single linked list
- 1. DATA STRUCTURE ASSIGNMENT - I SINGLE LINKED LIST IMPLEMENTATION -BY B.ABDUL KALAM ASHAD B.ANISH KUMAR MOHAN RAJ D.SAPTHAGIRINATHAN SUDHARSHAN
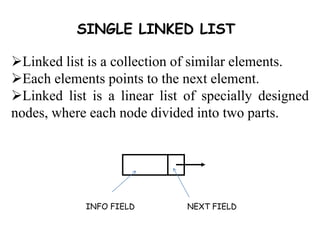
- 2. SINGLE LINKED LIST ÔÉòLinked list is a collection of similar elements. ÔÉòEach elements points to the next element. ÔÉòLinked list is a linear list of specially designed nodes, where each node divided into two parts. INFO FIELD NEXT FIELD
- 3. ÔÉò Info field: it contains necessary information about the items of the list to be stored and processed. ÔÉòNext field: it contains address of the next node. This field is used to access the next data item in other head 48 17 142
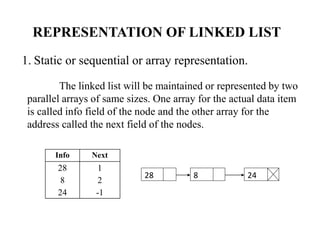
- 4. REPRESENTATION OF LINKED LIST 1. Static or sequential or array representation. The linked list will be maintained or represented by two parallel arrays of same sizes. One array for the actual data item is called info field of the node and the other array for the address called the next field of the nodes. Info Next 28 1 8 2 24 -1 28 8 24
- 5. 2. Dynamic or pointers or linked representation. The size of the linked list may increase or decrease according to the requirement of application so dynamic representation of linked list do not have limitation and use space proportional to the actual number of elements of the list. Features: It wants ultimate size of the linked list to declare in advance. Array implementation of the linked list is very simple and efficient in random access of the elements.
- 6. OPERATION ON SINGLE LINKED LIST Creating linked list: ÔÉòTo create a linked list we have to maintain the list of free nodes in array implementation. ÔÉòInitially all the nodes are empty and link to one another in sequence. ÔÉòThe next field of the last node contains -1 to indicate the end of the list. Example: Free=0; For(i=0;i<size;i++) List [i].next=i+1; list[i].next= -1;
- 7. Traversing a linked list: This operation is used to visit each one of the list exactly once in order to access the info stored in nodes. Algorithm: 1: if start=null a: print “list is empty” b: exit End if. 2: Set ptr = start 3: Repeat steps 4 and 5 until ptr! =null 4: access and apply ptr info. 5: set ptr= ptr next End repeat 6: Exit
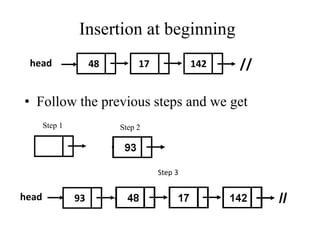
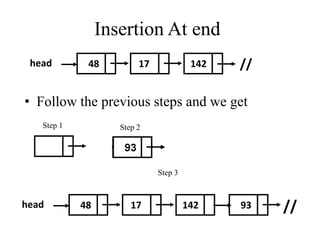
- 8. Insertion of an element into the linked list at various positions: Insertion of node into a linked list requires a free node in which the information can be inserted and then the node can be inserted into the linked list. ÔÉòBefore header or at beginning. ÔÉòAt the end of list. ÔÉòAt the specified position.
- 9. Insertion at beginning head 48 17 142 // • Follow the previous steps and we get Step 1 Step 2 head 93 Step 3
- 10. Insertion At end head 48 17 142 // • Follow the previous steps and we get 93 Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 head 48 17 142 //
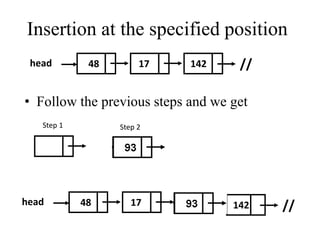
- 11. Insertion at the specified position ÔÉòTo insert a new node at the specified position we have to search position in the list. ÔÉòThen we can insert the node after the position. Let the address of the specified node be kept in ptr. ÔÉòAdjust the pointer so that next pointer so that next pointer of the specified node pointed by the ptr. ÔÉòThe next pointer of the specified node will point to the next pointer of the node pointed by new ptr.
- 12. Insertion at the specified position head 48 17 142 // • Follow the previous steps and we get Step 1 Step 2 head 48 17 142 //
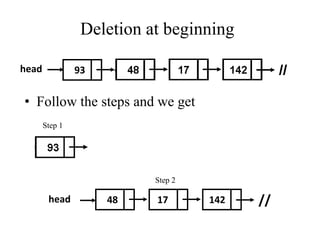
- 13. Deletion an element from the linked list If the node be deleted, that element should be search all over the list still the node find. Then it should be deleted. As like as insertion the deletion is also performed in three ways. ÔÉòDeletion at the beginning position of the linked list. ÔÉòDeletion at the ending position of linked list. ÔÉòDeletion at a specified position in linked list.
- 14. Deletion at beginning head 93 • Follow the steps and we get Step 1 Step 2 head 48 17 142 //
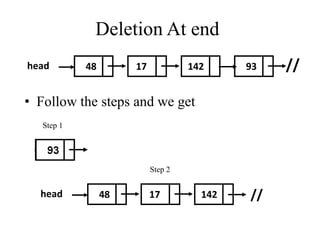
- 15. Deletion At end head 48 17 142 // • Follow the steps and we get 93 Step 1 Step 2 head 48 17 142 //
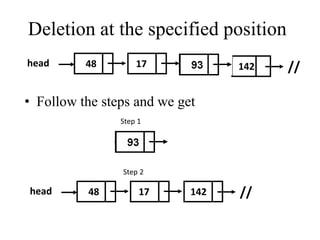
- 16. Deletion at the specified position head 48 17 142 // • Follow the steps and we get Step 1 Step 2 head 48 17 142 //
- 17. ALGORITHM 1. If start =NULL 2. Print”over flow” 3. Return 4. End if 5. Set ptr=start 6. Assign value=startinfo 7. Set start=startnext(second node becomes the first node). 8. Release the node pointed by ptr to the memory heap. 9. Exit.




![OPERATION ON SINGLE LINKED LIST
Creating linked list:
ÔÉòTo create a linked list we have to maintain the list of free
nodes in array implementation.
ÔÉòInitially all the nodes are empty and link to one another in
sequence.
ÔÉòThe next field of the last node contains -1 to indicate the end
of the list.
Example:
Free=0;
For(i=0;i<size;i++)
List [i].next=i+1;
list[i].next= -1;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/team7-141211075713-conversion-gate02/85/single-linked-list-6-320.jpg)