System unit & its components
- 1. Lecture # 3 11/16/2012 Designed by Prof. Anosha Khan PGC 1
- 2. ’éĪ It contains system unit electronic components of the computers used to process data system unit system unit system unit 11/16/2012 Designed by Prof. Anosha Khan PGC 2
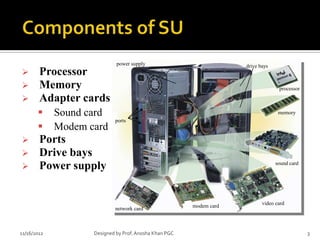
- 3. power supply drive bays ’āś Processor ’āś Memory processor ’āś Adapter cards ’é¦ Sound card memory ports ’é¦ Modem card ’āś Ports ’āś Drive bays ’āś Power supply sound card video card modem card network card 11/16/2012 Designed by Prof. Anosha Khan PGC 3
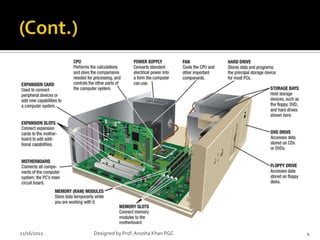
- 4. 11/16/2012 Designed by Prof. Anosha Khan PGC 4
- 5. ’éĪ Circuit board: thin board containing chipsŌĆövery small pieces of silicon or other semi-conducting material onto which integrated circuits are embeddedŌĆöand other electronic components ’éĪ Mother Board ’āś Main circuit board in system unit ’āś Contains adapter cards, processor chips, and memory chips ’āś Connects all components ’āś Allows communication between devices ’āś Also called system board 11/16/2012 Designed by Prof. Anosha Khan PGC 5
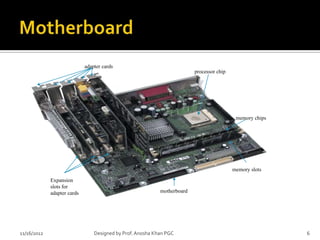
- 6. adapter cards processor chip memory chips memory slots Expansion slots for adapter cards motherboard 11/16/2012 Designed by Prof. Anosha Khan PGC 6
- 7. ’éĪ Small piece of semi- conducting material on which integrated circuits are etched ’āś Integrated circuits contain many microscopic pathways capable of carrying electrical current 11/16/2012 Designed by Prof. Anosha Khan PGC 7
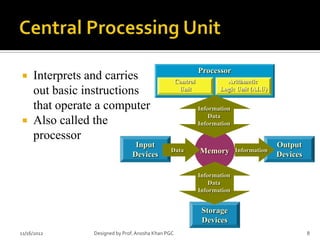
- 8. Processor ’éĪ Interprets and carries Control Control Arithmetic Arithmetic out basic instructions Unit Unit Logic Unit (ALU) Logic Unit (ALU) that operate a computer Information Data ’éĪ Also called the Information processor Input Output Devices Data Memory Information Devices Information Data Information Storage Devices 11/16/2012 Designed by Prof. Anosha Khan PGC 8
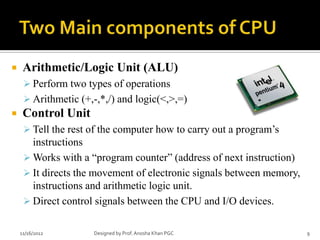
- 9. ’éĪ Arithmetic/Logic Unit (ALU) ’āś Perform two types of operations ’āś Arithmetic (+,-,*,/) and logic(<,>,=) ’éĪ Control Unit ’āś Tell the rest of the computer how to carry out a programŌĆÖs instructions ’āś Works with a ŌĆ£program counterŌĆØ (address of next instruction) ’āś It directs the movement of electronic signals between memory, instructions and arithmetic logic unit. ’āś Direct control signals between the CPU and I/O devices. 11/16/2012 Designed by Prof. Anosha Khan PGC 9
- 10. ’éĪ There are four operations of Machine Cycle Step 1. Fetch Obtain program instruction or data item from memory Step 2. Decode Translate instruction into commands Step 3. Execute Carry out command Step 4. Store Write result to memory 11/16/2012 Designed by Prof. Anosha Khan PGC 10
- 11. ’āś CPU begins fetching second instruction before completing machine cycle for first instruction ’āś Results in faster processing 11/16/2012 Designed by Prof. Anosha Khan PGC 11
- 12. ’éĪ Important measurement indicating speed ’é¦ Located on a small chip ’é¦ Produces electrical beats(impulse) ’éĪ Expressed in gigahertz (1 GH=1 billion ticks of system clock per second) ’éĪ Faster clock speed, faster computer ’éĪ the clock speed determines how many instructions per second the processor can execute ’éĪ Processor speed can also be measured in millions of instructions per second (MIPS) 11/16/2012 Designed by Prof. Anosha Khan PGC 12
- 13. ’éĪ Registers ’éĪ Page # 145, topic: Registers ’éĪ Cache ’éĪ System Clock ’éĪ RAM 11/16/2012 Designed by Prof. Anosha Khan PGC 13
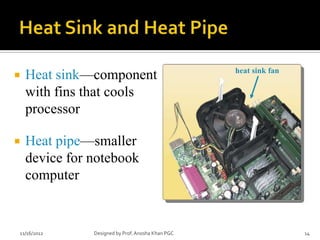
- 14. heat sink fan ’éĪ Heat sinkŌĆöcomponent with fins that cools processor ’éĪ Heat pipeŌĆösmaller device for notebook computer 11/16/2012 Designed by Prof. Anosha Khan PGC 14
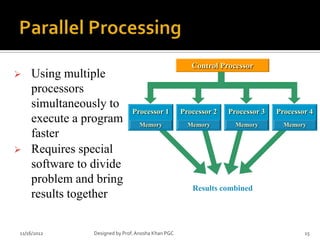
- 15. Control Processor ’āś Using multiple processors simultaneously to Processor 1 Processor 2 Processor 3 Processor 4 execute a program Memory Memory Memory Memory faster ’āś Requires special software to divide problem and bring Results combined results together 11/16/2012 Designed by Prof. Anosha Khan PGC 15
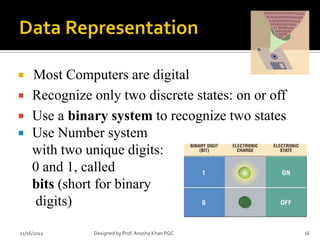
- 16. ’éĪ Most Computers are digital ’éĪ Recognize only two discrete states: on or off ’éĪ Use a binary system to recognize two states ’éĪ Use Number system with two unique digits: 0 and 1, called bits (short for binary digits) 11/16/2012 Designed by Prof. Anosha Khan PGC 16
- 17. ’āś Eight bits grouped together as a unit ’āś Provides enough different combinations of 0s and 1s to represent 256 individual characters ’é¦ Numbers ’é¦ Uppercase and lowercase letters ’é¦ Punctuation marks 11/16/2012 Designed by Prof. Anosha Khan PGC 17
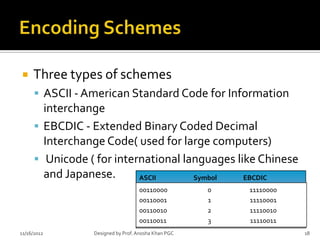
- 18. ’éĪ Three types of schemes ’é¦ ASCII - American Standard Code for Information interchange ’é¦ EBCDIC - Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code( used for large computers) ’é¦ Unicode ( for international languages like Chinese and Japanese. ASCII Symbol EBCDIC 00110000 0 11110000 00110001 1 11110001 00110010 2 11110010 00110011 3 11110011 11/16/2012 Designed by Prof. Anosha Khan PGC 18
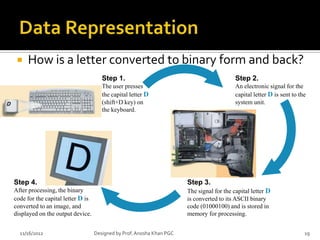
- 19. ’éĪ How is a letter converted to binary form and back? Step 1. Step 2. The user presses An electronic signal for the the capital letter D capital letter D is sent to the (shift+D key) on system unit. the keyboard. Step 4. Step 3. After processing, the binary The signal for the capital letter D code for the capital letter D is is converted to its ASCII binary converted to an image, and code (01000100) and is stored in displayed on the output device. memory for processing. 11/16/2012 Designed by Prof. Anosha Khan PGC 19
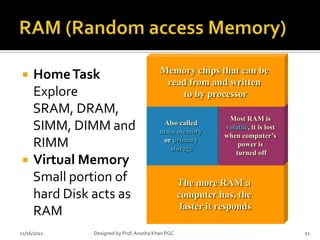
- 20. ’āś Electronic components that store instructions, data, and results ’āś Consists of one or more chips on motherboard or other circuit board ’āś Before running a Program must be loaded into the memory ’āś Memory slots on motherboard hold memory modules ’āś RAM (random access memory): temporary memory that the computer uses ’é¦ Consists of chips connected to a memory module which is connected to the motherboard ’é¦ Hold data and program instructions while they are needed. ’é¦ RAM is volatile, its content is lost when the computer is shut off 11/16/2012 Designed by Prof. Anosha Khan PGC 20
- 21. Memory chips that can be ’éĪ Home Task read from and written Explore to by processor SRAM, DRAM, Most RAM is SIMM, DIMM and Also called main memory volatile, it is lost when computerŌĆÖs RIMM or primary storage power is turned off ’éĪ Virtual Memory Small portion of The more RAM a hard Disk acts as computer has, the faster it responds RAM 11/16/2012 Designed by Prof. Anosha Khan PGC 21
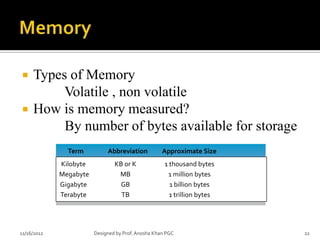
- 22. ’éĪ Types of Memory Volatile , non volatile ’éĪ How is memory measured? By number of bytes available for storage Term Abbreviation Approximate Size Kilobyte KB or K 1 thousand bytes Megabyte MB 1 million bytes Gigabyte GB 1 billion bytes Terabyte TB 1 trillion bytes 11/16/2012 Designed by Prof. Anosha Khan PGC 22
- 23. RAM Operating system Operating system instructions interface Step 1. When you start the computer, certain operating system files load into RAM from the hard disk. The operating system displays the user interface on the screen. Word processing Word processing program instructions program window Step 2. When you start a word processing program, the programŌĆÖs instructions load into RAM from the hard disk. The word processing program, along with the Web Browser and certain operating system instructions are in RAM. The word processing program window is displayed on the screen. 11/16/2012 Designed by Prof. Anosha Khan PGC 23
- 24. ’éĪ It helps to increase speed of computer ’éĪ It stores frequently used data and instructions ’éĪ Two types of cache Memory Cache and Disk Cache ’é¦ Memory Cache ’āś L1: built directly in processor, less memory ’āś L2:slower but has larger capacity ATC (advanced transfer cache) is a type of L2 cache ’āś L3:it is on motherboard separate from processor 11/16/2012 Designed by Prof. Anosha Khan PGC 24
- 25. ’éĪ A register is a single storage location within the CPU ’éĪ Unlike memory, which is ŌĆ£outsideŌĆØ the CPU ’éĪ Examples of registers: ’é¦ Accumulator (ACC) ’é¦ Program counter (PC) ’é¦ Instruction register (IR) ’é¦ Memory address register (MAR) ’é¦ Memory data register (MDR) ’é¦ Status register ’éĪ General purpose registers (R0, R1, ŌĆ”) ’é¦ Included on some CPUs ’é¦ Used for high-speed temporary storage of program variables 11/16/2012 Designed by Prof. Anosha Khan PGC 25
- 26. ’éĪ Memory chips that store permanent data and instructions ’éĪ Nonvolatile memory, it is not lost when computerŌĆÖs power is turned off ’éĪ PROM (programmable ROM) ’éĪ EEPROM (Electrically erasable read-only memory) 11/16/2012 Designed by Prof. Anosha Khan PGC 26
- 27. ’āś Nonvolatile memory that can be erased electronically and reprogrammed ’āś Used with PDAs, digital cameras, digital cellular phones, music players, digital voice recorders, and pagers 11/16/2012 Designed by Prof. Anosha Khan PGC 27
- 28. ’éĪ CMOS stands for Complementary metal-oxide semiconductor memory ’éĪ It is used to store configuration information about the computer ’éĪ Uses battery power to retain information when other power is turned off ’éĪ Stores date, time, and computerŌĆÖs startup information 11/16/2012 Designed by Prof. Anosha Khan PGC 28
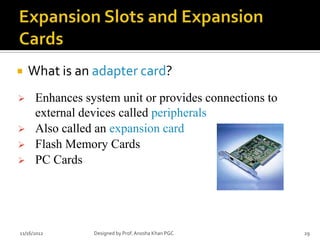
- 29. ’éĪ What is an adapter card? ’āś Enhances system unit or provides connections to external devices called peripherals ’āś Also called an expansion card ’āś Flash Memory Cards ’āś PC Cards 11/16/2012 Designed by Prof. Anosha Khan PGC 29
- 30. ’éĪ What is an expansion slot? ’āś An opening, or socket, on the motherboard that can hold an adapter card ’āś With Plug and Play, the computer automatically configures cards and other devices as you install them 11/16/2012 Designed by Prof. Anosha Khan PGC 30
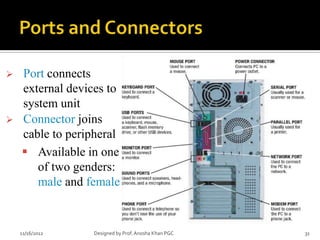
- 31. ’āś Port connects external devices to system unit ’āś Connector joins cable to peripheral ’é¦ Available in one of two genders: male and female 11/16/2012 Designed by Prof. Anosha Khan PGC 31
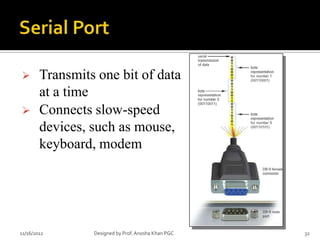
- 32. ’āś Transmits one bit of data at a time ’āś Connects slow-speed devices, such as mouse, keyboard, modem 11/16/2012 Designed by Prof. Anosha Khan PGC 32
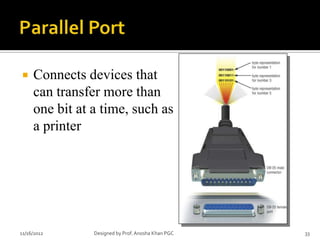
- 33. ’éĪ Connects devices that can transfer more than one bit at a time, such as a printer 11/16/2012 Designed by Prof. Anosha Khan PGC 33
- 34. ’éĪ Connect parts of the CPU to each other ’éĪ Connect the CPU to other devices on the system board. ’éĪ Data roadway for traveling bits ’é¦ Measured as bus width( number of bits transmitted at one time) ’é¦ More lanes, faster traffic ’éĪ Two basic categories of Expansion BUSES ’é¦ System buses ( connect CPU to Memory) ’é¦ Expansion buses ( connect CPU to slots on the system board) ’é¦ Data Bus (Page # 148) ’é¦ Address Bus__Connects only CPU & RAM(Page # 148) ’é¦ BUS standard (chapter 4 page 148) 11/16/2012 Designed by Prof. Anosha Khan PGC 34