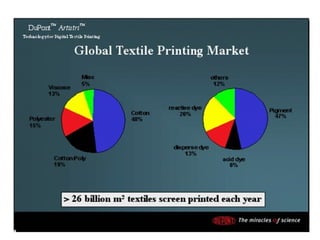
textile printing
- 1. A JOURNEY INTO THE WORLD OF PRINTING By:- AIBA KUSHAL SWETA
- 2. • Printing can also be defined as localized dyeing. • Defined as the application of dye or pigment in a different pattern on the fabric and by subsequent after treatment of fixing the dye or pigment to get a particular design. • Sometimes a printed fabric can be identified by looking at the back side of fabric where there is no design or color as face side. • In cotton, dyes like vat, reactive are used • In manmade, dyes like disperse and cationic are used
- 4. DIFFERENT STYLES OF PRINTING There are three basic approaches to printing a color on a fabric 1. DIRECT PRINTING 2. DISCHARGE PRINTING 3. RESIST PRINTING
- 5. DIRECT PRINTING • In this type of printing dye is applied onto the fabric by carved block, stencil, screen, engraved roller etc. • The dye is imprinted on the fabric in paste form and any desired pattern may be produced • Example:-Block Printing, Roller Printing, Screen Printing etc.
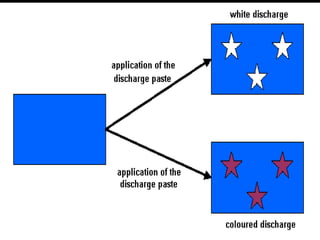
- 9. DISCHARGE PRINTING • In this method the fabric is dyed and then printed with a chemical that will destroy the color in designed areas. • Sometimes the base color is removed and another color printed in its place.
- 13. RESIST PRINTING • In this method bleached fabric are printed with a resist paste ( a resinous substance that cannot be penetrated when the fabric is immersed in a dye ). • The dye will only affect only the parts that are not covered by the resist paste . • After the fabric has passed through a subsequent dyeing process the resist paste is removed, leaving a pattern on a dark background
- 14. DIFFERENT TYPES OF PRINTING • BLOCK PRINTING • ROLLER PRINTING • SCREEN PRINTING • FLAT-SCREEN PRINTING • ROTARY PRINTING • TRANSFER PRINTING • STENCIL PRINTING • DIGITAL PRINTING • BATIK PRINTING • TIE & DYE
- 15. BLOCK PRINTING • It is the oldest and simplest way of printing • In this method a wooden block with a raised pattern on the surface was dipped into the printing colorant and then pressed face down on to fabric. • The desired pattern was obtained by repeating the process using different colors. • Generally the wooden block is carved out of hand • Printing is done manually
- 16. BLOCK PRINTING
- 17. BLOCK PRINTING
- 18. BLOCK PRINTING
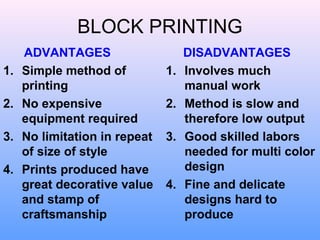
- 19. BLOCK PRINTING ADVANTAGES DISADVANTAGES 1. Simple method of 1. Involves much printing manual work 2. No expensive 2. Method is slow and equipment required therefore low output 3. No limitation in repeat 3. Good skilled labors of size of style needed for multi color 4. Prints produced have design great decorative value 4. Fine and delicate and stamp of designs hard to craftsmanship produce
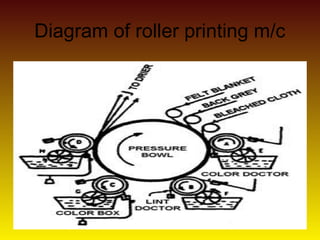
- 20. ROLLER PRINTING • It is the machine method of printing designs on cloths by engraved rollers. • The design is engraved on the surface of a metal roller, to which dye is applied, and the excess is scraped off the roller's surface, leaving dye in the engraved sections. When it rolls across the fabric, the dye on the roller transfers to the fabric.
- 21. Diagram of roller printing m/c
- 23. ROLLER PRINTING
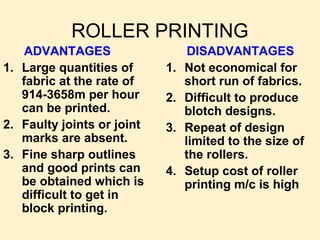
- 24. ROLLER PRINTING ADVANTAGES DISADVANTAGES 1. Large quantities of 1. Not economical for fabric at the rate of short run of fabrics. 914-3658m per hour 2. Difficult to produce can be printed. blotch designs. 2. Faulty joints or joint 3. Repeat of design marks are absent. limited to the size of 3. Fine sharp outlines the rollers. and good prints can 4. Setup cost of roller be obtained which is printing m/c is high difficult to get in block printing.
- 25. STENCIL PRINTING • It is one of the oldest way of printing. • In it color is applied to the fabric by brushing or spraying the interstices of a pattern cut out from a flat sheet of metal or waterproof paper or plastic sheet or laminated sheet. • A stencil is prepared by cutting out a design from a flat sheet of paper, metal, or plastic.
- 26. A simple stencil design
- 27. Example of stencil printing
- 28. STENCIL PRINTING • ADVANTAGES • DISADVANTAGES 1. Simple and cost 1. Good design is effective. difficult to obtain. 2. Stencils can be 2. Process is laborious. made rapidly and 3. Not suitable for large can be used for scale production. small orders. 3. Color combination is good in it.
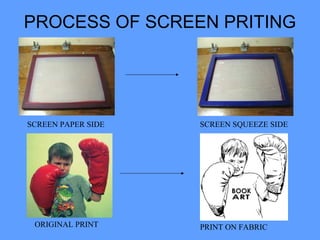
- 29. SCREEN PRINTING • It involves the application of the printing paste through a fine screen placed in contact with the fabric to be printed. • A design is created in reverse on the screen by blocking areas of the screen with a material such as an opaque paint. • The screen is then placed over the fabric and the printing paste is forced through the open areas of the screen using a flexible synthetic rubber or steel blade known as a squeegee.
- 30. PROCESS OF SCREEN PRITING SCREEN PAPER SIDE SCREEN SQUEEZE SIDE ORIGINAL PRINT PRINT ON FABRIC
- 34. SCREEN PRINTING • ADVANTAGES • DISADVANTAGES 1. Simple and cost 1. For high production effective. large no. of tables 2. Quick pattern required. making 2. Delicate shading 3. 16 colors can be difficult to obtain. used in a design. 3. Screen clogging 4. Sharp lines and may be there in fine features easily areas. produced.
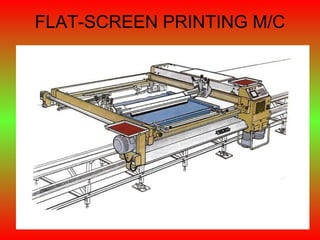
- 35. FLAT-SCREEN PRINTING • It is the advanced version of screen printing by using automatic m/c to do work • It consists of printing table, conveyor belt, number of screens, mechanism to print on the fabric, etc. • First the fabric is brought on the printing table through a feeding arrangement and it is gummed to the conveyor belt on the table
- 36. • Conveyor brings fabric periodically under screen and stops while the screen are lowered on the required parts of the fabric. • Printing paste is distributed throughout the full length of the screen. • The squeeze is pressed to the screen . • One or more strokes of the squeeze ensure simultaneous printing of the pattern by the common action of all screens which applies printing paste as required by the color in the design.
- 38. FLAT SCREEN PRINTING • ADVANTAGES • DISADVANTAGES 1. Greater production 1. A big setup required than manual screen for more number of printing screens 2. Printing with different 2. Prints with more repeat can be made colors may not be easily possible 3. Good print is 3. Printing paste not obtained evenly controlled
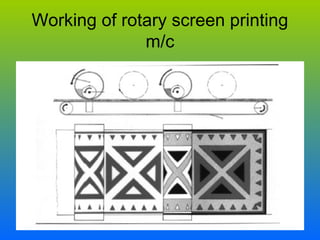
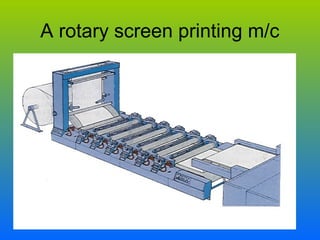
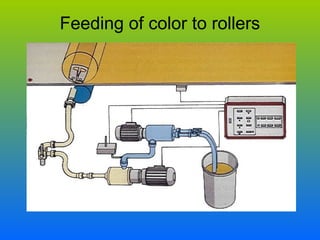
- 39. ROTARY SCREEN PRINTING • Rotary screen printing involves a series of revolving metal cylinder , each with revolving screens, each with a stationary squeegee inside which forces the print paste onto the fabric. • Twenty or more colours can be printed at the same time. • The process is much quicker and more efficient than flat screen printing .
- 40. Working of rotary screen printing m/c
- 41. A rotary screen printing m/c
- 42. Feeding of color to rollers
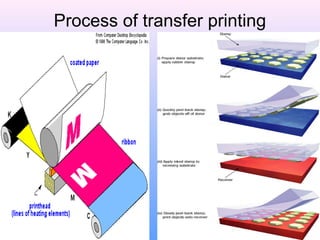
- 43. TRANSFER PRINTING • It is a indirect method of printing in which dyes are transferred from paper to a thermoplastic fabric under controlled conditions of temperature, time and pressure. • The image is first engraved on a copper plate. • Then pigment is applied on these plates. • The image is then transferred to a piece of paper, with a layer of glue applied . • This is then placed on the fabric and heat and pressure applied which fixes the print onto fabric.
- 44. Process of transfer printing
- 46. TRANSFER PRINTING • ADVANTAGES • DISADVANTAGES 1. Operation is simple 1. Process applicable and no expensive to synthetic fabric m/c is required. like polyester . 2. No after treatment of 2. Color range is fabric required limited. 3. Print on fabric is of 3. Cost of printed excellent quality paper high. 4. Not economical for small orders.
- 47. RESIST PRINTING • There are two types of resist printing • BATIK PRINTING • TIE & DIE PRINTING
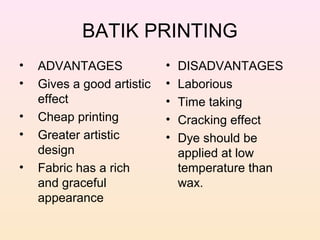
- 48. BATIK PRINTING • Originated on island of Java and is a cottage based industry. • Batik is derived from word “AMBATIK” • The resist-dyeing process, whereby designs are made with wax on a fabric which is subsequently immersed in a dye to absorb the color on the unwaxed portions, is known as batik printing. • Special feature is the fine lines of color running irregularly across the fabric.
- 51. BATIK PRINTING • ADVANTAGES • DISADVANTAGES • Gives a good artistic • Laborious effect • Time taking • Cheap printing • Cracking effect • Greater artistic • Dye should be design applied at low • Fabric has a rich temperature than and graceful wax. appearance
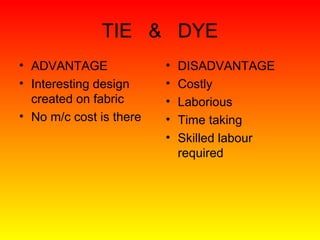
- 52. TIE & DYE • It is same as that of batik printing but here the dye is resisted by knots that are tied in the cloth before it is immersed in dye bath. • The outside of the knotted portion is dyed, but inside is not penetrated if the knot is firmly tied. • This gives a characteristic blurred or mottled effect .
- 54. TIE & DYE • ADVANTAGE • DISADVANTAGE • Interesting design • Costly created on fabric • Laborious • No m/c cost is there • Time taking • Skilled labour required
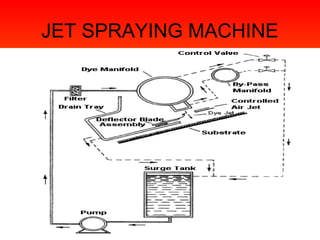
- 55. DIGITAL PRINTING • It is the more advanced type of printing. • This includes :- Jet spray printing Electrostatic printing Photo printing Differential printing
- 59. PRINTS
- 60. CLASSICAL Also known as ethnic or traditional print. In this print classical motifs or traditional collections are used such as mango, elephant with the chariots, old musical instruments etc. the culture of any particular place can also be considered such as tie and dye , batik, block of Rajasthan etc
- 61. FLORAL PRINT It has the print of varieties of flower either in bunch or single spotted , huge or small , combination of leaves and other addings. Color combination is very important.
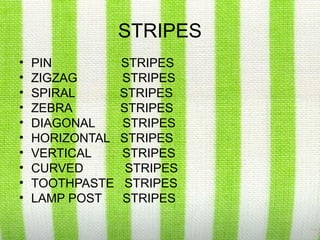
- 62. STRIPES • PIN STRIPES • ZIGZAG STRIPES • SPIRAL STRIPES • ZEBRA STRIPES • DIAGONAL STRIPES • HORIZONTAL STRIPES • VERTICAL STRIPES • CURVED STRIPES • TOOTHPASTE STRIPES • LAMP POST STRIPES
- 63. PIN STRIPES • THESE ARE STRIPES WHICH IS PRINTED LINES AT HAIRY DISTANCE AND MOSTLY TWO OR THREE COLORS ARE USED INCLUDING THE BACKGROUND.
- 64. ZIGZAG STRIPES • IT CAN COME IN HORIZONTAL OR VERTICAL BUT IN THE SHAPE OF ZIGZAG.
- 65. SPIRAL STRIPES • THE PRINT LOOKS LIKE A STRETCHED SPRING AT MEDIUM PRESSURE, THIS CAN EITHER BE VERTICAL OR HORIZONTAL.
- 66. CURVED STRIPES • THIS PRINT HAS THE EFFECT OF A WAVE FOLLOWED EITHER VERTICAL/HORIZONTAL.
- 67. TOOTHPASTE STRIPE • THIS STRIPE CAN BE MULTICOLORED AND THE DISTANCE CAN VARY BUT THE WIDTH OF EACH STRIPE SHOULD BE RANGING FROM 0.5-1.5CMS THE WIDTH OF THE TOOTHPASTE.
- 68. ZEBRA STRIPES • IN THIS STRIPES ONLY TWO COLORS ARE USED AND MOSTLY NEUTRAL COLORED SCHEME IS SEEN . • THESE STRIPES ARE PLACED AT EQUIDISTANCE. • THE WIDTH OF EACH STRIPE WILL NOT BE MORE THAN 1.0CM
- 69. LAMP POST STRIPE • THE WIDTH STARTS FROM 3-5CM. • IT CAN BE COMPOUND STRIPES. • THE PRINT HAS RUNNING LINES OF FIXED WIDTH.
- 70. CHECK PRINTS • THESE ARE GOT BY INTERSECTING HORIZONTAL AND VERTICAL LINES AT 90 DEG ANGLES. • IT IS OF 4 – TYPES • PLAIDS • MADRAS CHECK • BOMBAY CHECK • OXFORD CHECK
- 71. PLAIDS • PLAIDS ARE SIMPLE CHECK WHERE ALL THE SQUARES ARE OF EQUAL SIZE AND IT HAS THE COMBINATION OF ANY TWO COLORS WHICH ARE MOSTLY USED FOR SCHOOL UNIFORMS. • LOOKS LIKE THE CHECKS IN A CHESS BOARD
- 72. MADRAS CHECK • IT HAS GOT NO MORE THAN 2 OR 3 VERTICAL STRIPES WITH EQUAL(SINGLE) HORIZONTAL STRIPES. • COLORS USED BLUE, RED, ORANGE, ETC • USED FOR LUNGIS, BURMUDAS AND COATS
- 73. BOMBAY CHECKS • THESE CHECKS ARE MOSTLY AVAILABLE IN LIGHT COLORS. • HERE NO PROPER NUMBER OF STRIPES CAN BE COUNTED EITHER HORIZONTALLY OR VERTICALLY BUT STRIPES ARE VERY CLOSELY PRINTED • USED IN SHIRTS
- 74. OXFORD CHECK • THIS IS FOUND IN DARK COLORS WITH WHITE COMBINATION. • HERE THE STRIPES PRINTED HORIZONTALLY WILL BE EQUAL TO THE STRIPES PRINTED VERTICALLY AND AT EQUAL THICKNESS PLACED AT EQUIDISTANCE • USED IN UNIFORMS, MAT, BED COVERS, DRAPERIES ETC
- 75. DOTS • THESE ARE SPOTS EITHER DESIGNED OR PLAIN IN DIFFERENT COLORS • 3 – TYPES • BIG DOTS(3-10CM) • SMALL DOTS(PIN- 1.5CM) • POLKA DOTS(MIXTURE OF ABOVE)
- 76. GEOMETRICAL PRINTS • THIS IS THE PRINT WHERE ALL THE GEOMETRICAL INSTRUMENT DESIGNS ARE CREATED AND THE MATHEMATICAL SIGNS ARE USED SUCH AS PLUS, MINUS, MULTIPLICATION DIVISION ETC.
- 77. DIRECTIONAL PRINTS • ANY PRINT WHICH IS DESIGNED DIRECTIONALLY EITHER HORIZONTAL, VERTICAL OR DIAGONAL IS CALLED THE DIRECTIONAL PRINTS. • ITS FEATURE IS TO FOLLOW THE DIRECTION OF THE FIRST ONE. • USED IN EGYPTIAN DRESS
- 78. SELF PRINTS • ANY DESIGN WHICH HAS TO BE PRINTED SHOULD BE OF THE SAME SHADES OF THE BACKGROUND COLOR. • RUBBER PRINT
- 79. COMPUTERISED PRINT • THE DESIGN IS TAKEN FROM COMPUTER GRAPHIC DESIGN AND VIDEO GAMES . • CAN BE USED FOR CHILDREN AND TEENAGERS.
- 80. WILD PRINT • THE EFFECT OF FOREST WITH OR WITHOUT ANIMALS, NATURE ARE USED IN THIS PRINT • MOSTLY DULL COLORS ARE USED.
- 81. ANIMAL PRINT • THE IMPORTANCE IS GIVEN TO THE SKIN TEXTURE OF THE ANIMALS AND THEIR PRINTS SUCH AS ZEBRA, CHEETAH, TIGER, DEER, SNAKE ETC
- 82. ABSTRACT PRINT • THIS PRINT IS MADE USING IRREGULAR SHAPES WITH MATCHING COLOR SCHEME.
- 83. NUMERICAL PRINT • HERE THE NUMBER 0-9 ARE USED. • SOME TIMES WITH OR WITHOUT MATHEMATICAL SIGNS
- 84. ALPHABETICAL PRINTS • THIS PRINT IS MADE USING ALPHABETS, WORDINGS ETC • EG: NEWSPAPER PRINT
- 85. CHILDREN PRINT • THE PRINT CONSISTS OF DESIGNS WHICH CAN EMPHASIZE THE CHILDREN”S MOOD SUCH AS CARTOONS, CHOCLATES, FRUITS, ICE CREAM ETC
- 86. PHOTO PRINT • THE PHOTOS OF THE FAMOUS STARS, POP SINGERS, OLD CARS ETC ARE PRINTED ON T-SHIRTS WHICH ARE CALLED PHOTOPRINT
- 87. MARBLE PRINT • THIS PRINT LOOKS LIKE A MARBLE FINISH