Target Audience Analysis (UNFINISHED)
- 1. TARGET AUDIENCE ANALYSIS Critical Responses Contents Research Techniques Classification of Audiences Audience Effects Theory Skyfall Trailer Analysis Comparision of two other Products, The Hobbit and Star Trek In Darkness EMILY GRACE
- 2. RESEARCH TECHNIQUES Main Types of Research: Qualitative, Quantitative, Primary and Secondary Categories of Research: Market, Audience and Production
- 3. THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE Qualitative research are of peopleĪ»s opinions of products and/or subjects. Quantitative Research involves the gathering of factual data from numbers, graphs and charts, for which is easily measured.
- 8. CLASSIFICATION OF AUDIENCES Demographics- things that are both easy to measure and factual which is Quantitive-Information Psychographic- Opinions of the People which is Qualitative Information (Emotions) Geo-demographic- the target audience in certain areas
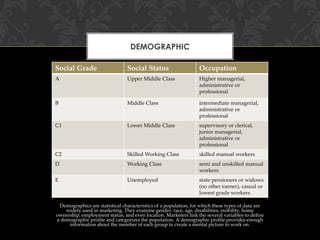
- 9. DEMOGRAPHIC Social Grade Social Status Occupation A Upper Middle Class Higher managerial, administrative or professional B Middle Class intermediate managerial, administrative or professional C1 Lower Middle Class supervisory or clerical, junior managerial, administrative or professional C2 Skilled Working Class skilled manual workers D Working Class semi and unskilled manual workers E Unemployed state pensioners or widows (no other earner), casual or lowest grade workers Demographics are statistical characteristics of a population, for which these types of data are widely used in marketing. They examine gender, race, age, disabilities, mobility, home ownership, employment status, and even location. Marketers link the several variables to define a demographic profile and categorizes the population. A demographic profile provides enough information about the member of each group to create a mental picture to work on.
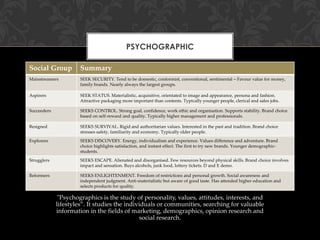
- 10. PSYCHOGRAPHIC Social Group Summary Mainstreamers SEEK SECURITY. Tend to be domestic, conformist, conventional, sentimental ©C Favour value for money, family brands. Nearly always the largest groups. Aspirers SEEK STATUS. Materialistic, acquisitive, orientated to image and appearance, persona and fashion. Attractive packaging more important than contents. Typically younger people, clerical and sales jobs. Succeeders SEEKS CONTROL. Strong goal, confidence, work ethic and organisation. Supports stability. Brand choice based on self-reward and quality. Typically higher management and professionals. Resigned SEEKS SURVIVAL. Rigid and authoritarian values. Interested in the past and tradition. Brand choice stresses safety, familiarity and economy. Typically older people. Explorers SEEKS DISCOVERY. Energy, individualism and experience. Values difference and adventure. Brand choice highlights satisfaction, and instant effect. The first to try new brands. Younger demographicstudents. Strugglers SEEKS ESCAPE. Alienated and disorganised. Few resources beyond physical skills. Brand choice involves impact and sensation. Buys alcohols, junk food, lottery tickets. D and E demo. Reformers SEEKS ENLIGHTENMENT. Freedom of restrictions and personal growth. Social awareness and independent judgment. Anti-materialistic but aware of good taste. Has attended higher education and selects products for quality. "Psychographics is the study of personality, values, attitudes, interests, and lifestylesĪ▒. It studies the individuals or communities, searching for valuable information in the fields of marketing, demographics, opinion research and social research.
- 11. AUDIENCE EFFECTS THEORY The Ī░Hypodermic NeedleĪ▒ Model Cultivation Theory The Desensitisation Theory Copycat Theory HallĪ»s Encoding ©C Decoding model Reception Theory
- 12. THE Ī░HYPODERMIC NEEDLEĪ▒ THEORY ? Where the audience is seen as Ī░empty vesselsĪ▒ who play no role in interacting with the media concerned, accepting the content of the text with no complaint. ? Texts function in a onedirectional communication process. ? Many theorists have noted many problems with Effects theory. ? They feel it is out of date and that it vastly underestimates the audiences of the present. ? This has led to more complex theories about active audience participation.
- 13. CULTIVATION THEORY ? The more the TV audience audience watches or views a certain media text, the more likely it is that they will develop certain ideas about the world. ? The worry with is that these will be Ī«falseĪ» views. ? The problem with this view is that it does not acknowledge that viewers may gain knowledge of the world from other different sources, including multimedia and the internet.
- 14. THE DESENSITISATION AND COPYCAT THEORY ? Audiences who are exposed to extreme media messages will become Ī░immuneĪ▒ to them once viewed, meaning that long-term exposure can result in audience Ī░desensitisationĪ▒ to such imagery. ? Inoculation theory has been used in attempts to blame violent media for such alleged influences. ? Like the Hypodermic Needle model, has more recently been criticized for its assumption that audiences are passive. ? The theory itself had been concluded as outdated by Psychologists. ? Very little research has been done to test this assertion. ? It is a theory that is maintained by the press rather than research.
- 15. HALLĪ»S ENCODING ©C DECODING MODEL ? Developed by Stuart Hall, a theory of an active audience examines the link between the text and the receiver. ? Encoding is the process by which a text is constructed by its producers. ? Decoding is the process by which the audience reads, understands and interprets a text. ? Within the theory, it states that itĪ»s polysemic, where the audience interprets the information given differently between each person, depending on their culture and the many faces of their identity.
- 16. RECEPTION THEORY ? It focuses on the role of the audience in the interpretation of a text. ? Suggesting that audiences play an active role in reading texts and that each person has the ability to interpret the same text differently. He termed these different Ī«readingsĪ» of the ideologies in media texts as ? The preferred reading ? The negotiated reading ? The oppositional reading
- 17. TRAILER ANALYSIS Skyfall The Hobbit Star Trek Into The Darkness
- 18. SKYFALL TRAILER Skyfall Official Trailer
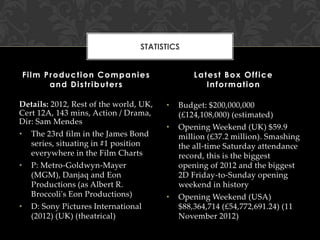
- 19. STATISTICS Film Production Companies and Distributers Details: 2012, Rest of the world, UK, Cert 12A, 143 mins, Action / Drama, Dir: Sam Mendes ? The 23rd film in the James Bond series, situating in #1 position everywhere in the Film Charts ? P: Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer (MGM), Danjaq and Eon Productions (as Albert R. Broccoli's Eon Productions) ? D: Sony Pictures International (2012) (UK) (theatrical) Latest Box Office Information ? Budget: $200,000,000 (?124,108,000) (estimated) ? Opening Weekend (UK) $59.9 million (?37.2 million). Smashing the all-time Saturday attendance record, this is the biggest opening of 2012 and the biggest 2D Friday-to-Sunday opening weekend in history ? Opening Weekend (USA) $88,364,714 (?54,772,691.24) (11 November 2012)
- 20. GENRE
- 22. NARRATIVE Bond's mission is to keep a computer drive that has a list of British agents from being used against them. He chases the man who has it and they have a brawl on top of a train. Eve, an agent sent to assist Bond has them in her cross hairs but hesitates to take the shot because she might hit Bond but M orders her to take it. She does, and hits Bond who falls into the river and is believed to be dead. A few months later, the British government is upset with MI6 for losing the list; specifically with M. She is told that she'll be allowed to retire but she refuses to leave till the matter is resolved. So she returns to HQ to work on it but as she arrives, there's an explosion. In the meantime, Bond, who is not dead, has been laying low. When he learns of what happened, he returns. And M tasks him with finding the one who has the information. He eventually learns that the man who has it, is someone from M's past and who has it in for her. (IMDB)
- 23. REPRESENTATION
- 24. RESPONSE
- 25. COMPARISON OF OTHER TRAILERS The Hobbit: An Unexpected Journey Star Trek Into Darkness The Hobbit Official Trailer Star Trek Into Darkness Official Trailer
- 26. THE HOBBIT: AN UNEXPECTED JOURNEY
- 27. STAR TREK INTO DARKNESS