Subcool 2
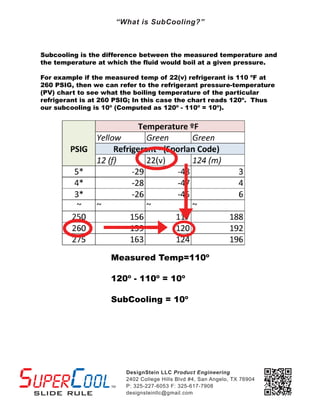
- 1. DesignStein LLC Product Engineering 2402 College Hills Blvd #4, San Angelo, TX 76904 P: 325-227-6053 F: 325-617-7908 designsteinllc@gmail.com Subcooling is the difference between the measured temperature and the temperature at which the fluid would boil at a given pressure. For example if the measured temp of 22(v) refrigerant is 110 ┬║F at 260 PSIG, then we can refer to the refrigerant pressure-temperature (PV) chart to see what the boiling temperature of the particular refrigerant is at 260 PSIG; In this case the chart reads 120┬║. Thus our subcooling is 10┬║ (Computed as 120┬║ - 110┬║ = 10┬║). Measured Temp=110┬║ 120┬║ - 110┬║ = 10┬║ SubCooling = 10┬║ ŌĆ£What is SubCooling?ŌĆØ