Synthetic seed
- 1. Presented by â Divya Joshi A0999318020 Submitted to- Dr. Amit kharakwal
- 2. ï§Synthetic seeds are defined as artificially encapsulated somatic embryos, shoot buds, cell aggregates, or any other tissue that can be used for sowing as a seed and that possess the ability to convert into a plant under in vitro or ex vitro conditions and that retain this potential also after storage ï§ They are also called âsynseedsâ or âartificial seedsâ
- 3. ï§Earlier, synthetic seeds were referred only to the somatic embryos that were of economic use in crop production and plant delivery to the field or greenhouses. In the recent past, however, other micropropagules like shoot buds, shoot tips, organogenic or embryogenic etc. ï§The first synthetic seed was produced by KITTO and JANICK in 1982 in carrot
- 4. âĒ DESICCATED SYNTHETIC SEEDS- Desiccated synthetic seeds are produced nacked or polyoxyethylene glycol encapsulated somatic embryos. This type of synthetic seeds is produced in desiccation tolerant species plant. âĒ HYDRATED SYNTHETIC SEEDS- Hydrated synthetic seeds are produced by encapsulating the somatic embryos in hydrogels like sodium alginate, potassium alginate, carrageenan, sodium pectate or sodium alginate with gelatine.
- 5. (a)Plant propagule -(somatic embryo or shoot bud) somatic embryos are bipolar structures with both apical and basal meristematic regions, which are capable of forming shoot and root, respectively. (b) Matrix, -is a gelling material encapsulating plant propagules which incorporate nutrients, biofertlizers, pesticides, nitrogen - fixing bacteria, antibiotics or other essential additives.
- 6. (c) Seed shell -these are the artificial seed coats prepared with complex mixture of alginate- gelatin which was used to develop the coat system for encapsulation. The concept of artificial seed technology has been applied, successfully in large numbers of plants
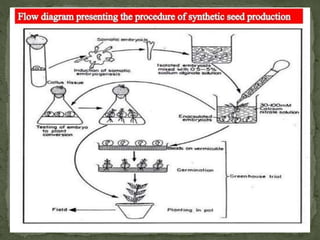
- 8. Gel complexation via a dropping procedure- ï§It is a most useful encapsulation system . Drip 2-3 % sodium alginate drops from at the tip of the funnel and the somatic embryos are inserted
- 9. ï§Keeep the encapsulated embryos complex in calcium salt for 20 min ï§Rinsed the capsules in water and the stored in a air tight container Molding â In the second method, isolated somatic embryos are mixed in a temperature- dependent gel such as gel-rite and placed in the well of a micro- titer plate and its forms gel when temperature is cooled down