System Analysis And Design Management Information System
- 1. 1 -
- 2. Many failed systems were abandoned because analysts tried to build wonderful systems without understanding the organization. The primarily goal is to create value for the organization. 1 -
- 3. The systems analyst is a key person analyzing the business, identifying opportunities for improvement, and designing information systems to implement these ideas. It is important to understand and develop through practice the skills needed to successfully design and implement new information systems. 1 -
- 4. 1 -
- 5. The project -- Moves systematically through phases where each phase has a standard set of outputs Produces project deliverables Uses deliverables in implementation Results in actual information system Uses gradual refinement 1 -
- 6. Planning (Why build the system? How should the team go about building it?) Analysis (Who uses system, what will it do, where and when will the system be used?) Design (How will the system work?) Implementation (System delivery) 1 -
- 7. 1 - A simple process for making lunch
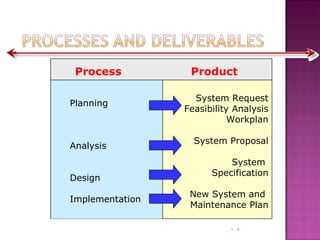
- 8. 1 - Process Product Planning Analysis Design Implementation System Request Feasibility Analysis Workplan System Proposal System Specification New System and Maintenance Plan
- 9. 1 -
- 10. A formalized approach to implementing the SDLC A series of steps and deliverables Methodology Categories 1 - Process-Centered Data-Centered Object-Oriented Structured Design Rapid Application Development Agile Development
- 11. 1 -
- 12. 1 - Pros Cons Identifies systems requirements long before programming begins Minimizes changes to requirements as project progresses Design must be specified on paper before programming begins Long time between system proposal and delivery of new system
- 13. 1 -
- 14. 1 - Pros Cons Reduces Schedule Time Less Chance of Rework Still Uses Paper Documents Sub-projects May Be Difficult to Integrate
- 15. 1 - Spiral Model
- 16. 1 -
- 17. Incorporate special techniques and tools: CASE tools JAD sessions Fourth generation/visualization programming languages Code generators 1 -
- 18. Phased development A series of versions developed sequentially Prototyping System prototyping Throw-away prototyping Design prototyping 1 -
- 19. 1 - Insert Figure 1-4 here
- 20. 1 - Pros Cons Users Get a System To Use Quickly Users Can Identify Additional Needs For Later Versions Users Work with a System that is Intentionally Incomplete
- 21. 1 -
- 22. 1 - Pros Cons Users Interact with Prototype Very Quickly Users Can Identify Needed Changes And Refine Real Requirements Tendency to do Superficial Analysis Initial Design Decisions May Be Poor
- 23. 1 -
- 24. 1 - Pros Cons Risks are Minimized Important Issues are Understood Before the Real System is Built May Take Longer Than Prototyping
- 25. 1 -
- 26. 1 - Pros Cons Fast Delivery of Results Works Well in Projects With Undefined or Changing Requirements Requires Discipline Works Best in Small Projects Requires Much User Input
- 27. Clear user requirements Familiarity with technology Complexity of system Reliability of system Time schedule Schedule visibility 1 -
- 28. 1 -
- 29. Business analyst Systems analyst Infrastructure analyst Change management analyst Project manager 1 -
- 30. The Systems Development Lifecycle consists of four stages: Planning, Analysis, Design, and Implementation There are six major development methodologies : the waterfall method, the parallel development method, the phased development method, system prototyping, design prototyping, and agile development. There are five major team roles : business analyst, systems analyst, infrastructure analyst, change management analyst and project manager. 1 -