Tempi semplici
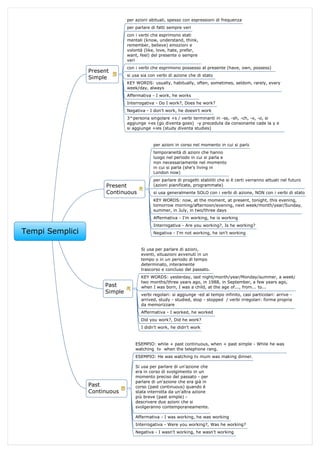
- 1. Tempi Semplici Present Simple per azioni abituali, spesso con espressioni di frequenza per parlare di fatti sempre veri con i verbi che esprimono stati mentali (know, understand, think, remember, believe) emozioni e volontà (like, love, hate, prefer, want, feel) del presente o sempre veri con i verbi che esprimono possesso al presente (have, own, possess) si usa sia con verbi di azione che di stato KEY WORDS: usually, habitually, often, sometimes, seldom, rarely, every week/day, always Affermativa - I work, he works Interrogativa - Do I work?, Does he work? Negativa - I don't work, he doesn't work 3^persona singolare +s / verbi terminanti in -ss, -sh, -ch, -x, -o, si aggiunge +es (go diventa goes) -y preceduta da consonante cade la y e si aggiunge +ies (study diventa studies) Present Continuous per azioni in corso nel momento in cui si parla temporaneità di azioni che hanno luogo nel periodo in cui si parla e non necessariamente nel momento in cui si parla (she's living in London now) per parlare di progetti stabiliti che si è certi verranno attuati nel futuro (azioni pianificate, programmate) si usa generalmente SOLO con i verbi di azione, NON con i verbi di stato KEY WORDS: now, at the moment, at present, tonight, this evening, tomorrow morning/afternoon/evening, next week/month/year/Sunday/ summer, in July, in two/three days Affermativa - I'm working, he is working Interrogativa - Are you working?, Is he working? Negativa - I'm not working, he isn't working Past Simple Si usa per parlare di azioni, eventi, situazioni avvenuti in un tempo o in un periodo di tempo determinato, interamente trascorso e concluso del passato. KEY WORDS: yesterday, last night/month/year/Monday/summer, a week/ two months/three years ago, in 1988, in September, a few years ago, when I was born, I was a child, at the age of..., from... to... verbi regolari: si aggiunge -ed al tempo infinito, casi particolari: arrive - arrived, study - studied, stop - stopped / verbi irregolari: forma propria da memorizzare Affermativa - I worked, he worked Did you work?, Did he work? I didn't work, he didn't work Past Continuous ESEMPIO: while + past continuous, when + past simple - While he was watching tv when the telephone rang. ESEMPIO: He was watching tv mum was making dinner. Si usa per parlare di un'azione che era in corso di svolgimento in un momento preciso del passato - per parlare di un'azione che era già in corso (past continuous) quando è stata interrotta da un'altra azione più breve (past simple) - descrivere due azioni che si svolgeranno contemporaneamente. Affermativa - I was working, he was working Interrogativa - Were you working?, Was he working? Negativa - I wasn't working, he wasn't working