Thalamus
- 1. THALAMUS DR. ANITA CHOUDHARY PROFESSOR &H.O.D R.D.G.M.C Ujjain
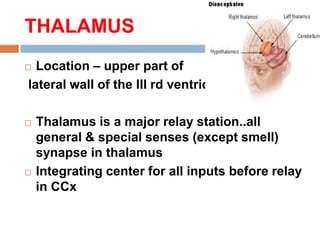
- 2. THALAMUS  Location – upper part of lateral wall of the III rd ventricle.  Thalamus is a major relay station..all general & special senses (except smell) synapse in thalamus  Integrating center for all inputs before relay in CCx
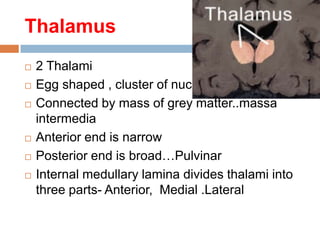
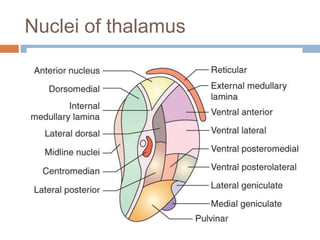
- 3. Thalamus  2 Thalami  Egg shaped , cluster of nuclei  Connected by mass of grey matter..massa intermedia  Anterior end is narrow  Posterior end is broad…Pulvinar  Internal medullary lamina divides thalami into three parts- Anterior, Medial .Lateral
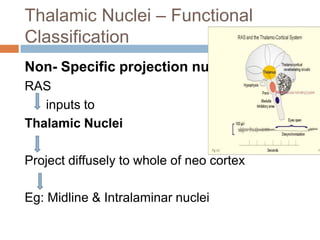
- 5. Thalamic Nuclei – Functional Classification Non- Specific projection nuclei RAS inputs to Thalamic Nuclei Project diffusely to whole of neo cortex Eg: Midline & Intralaminar nuclei
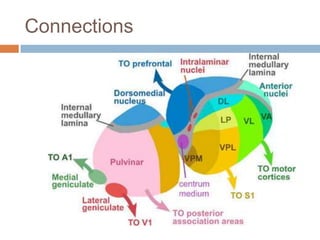
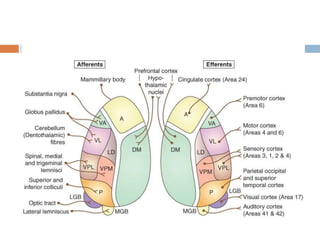
- 6. Connections
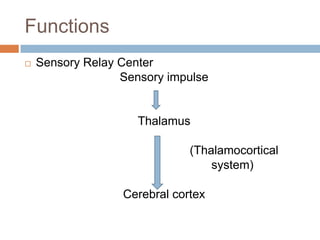
- 8. Functions ÔÇ® Sensory Relay Center Sensory impulse Thalamus (Thalamocortical system) Cerebral cortex
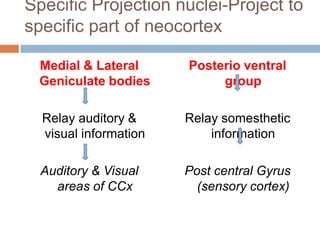
- 9. Specific Projection nuclei-Project to specific part of neocortex Medial & Lateral Geniculate bodies Relay auditory & visual information Auditory & Visual areas of CCx Posterio ventral group Relay somesthetic information Post central Gyrus (sensory cortex)
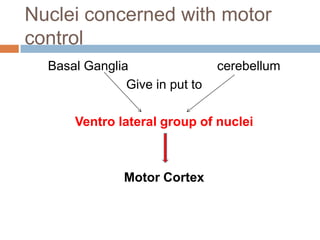
- 10. Nuclei concerned with motor control Basal Ganglia cerebellum Give in put to Ventro lateral group of nuclei Motor Cortex
- 11. Nuclei concerned with memory & emotions Mammilary bodies give inputs to Anterior group of nuclei Limbic cortex Recent memory & emotions
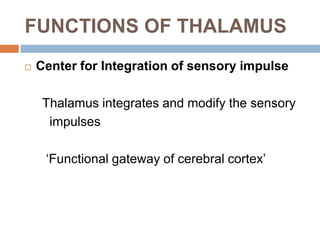
- 12. FUNCTIONS OF THALAMUS  Center for Integration of sensory impulse Thalamus integrates and modify the sensory impulses ‘Functional gateway of cerebral cortex’
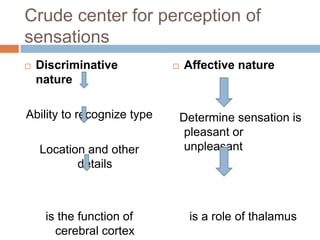
- 13. Crude center for perception of sensations ÔÇ® Discriminative nature Ability to recognize type Location and other details is the function of cerebral cortex ÔÇ® Affective nature Determine sensation is pleasant or unpleasant is a role of thalamus
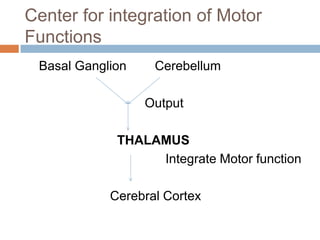
- 14. Center for integration of Motor Functions Basal Ganglion Cerebellum Output THALAMUS Integrate Motor function Cerebral Cortex
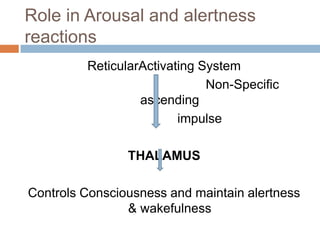
- 15. Role in Arousal and alertness reactions ReticularActivating System Non-Specific ascending impulse THALAMUS Controls Consciousness and maintain alertness & wakefulness
- 16. Role in emotional aspect of behavior  As it is a part of Limbic system (Papez circuit)  Recent memory and Emotions  Role in language – Cortical and Sub-cortical connections Speech
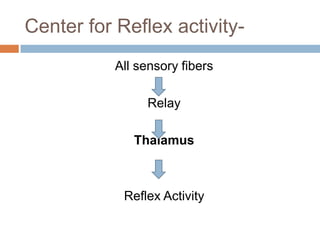
- 17. Center for Reflex activity- All sensory fibers Relay Thalamus Reflex Activity
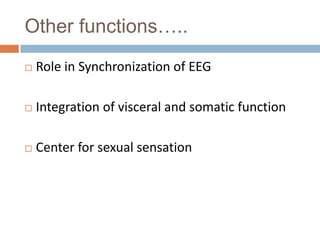
- 18. Other functions…..  Role in Synchronization of EEG  Integration of visceral and somatic function  Center for sexual sensation
- 19. THALAMIC SYNDROME Disturbance of emotional response to sensory experience Cause : Blockage of thalamogeniculate branch of posterior cerebral artery ÔÇ® Damage of Ventro-posterior lateral nuclei(VPL) ÔÇ® Damage of Ventro- posterior medial nuclei (VPM)
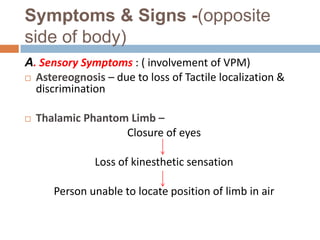
- 20. Symptoms & Signs -(opposite side of body) A. Sensory Symptoms : ( involvement of VPM)  Astereognosis – due to loss of Tactile localization & discrimination  Thalamic Phantom Limb – Closure of eyes Loss of kinesthetic sensation Person unable to locate position of limb in air
- 21.  Thalamic Over reaction : Decrease Threshold for Pain, touch and temperature- exaggerated & disagreeable sensation  Amelognosia – Illusion felt by patients that his limb is absent
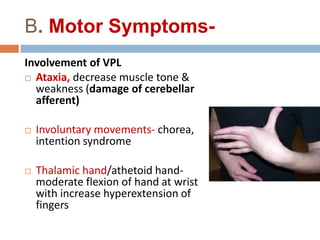
- 22. B. Motor Symptoms- Involvement of VPL ÔÇ® Ataxia, decrease muscle tone & weakness (damage of cerebellar afferent) ÔÇ® Involuntary movements- chorea, intention syndrome ÔÇ® Thalamic hand/athetoid hand- moderate flexion of hand at wrist with increase hyperextension of fingers
- 23. Korsakoff’s Syndrome  Refers to lesion of MEDIODORSAL NUCLEUS of thalamus Characteristic feature:  Difficult to remember new information
- 24. Frontal lobectomy ÔÇ® Connection of dorsal nuclei of thalamus with frontal lobe is surgically removed ÔÇ® For relief of unbearable pain
- 25. THANK YOU