String matching algorithms
- 1. Presented By:- Ashika Pokiya(12TI083) Guide by:- Nehal Patel STRING MATCHING ALGORITHMS
- 2. WHAT IS STRING MATCHING ŌĆó In computer science, string searching algorithms, sometimes called string matching algorithms, that try to find a place where one or several string (also called pattern) are found within a larger string or text.
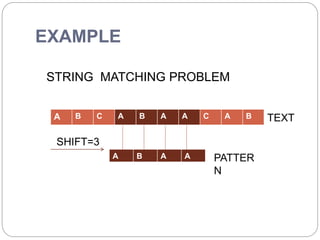
- 3. EXAMPLE STRING MATCHING PROBLEM A B C A B A A C A B A B A A TEXT PATTER N SHIFT=3
- 4. STRING MATCHING ALGORITHMS There are many types of String Matching Algorithms like:- 1) The Naive string-matching algorithm 2) The Rabin-Krap algorithm 3) String matching with finite automata 4) The Knuth-Morris-Pratt algorithm But we discuss about 2 types of string matching algorithms. 1) The Naive string-matching algorithm 2) The Rabin-Krap algorithm
- 5. THE NAIVE ALGORITHM The naive algorithm finds all valid shifts using a loop that checks the condition P[1ŌĆ”.m]=T[s+1ŌĆ”. s+m] for each of the n- m+1 possible values of s.(P=pattern , T=text/string , s=shift) NAIVE-STRING-MATCHER(T,P) 1) n = T.length 2) m = P.length 3) for s=0 to n-m 4) if P[1ŌĆ”m]==T[s+1ŌĆ”.s+m] 5) printfŌĆØ Pattern occurs with shift ŌĆØ s
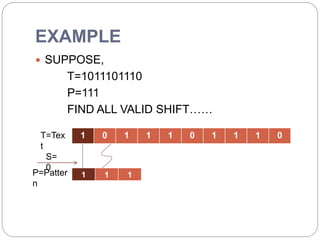
- 6. EXAMPLE ’éŚ SUPPOSE, T=1011101110 P=111 FIND ALL VALID SHIFTŌĆ”ŌĆ” 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0T=Tex t 1 1 1P=Patter n S= 0
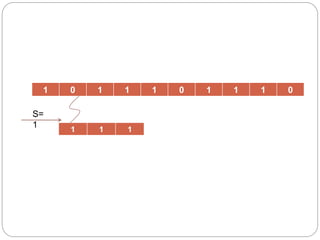
- 7. 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 S= 1
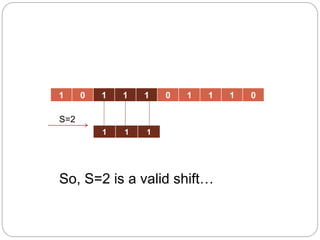
- 8. 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 S=2 So, S=2 is a valid shiftŌĆ”
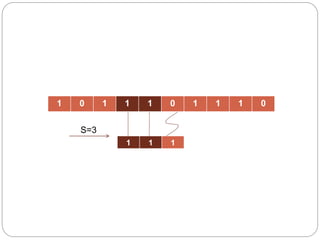
- 9. 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 S=3
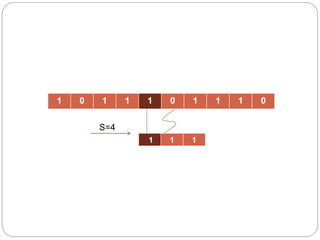
- 10. 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 S=4
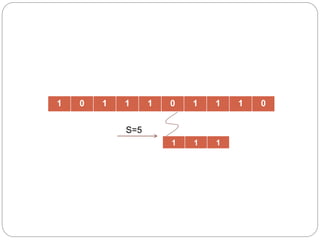
- 11. 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 S=5
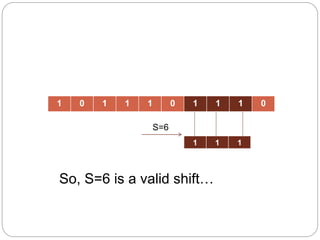
- 12. 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 S=6 So, S=6 is a valid shiftŌĆ”
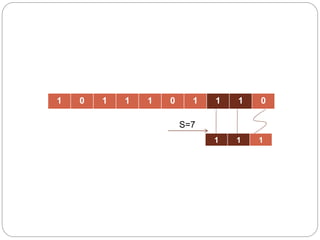
- 13. 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 S=7
- 14. THE RABIN-KARP ALGORITHM ’éŚ Rabin and Karp proposed a string matching algorithm that performs well in practice and that also generalizes to other algorithms for related problems, such as two-dimentional pattern matching.
- 15. ALGORITHM RABIN-KARP-MATCHER(T,P,d,q) 1) n = T.length 2) m = P.length 3) h = d^(m-1) mod q 4) p = 0 5) t = 0 6) for i =1 to m //pre-processing 7) p = (dp + P[i]) mod q 8) t = (d t + T[i]) mod q 9) for s = 0 to n ŌĆō m //matching 10) if p == t 11) if P[1ŌĆ”m] == T[s+1ŌĆ”. s+m] 12) printf ŌĆ£ Pattern occurs with shift ŌĆØ s 13) if s< n-m 14) t+1 = (d(t- T[s+1]h)+ T[s+m+1]) mod q
- 16. EXAMPLE Pattern P=26, how many spurious hits does the Rabin Karp matcher in the text T=3 1 4 1 5 9 2 6 5 3 5ŌĆ” ŌĆó T = 3 1 4 1 5 9 2 6 5 3 5 P = 2 6 Here T.length=11 so Q=11 and P mod Q = 26 mod 11 = 4 Now find the exact match of P mod QŌĆ”
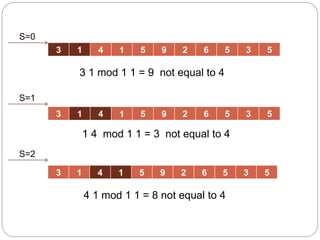
- 17. 3 1 4 1 5 9 2 6 5 3 5 3 1 4 1 5 9 2 6 5 3 5 3 1 mod 1 1 = 9 not equal to 4 1 4 mod 1 1 = 3 not equal to 4 4 1 mod 1 1 = 8 not equal to 4 3 1 4 1 5 9 2 6 5 3 5 S=1 S=0 S=2
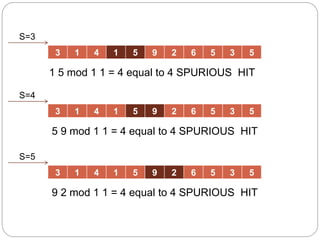
- 18. 3 1 4 1 5 9 2 6 5 3 5 3 1 4 1 5 9 2 6 5 3 5 3 1 4 1 5 9 2 6 5 3 5 1 5 mod 1 1 = 4 equal to 4 SPURIOUS HIT 5 9 mod 1 1 = 4 equal to 4 SPURIOUS HIT 9 2 mod 1 1 = 4 equal to 4 SPURIOUS HIT S=3 S=4 S=5
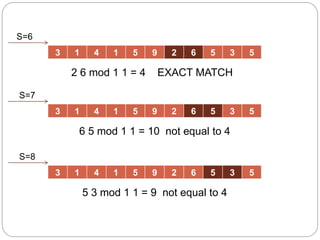
- 19. 3 1 4 1 5 9 2 6 5 3 5 3 1 4 1 5 9 2 6 5 3 5 3 1 4 1 5 9 2 6 5 3 5 2 6 mod 1 1 = 4 EXACT MATCH 6 5 mod 1 1 = 10 not equal to 4 5 3 mod 1 1 = 9 not equal to 4 S=7 S=6 S=8
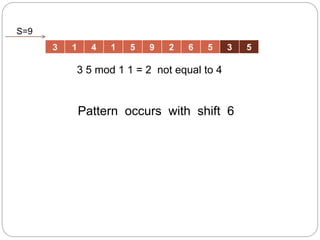
- 20. 3 1 4 1 5 9 2 6 5 3 5 3 5 mod 1 1 = 2 not equal to 4 S=9 Pattern occurs with shift 6
- 21. COMPARISSION ’éŚ The Naive String Matching algorithm slides the pattern one by one. After each slide, it one by one checks characters at the current shift and if all characters match then prints the match. ’éŚ Like the Naive Algorithm, Rabin-Karp algorithm also slides the pattern one by one. But unlike the Naive algorithm, Rabin Karp algorithm matches the hash value of the pattern with the hash value of current substring of text, and if the hash values match then only it starts matching individual characters.
- 22. THANK YOUŌĆ”
Editor's Notes
- #19: Spurious hit is when we have a match but it isnŌĆÖt an actual match to the pattern. When this happen, further testing is done.


![THE NAIVE ALGORITHM
The naive algorithm finds all valid shifts using a loop
that checks
the condition P[1ŌĆ”.m]=T[s+1ŌĆ”. s+m] for each of the n-
m+1
possible values of s.(P=pattern , T=text/string , s=shift)
NAIVE-STRING-MATCHER(T,P)
1) n = T.length
2) m = P.length
3) for s=0 to n-m
4) if P[1ŌĆ”m]==T[s+1ŌĆ”.s+m]
5) printfŌĆØ Pattern occurs with
shift ŌĆØ s](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stringmatchingalgorithms-150909124830-lva1-app6891/85/String-matching-algorithms-5-320.jpg)

![ALGORITHM
RABIN-KARP-MATCHER(T,P,d,q)
1) n = T.length
2) m = P.length
3) h = d^(m-1) mod q
4) p = 0
5) t = 0
6) for i =1 to m //pre-processing
7) p = (dp + P[i]) mod q
8) t = (d t + T[i]) mod q
9) for s = 0 to n ŌĆō m //matching
10) if p == t
11) if P[1ŌĆ”m] == T[s+1ŌĆ”. s+m]
12) printf ŌĆ£ Pattern occurs with shift ŌĆØ s
13) if s< n-m
14) t+1 = (d(t- T[s+1]h)+ T[s+m+1]) mod q](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stringmatchingalgorithms-150909124830-lva1-app6891/85/String-matching-algorithms-15-320.jpg)