Study of circuit breakers
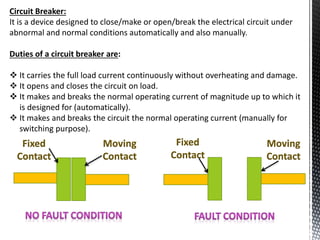
- 2. Circuit Breaker: It is a device designed to close/make or open/break the electrical circuit under abnormal and normal conditions automatically and also manually. Duties of a circuit breaker are: ? It carries the full load current continuously without overheating and damage. ? It opens and closes the circuit on load. ? It makes and breaks the normal operating current of magnitude up to which it is designed for (automatically). ? It makes and breaks the circuit the normal operating current (manually for switching purpose). Moving Contact Fixed Contact Moving Contact Fixed Contact
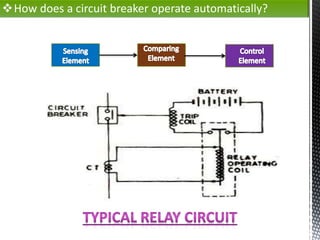
- 3. ?How does a circuit breaker operate automatically?
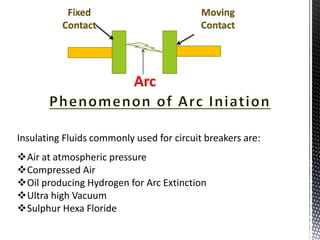
- 4. Fixed Contact Moving Contact Arc Insulating Fluids commonly used for circuit breakers are: ?Air at atmospheric pressure ?Compressed Air ?Oil producing Hydrogen for Arc Extinction ?Ultra high Vacuum ?Sulphur Hexa Floride
- 5. Arc Resistance depends on factors like: ?Degree of Ionization ?Length of the arc ?Cross section of arc Methods of Arc Quenching: 1) High Resistance Method: Arc resistance is made to increase with time so that current is reduced to a value insufficient to maintain the arc. 2) Low Resistance Method: Dielectric Medium between the contacts is built up more rapidly so that the arc fails to restrike and the current will be interrupted.
- 6. High Resistance Method: ? Lengthening of arc ? Reducing the cross section of the arc ? Splitting the arc Low resistance Method: ? Lengthening the gap ? High pressure in the vicinity of the arc ? Cooling the dielectric medium ? Blast Effect Significant Terms associated with Circuit Breakers: ? Arc Voltage ? Restriking Voltage ? Recovery Voltage ? Breaking Capacity ? Making Capacity ? Short Time Capacity
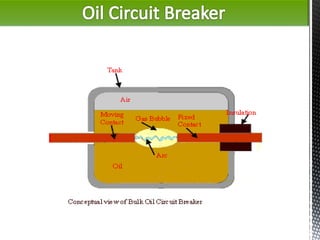
- 8. Pros of Oil Circuit Breakers: ?It absorbs the arc energy to decompose the oil into gasses which have excellent cooling properties. ?It acts as an insulator and permits smaller clearance between live conductors and earthed components. Cons of Oil Circuit Breakers: ?Oil is inflammable there is a risk of fire. ?Oil may form an explosive mixture when it comes in contact with air. ?Arcing products like carbon remain in the oil and its quality deteriorates with successive operations. This requires periodic checking and replacement of oil. Rating: Bulk Oil CB= Up to 12 KV Minimum Oil CB= 13.6 KV to 146 KV
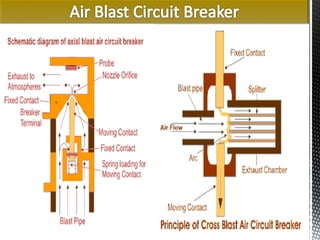
- 10. Pros of Air Blast Circuit Breakers: ?Risk of fire is totally eliminated. ?The size of the circuit breaker is reduced. ?High speed operation and suitable for frequent operation. ?Negligible maintenance. Cons of Air Blast Circuit Breakers: ?Air insulation is lesser than other medium like as oil etc. ?Considerable Maintenance required for the compressor plant which supplies air blast. Rating: 110 KV & above
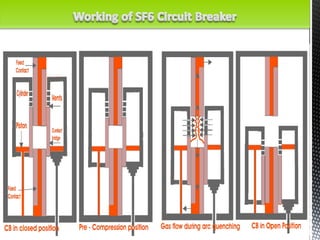
- 13. Pros of SF6 Circuit Breakers: ?Very Sort Arcing Time ?Can Interrupt very large currents due to high dielectric strength. ?Noiseless Operation due to its closed/sealed gas circuit. ?No problem of moisture. ?No risk of fire as SF6 is inflammable. ?Low Maintenance Cost. Cons of SF6 Circuit Breakers: ?SF6 Circuit Breakers are costly due to high cost of SF6. ?Since SF6 gas has to be reconditioned after every operation of the breaker additional equipment is needed for this purpose. Rating: 3.6 KV to 760 KV
- 15. Advantages of VCB: ?Compact & reliable. ?Less Maintenance and quite in operation. ?Withstand Lightning Surges. ?Small Power for control mechanism. ?Perfect breaking of any heavy fault current. ?No risk of Fire. Routine tests conducted on VCB: ? Voltage Test with different frequencies. ? High Voltage Test ? Timing Test ? Penetration Test ? Insulation Test
- 16. Conclusion: Therefore by using appropriate circuit breaker for appropriate operating voltages we can provide protection for busbar and electrical equipments like Power transformers, generators, C.T.ˇŻs , P.T.ˇŻs, wave traps etc. from different faults that occur in power system.