
- 17. String Methods ï substring(int begin): ï Returns substring from begin index to end of the String. ï Example: String s=ânacreâ; System.out.println(s.substring(2));//cre ï equals(): ï To perform content comparision where case is important. Example: String s=âjavaâ; System.out.println(s.equals(âjavaâ));//true ï concat(): Adding two strings we use this method Example: String s=ânacreâ; s= s.concat(âsoftwareâ); System.out.println(s);// nacresoftware
- 18. length() , charAt() int length(); char charAt(i); ïŪ Returns the number of characters in the string ïŪ Returns the char at position i. Character positions in strings are numbered starting from 0 â just like arrays. Returns: âProblem".length(); 7 âWindowâ. charAt (2); ân'
- 19. New features of String ï In 1.5 Version: ï Wrapper classes are introduced. Example. String s = Integer.toString(10); System.out.println(s);//10 ï In 1.7 Version: ï Java 7 extended the capability of switch case to use Strings also, earlier java versions doesnât support this. If you are implementing conditional flow for Strings, you can use if-else conditions and you can use switch case if you are using Java 7 or higher versions.
- 21. ï Limitation of String in Java ? ï What is mutable string? A string that can be modified or changed is known as mutable string. StringBuffer and StringBuilder classes are used for creating mutable string. ï Differences between String and StringBuffer in java? Main difference between String and StringBuffer is String is immutable while StringBuffer is mutable
- 22. Relations between StringBuffer, StringBuilder and StringToknizer: All These classes are final and subclass of Serializable.
- 23. StringBuffer ï StringBuffer is a synchronized and allows us to mutate the string. ï StringBuffer has many utility methods to manipulate the string. ï This is more useful when using in a multithreaded environment. ï Always modified in same memory location.
- 24. ï StringBuffer Constructor: ï 1. public StringBuffer() ï 2. public StringBuffer(int capacity) ï 3. public StringBuffer(String s) ï 4. public StringBuffer(CharSequence cs)
- 25. Method Use In StringBuffer ï 1. Append ï 2. Insert ï 3.Delete ï 4.Reverse ï 5.Replacing Character at given index
- 26. StringBuilder ï StringBuilder is the same as the StringBuffer class ï The StringBuilder class is not synchronized and hence in a single threaded environment, the overhead is less than using a StringBuffer.
- 27. StringTokenizer ï A token is a portion of a string that is separated from another portion of that string by one or more chosen characters (called delimiters). ï The StringTokenizer class contained in the java.util package can be used to break a string into separate tokens. This is particularly useful in those situations in which we want to read and process one token at a time; the BufferedReader class does not have a method to read one token at a time
- 28. Thank youâĶ













![Constructors
ï No Argument Constructors:
No-argument constructor creates an empty String. Rarely used.
Example: String empty=new String();
ï Copy Constructors:
Copy constructor creates a copy of an existing String . Also rarely used.
Example: String word = new String(âJavaâ);
String word2 = new String(word);
ï Other Constructors:
Most other constructors take an array as a parameter to create a String.
Example: char[] letters = {âJâ, âaâ, âvâ, âaâ};
String word = new String(letters);//âJavaâ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/string-141110045404-conversion-gate01/85/Java-String-16-320.jpg)











