Technology In CA Education
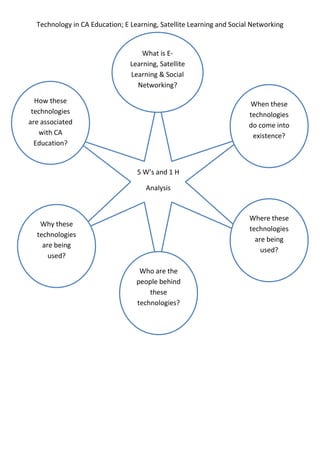
- 1. Technology in CA Education; E Learning, Satellite Learning and Social Networking 5 WŌĆÖs and 1 H Analysis What is E- Learning, Satellite Learning & Social Networking? When these technologies do come into existence? Where these technologies are being used? Who are the people behind these technologies? Why these technologies are being used? How these technologies are associated with CA Education?
- 2. 1. What is E-Learning, Satellite Learning and Social Networking? E-Learning E-Learning is the use of electronic media and information and communication technologies in education. It is broadly inclusive of all forms of education technology in learning and teaching. E-Learning includes numerous types of media that deliver text, audio, images, animation and streaming video and includes technology applications and processes such as audio or tape video, satellite TV, CD-ROM and computer based learning, as well as local intranet/extranet and web-based learning. The most important, ŌĆ£Successful e-learning depends on the self-motivation of individuals to take and complete the course effectivelyŌĆØ. There are different e-learning delivery methods so as to facilitate different people to learn in many different ways and at different times. Additionally, you will need a way to develop and manage e-learning. o Asynchronous E-learning Asynchronous e-learning lets people learn at any time. ’éĘ Self-Paced Courses The obvious advantage of self-paced course is convenience. People can get the training they need at any time. Self-paced courses can be delivered in many ways including ŌĆō Internet, Intranet or Local Area Networks. Self-paced courses usually have these features; ’é¦ Multimedia: A mix of text, graphics, animation, audio and video to enhance the learning process. ’é¦ Interactivity: An Instructional Strategy that helps a learner practice what they have learned.
- 3. ’é¦ Bookmarking: Lets the learner stop the course at any time and restart it from the same point. ’é¦ Tracking: Report the learnerŌĆÖs performance with a course to a Learning Management System(LCM) ’é¦ Simulation: Providing practise with a mock-up of a real system. ’é¦ Online Experts: Provide access to experts through chat or online discussions. ’é¦ Search: Search through a course to find information required to complete a task. ’é¦ Notes and Highlights: Mark one or more parts of a course that contain the most important information. ’éĘ Discussion Groups A discussion group is a collection of conversations that occur over time. Other names for discussion groups are message boards, bulletin boards and discussion forums. A discussion group might start out as a question from an individual. Sometime later, another individual responds to that question. Others can respond to the question (creating a thread) or they can start their own conversation (forming another thread). A threaded discussion might also start with a teacher asking an open-ended question that leads to a class discussion. Discussion groups can be used to support a group of people taking the same class or can be used to support people performing similar tasks. A discussion group is a very efficient way to provide expert answers to a large group people. A single answer to a common question can benefit many. o Synchronous E-Learning Synchronous e-Learning lets teachers conduct classes over the Internet. The synchronous technologies also allow people to interact with experts. ’éĘ Virtual Classrooms A virtual classroom duplicates the capabilities found in a real classroom. A virtual classroom provides: ’é¦ A place to meet: Students and teachers use their computers to go to a virtual meeting place instead of a classroom. ’é¦ Take attendance: A list of students is recorded. ’é¦ Lecture: Teachers can choose from a variety of synchronous technologies including ŌĆō ║▌║▌▀Ż presentation, Audio and Video Conferencing, Application sharing, Shared Whiteboard. ’é¦ Interaction with students: Students can indicate when they want to speak. Teachers can let students speak through audio and video conferencing, or both can use instant messaging and chat. ’é¦ Quizzes: Teachers can present questions to students. ’é¦ Breakout sessions: Students can work together in groups. Most companies that sell virtual classroom software provide all of these capabilities in single package. Eg SAP. ’éĘ Audio and Video Conferencing Audio-conferencing can be implemented in two ways: ’é¦ Computers connected to the Internet. Common names for this kind of implementation are IP Audio-Conferencing or Voice-over-IP.
- 4. ’é¦ Phone-conferences. People dial the same number to participate in an audio conference. Video-Conferencing can be implemented in two ways: ’é¦ Computers connected to the Internet. The computers need digital cameras. ’é¦ Special video conferencing devices that connect over the internet or phone lines. ’éĘ Chat Chat allows several people to communicate with each other. Each participant uses a computer to type their comments. The other participants can see the name of the person and their comments. ’éĘ Shared Whiteboard A shared whiteboard lets a group of people communicate by typing comments, drawing, highlighting and pointing. A shared whiteboard is a common feature within virtual classroom software packages. ’éĘ Application Sharing You can demonstrate how to use software applications to remote learners with sharing applications. ’éĘ Instant Messaging Instant messaging is similar to chat. One person communicates to another through typing. Instant messaging also provides some additional features. With instant messaging, you can keep a list of people that you might like to chat with and it indicates whether they are online, offline, available for chat or busy. o Development and Management ’éĘ Learning Management System A Learning Management System(LMS) manages the process of learning, provide reports, and manage access to self-paced courses. LMS also manage one or more of these: ’é¦ Administration ’é¦ Training Management ’é¦ Employee Management ’éĘ Learning Content Management Systems A Learning Content Management System(LCMS) support team-based development of self-paced courses. A LCMS typically providesŌĆō A library of media elements, Templates, Developments tools, Project Management tools, Quality Assurance tools. ’éĘ Knowledge Management Knowledge management systems provide direct support for employees as they do their job. Many types of systems are referred to as knowledge management systems including - Document Management, Knowledge Capture, Information portals, Search tools.
- 5. Satellite Learning Satellite Learning is a part of Synchronous E-Learning. It is about providing education and training solutions through satellite based ŌĆśVery Small Aperture Terminal(VSAT)ŌĆÖ technology. VSAT is a deviceŌĆōknown as a small private earth station that is used to transmit and receive data signal through a satellite. In it the professor delivers their lecture in a specially made studio classroom. Professor uses presentations, video, audio & digital content to effectively communicate, engage & interact with students. Through satellite, the lecture is telecast live to the various centers across the remote location. The students sitting in these classrooms receive the lecture clear as a real professor in a live classroom. The students can see the lecturer on the screen, listen & participate in the lecture through a computer & an LCD projector connected to the VSAT. Students can also ask questions to the professor & receive prompt answers. Video archive is also available for students. Video archive is recorded file of LIVE classes. The professor/faculty can constantly monitor students sitting in the class throughout the class.
- 6. Social Networking The use of dedicated websites and applications to interact with other users, or to find people with similar interest to oneŌĆÖs own. 2. When these technologies do come in existence? The Term E-Learning has only been in existence since 1999, when the word was first utilized at a Computer-Based Training(CBT) system seminar. Other words also began to spring up in search of an accurate description such as ŌĆ£online learningŌĆØ and ŌĆ£virtual learningŌĆØ. However, the principles behind e- learning have been well documented throughout history, and there is even evidence which suggests that early forms of e-learning existed as far back as the 19th century. 3. Where these technologies are being used? These technologies can be used at various places viz. ’éĘ Pre-Schools ’éĘ High-Schools ’éĘ Higher Education ’éĘ Corporate and Professional ’éĘ Students with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder(ADHD). 4. Who are the people behind these technologies? Long before the internet was launched, distance courses were being offered to provide students with education on particular subjects or skills. In the 1840ŌĆ▓s Isaac Pitman taught his pupils shorthand via correspondence. In 1924, the first testing machine was invented. This device allowed students to tests themselves. Then, in 1954, BF Skinner, a Harvard Professor, invented the ŌĆ£teaching machineŌĆØ, which enabled schools to administer programmed instruction to their students. It wasnŌĆÖt until 1960 however that the first computer based training program was introduced to the world. With the introduction of the computer and internet in the late 20th century, e-learning tools and delivery methods expanded. The first MAC in the 1980ŌĆ▓s enabled individuals to have computers in their homes, making it easier for them to learn about particular subjects and develop certain skill sets. In the 2000ŌĆ▓s, businesses began using e-learning to train their employees.
- 7. 5. Why these technologies are being used? For the following reason these technologies are being used: ’éĘ Cost effective and saves times as no tedious travelling. ’éĘ Learning 24/7, anywhere. ’éĘ It makes tracking of course progress(LMS). ’éĘ Convenience ’éĘ Best facilities for learning.(eg. Best Teachers) ’éĘ Query Solving ’éĘ Lectures missed can be viewed again. The concerns that arise with e-learning ’éĘ Isolation/Technology dependent. ’éĘ Health Related Concerns(like eyestrain, bad postures, and other physical problems). ’éĘ Technology failures like sun outage, downtime, system failure, etc. ’éĘ ItŌĆÖs discreet as everybody does not feel comfortable with e-learning. ’éĘ Computer cannot do everything. ’éĘ Power failure issues(especially in India). ’éĘ Internet Facility. ’éĘ IT Skills: ItŌĆÖs a bitter truth but many of CA students lack in basic IT Skills. 6. How these technologies are associated with CA Education? The technologies that are being used in CA Education a) Self-Paced Courses, a good initiative by ICAI in the form of LMS to provide good quality education uniformly across the country. The features of this LMS are: ’éĘ Multiplatform, Multi-Lingual, Multi-Facilities. ’éĘ Integrates all the levels of CA Education. ’éĘ Best Faculties. ’éĘ Bridges the geographical gaps. ’éĘ Separate ID for every student through which they can keep track of their courses. ’éĘ Quizzes. ’éĘ Detailed Summary about your track, quizzes, percentage completion of course. ’éĘ Downloadable study material, podcasts. ’éĘ A facility to provide the feedback. ’éĘ Blog Facility to interact with other students. Recently our institute has launched ŌĆ£ICAI Cloud CampusŌĆØ, which provides next generation interactive learning management system. It host Self-paced e-learning course discussed above, e- books, webcasts, real-time online mentoring to students and enables anywhere and anytime learning. It also hosts video/ audio lectures, articles training resources, articles placement portal, Board of Studies knowledge portal, examination portal, etcs. The Best thing that ICAI has done is providing all these things to the students free of cost which brings all the students at par. ICAI Cloud Campus also contains softcopy of study materials practice manuals, podcasts, powerpoint presentations, BOS announcements, all are downloadable for the students.
- 8. Above mentioned is the example of Online Self-Paced Courses. ICAI has already launched the offline self-paced package in the form of CPT Test Exam Simulation. b) Social Networking/Group Discussions With the advancement of social networking from 2004 onwards, many social networking websites came forwards like CACLUBINDIA, TAXGURU, CACLUB, FACEBOOK, TWEETER, etc. How do students & teachers use Social Networking outside of the traditional meeting & learning space? Types of students activities observed on social networking sites pages are either Administrator-driven or Mentee-driven. Mentor activities are also prevalent on the page & were driven by either mentor or mentee. Examples of Facebook page. ’éĘ Students Activities ’é¦ Respond to prompts/facebook activities(Administer driven activity): ŌĆ£How was Today's PAPER?ŌĆØ, ŌĆ£2 months left guys, start studying.ŌĆØ ’é¦ Ask questions about course (Mentee-driven activity): ŌĆ£Where can I join classes for CPT?ŌĆØ ’éĘ Mentor Activities ’é¦ Respond to Students question ŌĆ£Refer Class Page No. 453ŌĆØ ’é¦ Provide Resources: ŌĆ£Amendments for Nov. 14 available for download.ŌĆØ The only thing that a student need is self-motivation to get best out of it; else a student may end up in array by wasting time and getting confused. c) Virtual Classes/ Satellite Learning: (Discussed above) INFERENCE Technology change the way of CA education and make it easy for the students to learn even sitting at home. Everything has two sides but really our technology proves a beneficial component to all the CA students and credit goes to ICAI for implementing online portals and classes to CA students.





































![Whats Possible With Educational Technology With Notes2 Distributed [Autosaved]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/whats-possible-with-educational-technologywithnotes2-distributed-autosaved-1226049786579155-8-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
























