Structural grammar iii
- 1. University of Carabobo Education School Modern Language Department Subject: Pedagogical Grammar Professor: Evisol Farías Structural Grammar Integrantes: Martínez,Yosleni Ortega, Daniel Sánchez, Anais
- 2. Definition Main Main objectives and Conception of representatives Characteristics Language Basic principles Structural and concepts Grammar Contributions and Limitations Grammatical Organization Analysis of the sentence
- 3. Definition It is an approach to the written and the spoken language that focuses on the construction of sentences. It deals with the structure of the sentence and not necessarily with the words that are going to be used.
- 4. Main Representatives Saussure Bloomfield Fries Pike
- 5. Main objectives To analyze. Structural To describe. To limit. Grammar To describe.
- 6. Characteristics Descriptive Spoken language Scientific All forms of expression (language) are studied Inductive Grammar is described in its own terms Synchronic
- 7. Conception of Language LANGUE (SOCIAL) PAROLE (INDIVIDUAL) Essential Accessory Social product Individual product Homogeneous Heterogeneous Abstract Concrete Established Momentary
- 8. Basic principles and main concepts Prior Human speech Written and spoken Descriptiveness vs. Prescriptiveness Main concepts Saussure´s dichotomies Langue Parole Signified Signifier Diachronic Synchronic Description Prescription
- 9. Contributions Expressions Language Differentiation System Dichotomies Description Instrument of communication Analysis of the phonological system
- 10. The main limitations for this grammatical Limitations category are the following: Diachronic is not considered The language functions are not explained Semantic is not considered part of grammar
- 11. Grammatical Consist on dividing the language in the smallest units Organization of information following three levels of analysis: Phonology: the phones or speech sounds of the language Morphology: Classes of words and Inflectional forms Syntax: Relationships between the components of a sentence
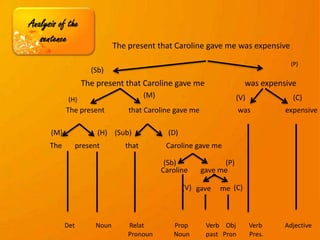
- 12. Analysis of the These are the common abbreviations for the sentence sentence analysis (Sb)= Subject (P) predicate (H) Head (M)= Modifier (V)= Verb (C)= complement (Sub)= subordinator (D) dependent unit
- 13. Analysis of the sentence The present that Caroline gave me was expensive (P) (Sb) The present that Caroline gave me was expensive (M) (V) (C) (H) The present that Caroline gave me was expensive (M) (H) (Sub) (D) The present that Caroline gave me (Sb) (P) Caroline gave me (V) gave me (C) Det Noun Relat Prop Verb Obj Verb Adjective Pronoun Noun past Pron Pres.
- 14. References Structural grammar. (n.d.) Structural grammar. [Online article]. Retrieved June 8, 2011, from the World Wide Web: http://jilaniwarsi.tripod.com/sg.pdf What is structural grammar? (2003). What is structural grammar? [Online article]. Retrieved June 10, 2011, from the World Wide Web: http://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-structural-grammar.htm












![References
Structural grammar. (n.d.) Structural grammar. [Online article].
Retrieved June 8, 2011, from the World Wide Web:
http://jilaniwarsi.tripod.com/sg.pdf
What is structural grammar? (2003). What is structural grammar?
[Online article]. Retrieved June 10, 2011, from the World Wide
Web: http://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-structural-grammar.htm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structuralgrammariii-120612183952-phpapp02/85/Structural-grammar-iii-14-320.jpg)