Structure of a neuron
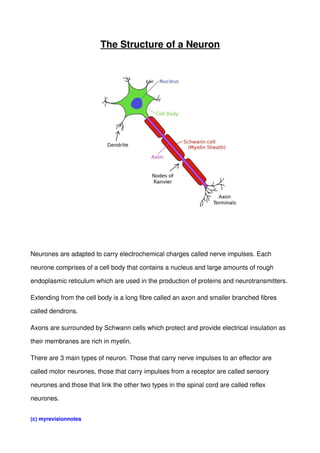
- 1. The Structure of a Neuron Neurones are adapted to carry electrochemical charges called nerve impulses. Each neurone comprises of a cell body that contains a nucleus and large amounts of rough endoplasmic reticulum which are used in the production of proteins and neurotransmitters. Extending from the cell body is a long fibre called an axon and smaller branched fibres called dendrons. Axons are surrounded by Schwann cells which protect and provide electrical insulation as their membranes are rich in myelin. There are 3 main types of neuron. Those that carry nerve impulses to an effector are called motor neurones, those that carry impulses from a receptor are called sensory neurones and those that link the other two types in the spinal cord are called reflex neurones. (c) myrevisionnotes