Sunscreen
- 2. Introduction Ancient Egyptians used extracts of rice, jasmine, and lupine plants. Again, these ingredients offered low levels of sun protection but were proven to be very beneficial to the skin and are still used in skin care products today. Sunscreen, also known as sunblock, is a lotion, spray, gel, foam (such as an expanded foam lotion or whipped lotion), stick or other topical product that absorbs or reflects some of the sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation and thus helps protect against sunburn.
- 3. Sunrays UVA (Longwave Radiation) (infrared rays) âĒ Range 320-400 nm âĒ Erythrogenic activity is weak. âĒ penetrates dermis âĒ Responsible for development of slow natural tan âĒ Most drug-induced photosensitivity rxn occurs
- 4. UVB (Middlewave Radiation)(visible rays) âĒ Range 290-320 nm âĒ Erythrogenic activity is the highest âĒ Produces new pigment formation, sunburn, âĒ Vit D synthesis âĒ Responsible for inducing skin cancer UVB rays will usually burn the superficial layers of your skin. It plays a key role in the development of skin cancer.
- 5. UVC (Shortwave or Germicidal Radiation) (ultraviolet rays) âĒ Range 100-290 nm. âĒ Does not reach the surface of the earth. âĒ Is emitted from artificial ultraviolet source
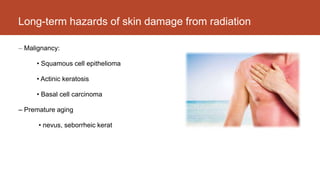
- 6. Long-term hazards of skin damage from radiation: â Malignancy: âĒ Squamous cell epithelioma âĒ Actinic keratosis âĒ Basal cell carcinoma â Premature aging âĒ nevus, seborrheic kerat
- 7. Sunscreen Classification Physical â Opaque formulations containing: âĒ titanium dioxide âĒ talc, kaolin âĒ zinc oxide âĒ ferric chloride âĒ icthyol, red petrolatum â Mechanism: scatters or reflects UV radiation due to large particle size
- 8. Chemical â Formulations containing one or more: âĒ PABA, PABA esters âĒ benzophenones âĒ cinnamates âĒ salicylates âĒ digalloyl trioleate âĒ anthranilates â Mechanism: absorbs UV radiation
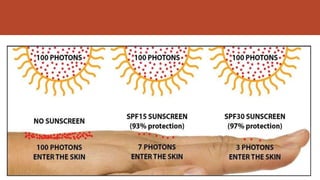
- 9. SPF (sun protective factor) SPF, or Sun Protection Factor,is a measure of how well a sunscreen will protect skin from UVB rays, the kind of radiation that causes sunburn, damages skin, and can contribute to skin cancer. Sun Protection Factor (SPF) =MED of Photoprotected Skin/ MED of Unprotected Skin MED is minimum dose of radiation which produces erythema â SPFs are determined indoors using xenon lamps which approximate the spectral quality of UV radiation âĒSPF 15 blocks 93% of UVB rays âĒSPF 30 blocks 97% of UVB rays âĒSPF 50 blocks 98% of UVB rays
- 11. Category Skin Type SPF 1. Always burns, never tans 15 > 2. Burns easily 15 3. Burns moderately, (avg caucasian) 10-15 4. Burns minimally, tans well (olive skinâ) 6-10 5. Rarely burns, tans profusely (brown skin) 4-6 6. Never burns (black skin) none
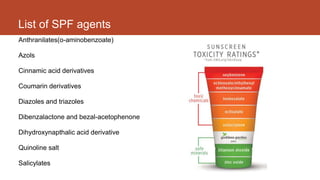
- 12. List of SPF agents Anthranilates(o-aminobenzoate) Azols Cinnamic acid derivatives Coumarin derivatives Diazoles and triazoles Dibenzalactone and bezal-acetophenone Dihydroxynapthalic acid derivative Quinoline salt Salicylates
- 13. Formula SUNTAN LOTION Glceryl p-aminobenzoate :-3.0% Propylene glycol ricinolate :-8.0% Glycerin :-10.0% Alcohol :-60.0% Perfume and color :- q.s (ability to absorb UV raysâthe ones that cause sunburn) ( It imparts emolliency and softening characteristics to the skin) (Freezing action)
- 14. Ideal characteristics of sunscreen 1. It should be resistan to water and perspiration.. 2. Itshould allow full transmission of radiation in the range of 300 to 400 NM for tanning effect 3. It should be non volatile. 4. It should have suitable solubility characteristic in suitable vehicle. 5. It should be stable to heat light and perspiration. 6. It should be non toxic, non irritant and non sensitizing. 7. It should be capable of retaining its son scaling property for several hours. 8. It should not stain on body cloth. 9. It should be neutral.
- 16. Thank you ð