Target Operating Model Definition
- 1. Target Operating Model Defining the business future state Version 1.2 February 2009
- 2. What is a target operating model ’é¦ A definition of the future state of an organisation ’āś People ’āś Process ’āś Technology ’āś Customers ’āś Markets / Geographies ’āś Products ’é¦ How do I get a target operating model ’āś No prescriptive approach to delivering a T.O.M. ’āś No commonly agreed principles as to what goes into a T.O.M. ’āś Each organisation will have different needs and different focus. 2 Copyright ┬® Maddison Ward 2006
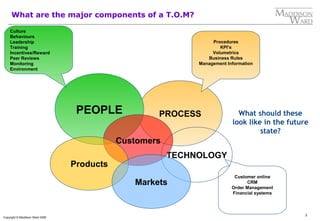
- 3. What are the major components of a T.O.M? Culture Behaviours Leadership Procedures Training KPIŌĆÖs Incentives/Reward Volumetrics Peer Reviews Business Rules Monitoring Management Information Environment PEOPLE PROCESS What should these look like in the future state? Customers TECHNOLOGY Products Customer online Markets CRM Order Management Financial systems 3 Copyright ┬® Maddison Ward 2006
- 4. The first challenge is to define the target In defining our target operating model, weŌĆÖre trying to answer the questions:- What kind of business do we want to be / what is our ŌĆ£visionŌĆØ? ’āśWhat is our value proposition (ie, why are we here?) ’āśWhat products / services should we be offering ’āśAt what pricing / margin ’āśWhat revenue and profitability targets should we have, over the next 5 years ’āśWhat cost base can we / should we support for the above ’āśWhat is our anticipated cost of sale ’āśWhat is our predicted cashflow ’āśHow do we present ourselves to our market and what do we stand for? (What is our brand strategy and value) ’āśHow do we make our customers aware of what we offer (What is our marketing strategy (ALT / BTL)) ’āśHow do we sell to our customers (What is our sales strategy (online / direct to consumer)) ’āśHow do we handle partner organisations (B2B) ’āśHow do we provide our customers with customer service (how do we handle their enquiries / complaints) ’āśFrom whom do we source our raw materials (What is our supplier strategy) ’āśHow do we distribute our products to our customers (What is our logistics / supply chain strategy) ’āśHow to we utilise IT to support our business (What is our IT strategy (insource / outsource)) ’āśWhat financial / governance processes and controls do we need These are frequently described in the overall business strategy (5 year plan):- 4 Copyright ┬® Maddison Ward 2006
- 5. The first challenge is to define the ŌĆ£end-stateŌĆØ We can then start to decompose these into models about how our business should look:- People ’āśWhat kind of people do we need? ’āśHow many of them? ’āśHow are they organised? ’āśWhere do they sit? ’āśHow do we measure them? ’āśWhat rewards / incentives do we have to put in place for them? ’āśWhat training do they need? ’āśWhat career / promotion prospects will we put in place for them? ’āśHow do we deal with performance issues? ’āśHow do we recruit them (or make them redundant from current state) Process ’āśWhat are our macro business processes (level 0) ’āśHow do they decompose into units of work (level 1+) ’āśHow do we measure their efficiency (KPIŌĆÖs) ’āśWhat volumetrics do we believe each process will have (how often will the process be used) ’āśHow much will each process cost to run ’āśWhat are the business rules for each process ’āśWhat triggers a business process (event, time, volume etc). ’āśWhat are the process hand-offs, and how does the organisation map to the process ’āśWhat systematic technology do we want to put in place to support each process (and how much value or cost saving does that bring compared to the technology total-cost-of-ownership ŌĆō ie, do the volumetrics stack up to the cost?) ’āśWhat management information do we need to measure the process Technology ’āśWhat systems do our colleagues need to support the business processes weŌĆÖre asking them to do ’āśHow do our customers interact with us through technology ’āśWhat level of automation do we want through the various channels/segments/touchpoints! 5 Copyright ┬® Maddison Ward 2006
- 6. Where do we begin? The commonly recognised starting point is the ŌĆ£customer experienceŌĆØ Customer Principles ’āśWhat products/services do we want to offer our customers ’āśHow do we want to interact with our customers ’āśHow much do we want them to do for themselves ’āśDo we want their online and offline experiences to be similar ’āśHow do we contact our customers ’āśHow often to we proactively communicate with our customers ’āśHow much do we spend on each customer, and how much is the customer worth to us ’āśWhat do we want our overall customer satisfaction target to be, as a result? Customer Journeys ’āśWhat segmentation of customers do we have ’āśHow do we want to treat each segment ’āśHow much value do we get from each segment ’āśWill the customer journey be the same for each segment ’āśWhat are the steps through the journey, what are the inputs and what do we expect the customer to do / feel at the end of each step. ’āśWho, in our organisation is the touch-point for the customer through each of the journey steps? ’āśHow do we measure customer satisfaction across each segment / journey (customer KPIŌĆÖs). Strategies ’āśCustomer Segmentation Model ’āśCustomer Contact Strategy ’āśCall-centre Strategy ’āśOnline / Social Media Strategy ’āśCustomer Value Proposition (s) This tries the articulate the ŌĆ£Customer I Wants, and the overall approach to how those I Wants might be addressed within the cost/revenue parameters of the overall business 6 Copyright ┬® Maddison Ward 2006
- 7. The first challenge is to define the ŌĆ£end-stateŌĆØ From which we can derive a set of colleague ŌĆ£I needsŌĆØ:- People ’āśOrganisation Design ’āśRemuneration / Compensation / Reward model ’āśOrganisation Volumetrics ’āśEstates Plan ’āśSkills / Competencies Assessment ’āśOrganisational Change Readiness Assessment ’āśJob Descriptions ’āśEmployee Contracts ’āśRelocation / Recruitment / Redundancy Plans ’āśTraining Plans Process ’āśLevel 0, 1 & 2 Process Maps & KPIs ’āśBusiness Rules Specifications ’āśWorkflow ’āśArchiving ’āśPhysical Security ’āśInterim processes (transitional state) ’āśManual procedures (for non-automated processes) Technology ’āśSystems requirements specification ’āśMI Requirements ’āśLists of Values specification ’āśUser Roles & Permissions ’āśData Requirements & Ownership (including retention) ’āśHelp Requirements ’āśScripting Requirements ’āśEnvironment Requirements ’āśSystem Service Level Requirements 7 Copyright ┬® Maddison Ward 2006
- 8. Business capabilities will have different focus For example, different emphasis on channels ŌĆō call-centre design vs online design PEOPLE PROCESS Knowledge TECHNOLOGY PEOPLE Call Centre PROCESS channel Collateral TECHNOLOGY Online channel CUSTOMERS ŌĆ” but the overall design needs to be holistic, or consciously not (based on the business strategy and/or customer principles 8 Copyright ┬® Maddison Ward 2006
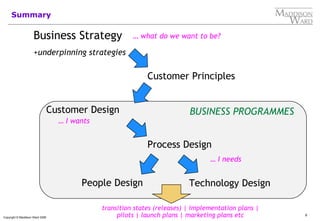
- 9. Summary Business Strategy ŌĆ” what do we want to be? +underpinning strategies Customer Principles Customer Design BUSINESS PROGRAMMES ŌĆ” I wants Process Design ŌĆ” I needs People Design Technology Design transition states (releases) | implementation plans | Copyright ┬® Maddison Ward 2006 pilots | launch plans | marketing plans etc 9
- 10. The first challenge is to define the ŌĆ£end-stateŌĆØ Example checklist 10 Copyright ┬® Maddison Ward 2006