1 of 1
Ad
Recommended
Sugar mill
Sugar millsometech
?
The document describes the sugar manufacturing process from planting sugarcane to packing final sugar products. It details each stage including planting, harvesting, processing, purification, crystallization, and packing. Various machines and methods are utilized throughout the process to ensure efficient extraction and refinement of sugar from raw cane.Sugar mill
Sugar millNikhil Kumar
?
This document discusses sugar mills and the sugar production process. It provides details on:
1) Global sugar production is led by Brazil, India, and the EU, who control over 45% of the market. India is the largest producer and consumer.
2) Sugar is produced through a chemical reaction between glucose and fructose that forms sucrose. The raw materials used are sugarcane and sugar beets.
3) Byproducts from sugar mills include bagasse, press mud, and wastewater which can be reused or treated through biological processes before disposal. Proper management of wastes is important to minimize environmental impact.Sugar manufacturing process
Sugar manufacturing processNajja Tariq
?
This document provides an overview of the sugarcane processing and sugar production process. It details each step from harvesting sugarcane to processing it in sugar mills to extract the juice, and then refining the juice to produce raw and refined sugar. The key steps involve crushing the sugarcane, extracting and clarifying the juice, evaporating and crystallizing it to produce raw sugar, and then further processing the raw sugar through affination, melting, purification and recrystallization to produce refined white sugar. Factors like temperature, moisture, light and compression are important for proper storage of sugar.Sugar industry Presentaion
Sugar industry Presentaionmalikumar242
?
The document provides information about the production process of sugar from sugarcane. It discusses that sugarcane is the primary raw material and needs to be processed immediately after harvesting. The processing involves crushing the sugarcane to extract juice, clarifying and concentrating the juice, crystallizing the sugar, centrifuging to separate molasses from the crystals, and finally drying the crystals before packaging. The overall production process aims to extract sugar from sugarcane in its pure form through various purification and separation steps.Sign up.to discovery morning (apr-2015)
Sign up.to discovery morning (apr-2015)Sign-Up.to
?
This document provides an overview of a discovery morning session on permission marketing. The objectives are to explore 12 key competence areas related to permission marketing, provide a self-assessment, and outline practical steps for improvement. The session will cover topics such as challenges in digital marketing, the importance of permission in marketing, best practices for data collection and management, design considerations for email marketing, and maximizing email delivery. Attendees will assess their current marketing strategies in several areas and identify opportunities for enhancement.LinkedIn ∫›∫›fl£Share: Knowledge, Well-Presented
LinkedIn ∫›∫›fl£Share: Knowledge, Well-Presented∫›∫›fl£Share
?
70 million professionals use LinkedIn ∫›∫›fl£Share to learn about any topic quickly and stand out.◊‘¬…–Õ»À≤ƒ§¨”˝§ƒ1on1•fl©`•∆•£•Û•∞§ŒΩÃø∆ï¯ °´¿€”ã2ÕÚ»À§Œ•fi•Õ•∏•„©`§À1on1—––fi§Úåg ©§∑§∆§≠§øåüÈTº“§¨Ω‚’h
◊‘¬…–Õ»À≤ƒ§¨”˝§ƒ1on1•fl©`•∆•£•Û•∞§ŒΩÃø∆ï¯ °´¿€”ã2ÕÚ»À§Œ•fi•Õ•∏•„©`§À1on1—––fi§Úåg ©§∑§∆§≠§øåüÈTº“§¨Ω‚’hsevenfoldbliss
?
≤øœ¬§Œ•’•ß©`•∫(◊¥ëB?∂ŒÎA)§À∫œ§Ô§ª§ø1on1•fl©`•∆•£•Û•∞§Ú––§ §®§∆§§§fi§π§´£ø
”–¡œºâ§Œ«ÈàÛ§Ú»´24•⁄©`•∏§À∂…§Í§™Ωϧ±§§§ø§∑§fi§π£°°æ—ß…˙•”•∏•≥•Ûµ⁄“ªªÿ≥ææ±≤‘æ±∏È∞ø∞ø∞≠±ı∑°≥ß3Œª ‹…Õ◊˜∆∑°øÕ∂◊ •Ì©`•Î•◊•Ï•§
°æ—ß…˙•”•∏•≥•Ûµ⁄“ªªÿ≥ææ±≤‘æ±∏È∞ø∞ø∞≠±ı∑°≥ß3Œª ‹…Õ◊˜∆∑°øÕ∂◊ •Ì©`•Î•◊•Ï•§info182988
?
µ⁄“ªªÿ≥ææ±≤‘æ±∏È∞ø∞ø∞≠±ı∑°≥ߧŒ3Œª§Àª‘§§§ø◊˜∆∑§«§π°£°æ—ß…˙•”•∏•≥•Ûµ⁄“ªªÿ≥ææ±≤‘æ±∏È∞ø∞ø∞≠±ı∑°≥ß1Œª ‹…Õ◊˜∆∑°ø•fi•§•≠•„•Í•¢•∏•„©`•À©`
°æ—ß…˙•”•∏•≥•Ûµ⁄“ªªÿ≥ææ±≤‘æ±∏È∞ø∞ø∞≠±ı∑°≥ß1Œª ‹…Õ◊˜∆∑°ø•fi•§•≠•„•Í•¢•∏•„©`•À©`info182988
?
µ⁄“ªªÿ≥ææ±≤‘æ±∏È∞ø∞ø∞≠±ı∑°≥ߧŒ1Œª§Àª‘§§§ø◊˜∆∑§«§π°£•÷•Ï•§•Û•∫•≥•Û•µ•Î•∆•£•Û•∞§Œ…‹ΩÈ◊ ¡œ
•÷•Ï•§•Û•∫•≥•Û•µ•Î•∆•£•Û•∞§Œ…‹ΩÈ◊ ¡œfurusakitomoaki
?
•÷•Ï•§•Û•∫•≥•Û•µ•Î•∆•£•Û•∞÷Í Ωª·…Á§Œª·…ÁΩBΩÈŸY¡œ§«§π°£
https://www.brains-consulting.co.jp/
More Related Content
Viewers also liked (6)
Sugar mill
Sugar millsometech
?
The document describes the sugar manufacturing process from planting sugarcane to packing final sugar products. It details each stage including planting, harvesting, processing, purification, crystallization, and packing. Various machines and methods are utilized throughout the process to ensure efficient extraction and refinement of sugar from raw cane.Sugar mill
Sugar millNikhil Kumar
?
This document discusses sugar mills and the sugar production process. It provides details on:
1) Global sugar production is led by Brazil, India, and the EU, who control over 45% of the market. India is the largest producer and consumer.
2) Sugar is produced through a chemical reaction between glucose and fructose that forms sucrose. The raw materials used are sugarcane and sugar beets.
3) Byproducts from sugar mills include bagasse, press mud, and wastewater which can be reused or treated through biological processes before disposal. Proper management of wastes is important to minimize environmental impact.Sugar manufacturing process
Sugar manufacturing processNajja Tariq
?
This document provides an overview of the sugarcane processing and sugar production process. It details each step from harvesting sugarcane to processing it in sugar mills to extract the juice, and then refining the juice to produce raw and refined sugar. The key steps involve crushing the sugarcane, extracting and clarifying the juice, evaporating and crystallizing it to produce raw sugar, and then further processing the raw sugar through affination, melting, purification and recrystallization to produce refined white sugar. Factors like temperature, moisture, light and compression are important for proper storage of sugar.Sugar industry Presentaion
Sugar industry Presentaionmalikumar242
?
The document provides information about the production process of sugar from sugarcane. It discusses that sugarcane is the primary raw material and needs to be processed immediately after harvesting. The processing involves crushing the sugarcane to extract juice, clarifying and concentrating the juice, crystallizing the sugar, centrifuging to separate molasses from the crystals, and finally drying the crystals before packaging. The overall production process aims to extract sugar from sugarcane in its pure form through various purification and separation steps.Sign up.to discovery morning (apr-2015)
Sign up.to discovery morning (apr-2015)Sign-Up.to
?
This document provides an overview of a discovery morning session on permission marketing. The objectives are to explore 12 key competence areas related to permission marketing, provide a self-assessment, and outline practical steps for improvement. The session will cover topics such as challenges in digital marketing, the importance of permission in marketing, best practices for data collection and management, design considerations for email marketing, and maximizing email delivery. Attendees will assess their current marketing strategies in several areas and identify opportunities for enhancement.LinkedIn ∫›∫›fl£Share: Knowledge, Well-Presented
LinkedIn ∫›∫›fl£Share: Knowledge, Well-Presented∫›∫›fl£Share
?
70 million professionals use LinkedIn ∫›∫›fl£Share to learn about any topic quickly and stand out.Recently uploaded (8)
◊‘¬…–Õ»À≤ƒ§¨”˝§ƒ1on1•fl©`•∆•£•Û•∞§ŒΩÃø∆ï¯ °´¿€”ã2ÕÚ»À§Œ•fi•Õ•∏•„©`§À1on1—––fi§Úåg ©§∑§∆§≠§øåüÈTº“§¨Ω‚’h
◊‘¬…–Õ»À≤ƒ§¨”˝§ƒ1on1•fl©`•∆•£•Û•∞§ŒΩÃø∆ï¯ °´¿€”ã2ÕÚ»À§Œ•fi•Õ•∏•„©`§À1on1—––fi§Úåg ©§∑§∆§≠§øåüÈTº“§¨Ω‚’hsevenfoldbliss
?
≤øœ¬§Œ•’•ß©`•∫(◊¥ëB?∂ŒÎA)§À∫œ§Ô§ª§ø1on1•fl©`•∆•£•Û•∞§Ú––§ §®§∆§§§fi§π§´£ø
”–¡œºâ§Œ«ÈàÛ§Ú»´24•⁄©`•∏§À∂…§Í§™Ωϧ±§§§ø§∑§fi§π£°°æ—ß…˙•”•∏•≥•Ûµ⁄“ªªÿ≥ææ±≤‘æ±∏È∞ø∞ø∞≠±ı∑°≥ß3Œª ‹…Õ◊˜∆∑°øÕ∂◊ •Ì©`•Î•◊•Ï•§
°æ—ß…˙•”•∏•≥•Ûµ⁄“ªªÿ≥ææ±≤‘æ±∏È∞ø∞ø∞≠±ı∑°≥ß3Œª ‹…Õ◊˜∆∑°øÕ∂◊ •Ì©`•Î•◊•Ï•§info182988
?
µ⁄“ªªÿ≥ææ±≤‘æ±∏È∞ø∞ø∞≠±ı∑°≥ߧŒ3Œª§Àª‘§§§ø◊˜∆∑§«§π°£°æ—ß…˙•”•∏•≥•Ûµ⁄“ªªÿ≥ææ±≤‘æ±∏È∞ø∞ø∞≠±ı∑°≥ß1Œª ‹…Õ◊˜∆∑°ø•fi•§•≠•„•Í•¢•∏•„©`•À©`
°æ—ß…˙•”•∏•≥•Ûµ⁄“ªªÿ≥ææ±≤‘æ±∏È∞ø∞ø∞≠±ı∑°≥ß1Œª ‹…Õ◊˜∆∑°ø•fi•§•≠•„•Í•¢•∏•„©`•À©`info182988
?
µ⁄“ªªÿ≥ææ±≤‘æ±∏È∞ø∞ø∞≠±ı∑°≥ߧŒ1Œª§Àª‘§§§ø◊˜∆∑§«§π°£•÷•Ï•§•Û•∫•≥•Û•µ•Î•∆•£•Û•∞§Œ…‹ΩÈ◊ ¡œ
•÷•Ï•§•Û•∫•≥•Û•µ•Î•∆•£•Û•∞§Œ…‹ΩÈ◊ ¡œfurusakitomoaki
?
•÷•Ï•§•Û•∫•≥•Û•µ•Î•∆•£•Û•∞÷Í Ωª·…Á§Œª·…ÁΩBΩÈŸY¡œ§«§π°£
https://www.brains-consulting.co.jp/
◊‘¬…–Õ»À≤ƒ§¨”˝§ƒ1on1•fl©`•∆•£•Û•∞§ŒΩÃø∆ï¯ °´¿€”ã2ÕÚ»À§Œ•fi•Õ•∏•„©`§À1on1—––fi§Úåg ©§∑§∆§≠§øåüÈTº“§¨Ω‚’h
◊‘¬…–Õ»À≤ƒ§¨”˝§ƒ1on1•fl©`•∆•£•Û•∞§ŒΩÃø∆ï¯ °´¿€”ã2ÕÚ»À§Œ•fi•Õ•∏•„©`§À1on1—––fi§Úåg ©§∑§∆§≠§øåüÈTº“§¨Ω‚’hsevenfoldbliss
?
Ad
sugar mill
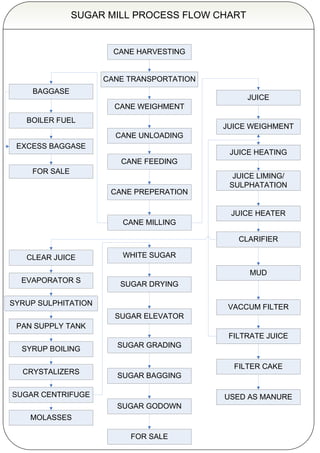
- 1. SUGAR MILL PROCESS FLOW CHART CANE HARVESTING CANE TRANSPORTATION BAGGASE JUICE CANE WEIGHMENT BOILER FUEL JUICE WEIGHMENT CANE UNLOADING EXCESS BAGGASE JUICE HEATING CANE FEEDING FOR SALE JUICE LIMING/ SULPHATATION CANE PREPERATION JUICE HEATER CANE MILLING CLARIFIER CLEAR JUICE WHITE SUGAR MUD EVAPORATOR S SUGAR DRYING SYRUP SULPHITATION VACCUM FILTER SUGAR ELEVATOR PAN SUPPLY TANK FILTRATE JUICE SUGAR GRADING SYRUP BOILING FILTER CAKE CRYSTALIZERS SUGAR BAGGING SUGAR CENTRIFUGE USED AS MANURE SUGAR GODOWN MOLASSES FOR SALE