Surgical One Page Flyer | ChloraPrep UK Infection Prevention & Control
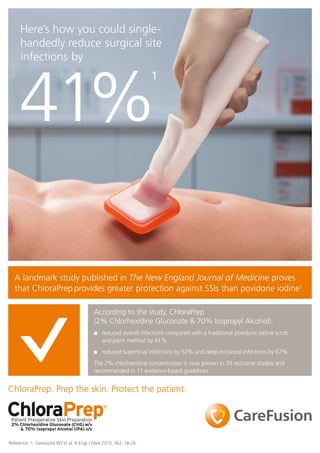
- 1. Here’s how you could single- handedly reduce surgical site infections by 41% 1 A landmark study published in The New England Journal of Medicine proves that ChloraPrep provides greater protection against SSIs than povidone iodine1 According to the study, ChloraPrep (2% Chlorhexidine Gluconate & 70% Isopropyl Alcohol): reduced overall infections compared with a traditional povidone iodine scrub and paint method by 41% reduced superficial infections by 52% and deep incisional infections by 67% The 2% chlorhexidine concentration is now proven in 39 outcome studies and recommended in 11 evidence-based guidelines ChloraPrep. Prep the skin. Protect the patient. Reference: 1. Darouiche RO et al. N Engl J Med 2010; 362: 18-26.
- 2. Range of surgical applicators Licensed, sterile, single use, ANTT™, latex free applicators available in the UK Coverage area: 15 cm x 15 cm clear 3ml NHS list price per applicator: £0.85 (ex. VAT and delivery) NHS supply chain order code: MRB306 Coverage area: 25 cm x 30 cm 10.5ml clear NHS list price per applicator: £2.92 (ex. VAT and delivery) NHS supply chain order code: MRB304 Coverage area: 50 cm x 50 cm 26ml clear NHS list price per applicator: £6.50 (ex. VAT and delivery) NHS supply chain order code: MRB305 Coverage area: 15 cm x 15 cm tinted 3ml NHS list price per applicator: £0.89 (ex. VAT and delivery) NHS supply chain order code: MRB494 Coverage area: 25 cm x 30 cm 10.5ml tinted NHS list price per applicator: £3.07 (ex. VAT and delivery) NHS supply chain order code: MRB495 Coverage area: 50 cm x 50 cm tinted 26ml NHS list price per applicator: £6.83 (ex. VAT and delivery) NHS supply chain order code: MRB496 For customer services and all other enquiries: Please telephone: 0800 0437 546 Email:enquiries@chloraprep.co.uk or visit: www.chloraprep.co.uk Prescribing Information skin. Avoid contact with eyes, mucous membranes, middle ear and neural tissue. ChloraPrep® (PL31760/0002) & ChloraPrep with Tint (PL31760-0001) 2% Should not be used in children under 2 months of age. Solution is flammable. Do not chlorhexidine gluconate w/v / 70% isopropyl alcohol v/v cutaneous solution. use with ignition sources until dry, do not allow to pool, and remove soaked materials Indication: Disinfection of skin prior to invasive medical procedures. Dosage & before use. Over-vigorous use on fragile or sensitive skin or repeated use may lead to administration: ChloraPrep – 0.67ml, 1.5ml, 3ml, 10.5ml, 26ml; ChloraPrep with local skin reactions. At the first sign of local skin reaction, application should be Tint – 3ml, 10.5ml, 26ml. Volume dependent on invasive procedure being undertaken. stopped. Per applicator costs (ex VAT) ChloraPrep – 0.67ml (SEPP) - 30p; 1.5ml Applicator squeezed to break ampoule and release antiseptic solution onto sponge. (FREPP) - 55p; 3ml - 85p; 10.5ml - £2.92; 26ml - £6.50. ChloraPrep with Tint – 3ml - Solution applied by gently pressing sponge against skin and moving back and forth 89p; 10.5ml - £3.07; 26ml - £6.83. Legal category: GSL. Marketing Authorisation for 30 seconds. The area covered should be allowed to air dry. Side effects, Holder: CareFusion UK 244 Ltd, 43 London Road, Reigate, Surrey RH2 9PW, UK. Date precautions & contra-indications: Very rarely allergic or skin reactions reported of preparation: July 2010. with chlorhexidine, isopropyl alcohol and Sunset Yellow. Contra-indicated for patients with known hypersensitivity to these constituents. For external use only on intact CHL109a Date of preparation: August 2010