The internet
- 2. ? It is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet Protocol Suite (TCP/IP) to serve billions of users worldwide. ? It is a network of networks that consists of millions of private, public, academic, business, and government networks of local to global scope that are linked by a broad array of electronic and optical networking technologies.
- 3. ? Easy access to sources of healthcare information. ? Constant source of up-to-date professional information. ? Helps in the expansion of nursing care standards from community and regional to national and international.
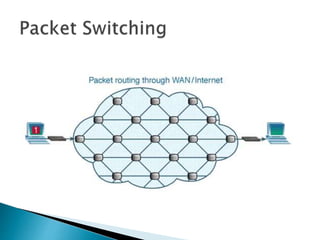
- 4. ? Conceptualized in the year 1957 during the launch of USSR’s project Sputnik. ? Creation of the Advanced Research Project Agency (ARPA) by President Eisenhower. ? It’s primary purpose is for the US to be able to communicate after a nuclear war. ? The plan was to devise a network that had no central authority and could be accessed at all times. ? Utilized the devised known as “packet switching” which was invented by Paul Barran.
- 6. ? In 1962, Dr. J.C.R. Licklider was chosen to lead the research to improve military use of computer technology thus they coined the ARPANET. ? The ARPANET stabilized the use of the net by providing security against interruption of communication, it also provided convenient service to scientists and researchers, allowing them to share were then scarce computer resources. ? In 1973 Vin Cerf and Bob Kahn, lead the creation of Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and the Internet Protocols.
- 7. ? The Internet Society (ISOC) is the overall organizing force that works behind the technology of the internet. ? It is an international, non-profit, professional membership organization with no governmental allegiances. ? The society works to maintain standards, develop public policy, provide education, and increase membership.
- 8. ? The functionality of the internet depends on the standardized communication protocols. ? Protocols determine how data will be transmitted between two devices, the type of error checking that will be performed, how data compression, if any is accomplished, how the sending computer will signal that it has finished sending a message, and how the receiving computer will signal that it has received a message.
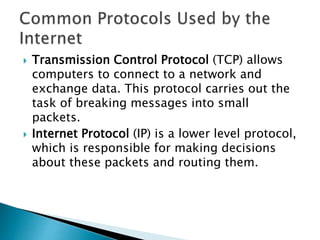
- 9. ? Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) allows computers to connect to a network and exchange data. This protocol carries out the task of breaking messages into small packets. ? Internet Protocol (IP) is a lower level protocol, which is responsible for making decisions about these packets and routing them.
- 10. ? Hypertext Transmission Protocol (HTTP), supports the World Wide Web(WWW). ? File Transmission Protocol (FTP) permits users to send all types of electronic files over the internet. ? Telnet allows users to access a distant computer.
- 11. ? It is a way of identifying other computers to perform the tasks required of them. ? Paul Mockapetris – the pioneer in the protocols that allow the DNS to work. ? Series of characters (usually letters) make up a domain name. (also called strings or labels) ? Right most label in a domain name is the “top level domain” (TLD)
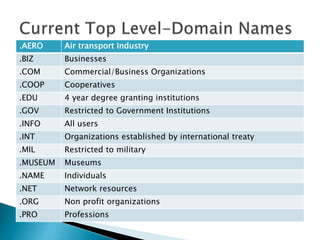
- 12. .AERO Air transport Industry .BIZ Businesses .COM Commercial/Business Organizations .COOP Cooperatives .EDU 4 year degree granting institutions .GOV Restricted to Government Institutions .INFO All users .INT Organizations established by international treaty .MIL Restricted to military .MUSEUM Museums .NAME Individuals .NET Network resources .ORG Non profit organizations .PRO Professions
- 13. ? It is a method of exchanging digital messages. ? E-mail systems are based on a store-and- forward model in which e-mail server computer systems accept, forward, deliver and store messages on behalf of users, who only need to connect to the e-mail infrastructure, typically an e-mail server, with a network-enabled device for the duration of message submission or retrieval.
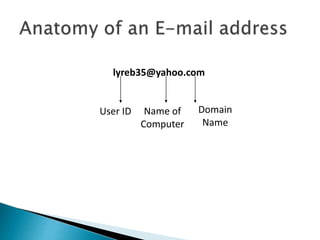
- 14. Name of Computer lyreb35@yahoo.com User ID Domain Name
- 15. ? Use Computer Courtesy ? Use Emoticons ? Be Brief Online ? DON’T SHOUT ? Pay Attention to Language Issues ? Think Before Posting ? Keep Personal Information Private ? Obey Copyright Laws ? Help Internet Newbies ? Be Aware of Cyberbullying
- 16. ? Credibility ? Content ? Disclosure ? Links ? Design ? Interactivity ? Caveats
- 18. Code of Ethics for Nurses affirms that the nurse “holds in confidence personal information” and “ensures that the use of technology… (is) compatible with the safety, dignity, and rights of the people.” (ICN, 2000)
- 19. Dependability is a measure of the extent to which a system can justifiably be relied on to deliver the services expected from it.
- 20. 1. System Reliability: The System consistently behaves in the same way. 2. Service availability: Required services are present and usable when they are needed. 3. Confidentiality: Sensitive to information is disclosed only to those authorized to see it. 4. Data integrity: Data are not corrupted or destroyed. 5. Responsiveness: The system responds to user input within an expected and acceptable time period. 6. Safety: The system does not cause harm
- 21. Guideline 1: Architect for Dependability Guideline 2: Anticipate Failures Guideline 3: Anticipate Success Guideline 4: Hire Meticulous Managers Guideline 5: Don’t Be Adventurous
- 22. “Administrative, physical, and technical safeguards should be followed to protect the confidentiality and integrity of health information and the availability of critical system services.”
- 23. 1. Security Management, including security analysis and risk management. 2. Assigned security responsibility. 3. Information access management, including the isolation of clearinghouse functions from other clinical functions. 4. Security awareness and training.
- 24. 5. Security incident procedures, including response and reporting. 6. Contingency planning, including data backup planning, disaster recovery planning, and planning for emergency mode operations. 7. Evaluation 8. Business Associate Contracts
- 25. 1. Access control, including unique user identification and an emergency access procedure. 2. Audit Controls 3. Data Integrity Protection 4. Person or entity authentication 5. Transmission Security
- 26. 1. Define the Internet 2. Give 2 important protocols used by the internet 3. Give at least 3 internet etiquettes. 4. Give at least 2 attribute of a dependable system.
- 28. ? It identifies essential, common, and core data elements to be collected for all patients/clients receiving nursing care. ? It is a standardize approach that facilitates the abstractions of these minimum, common, essential core data elements to describe nursing practice from both paper and electronic records.
- 29. ? It is intended for use in all settings where nurses provide care in acute care, ambulatory centers, home healthcare, community practices, occupational health, and school health. ? The aim of the NMDS is not to be redundant of other data sets, but rather to identify what are the minimal data needed to be collected from other records of patients receiving nursing care.
- 30. 1. Nursing Care 2. Patient or Client Demographics 3. Service Elements
- 31. 1. Nursing Diagnosis 2. Nursing Intervention 3. Nursing Outcomes 4. Intensity of Nursing Care
- 32. 1. Personal Identification 2. Date of Birth 3. Sex 4. Race and Ethnicity 5. Residence
- 33. ? Unique facility or service agency number ? Unique health record number or patient or client ? Unique number of principal registered nurse provider ? Episode admission or encounter date ? Discharge or termination date ? Disposition of patient or client ? Expected payer for most of this bill
- 34. 1. Access to comparable, minimum nursing care, and resources data on local, regional, national, and international levels. 2. Enhanced documentation of nursing care provided. 3. Identification of trends related to patient or client problems and nursing care provided. 4. Impetus to improved costing of nursing services
- 35. 5. Improved data for quality assurance evaluation 6. Impetus to further development and refinement of NI’s. 7. Comparative research on nursing care, including research on nursing diagnosis, nursing interventions, nursing outcomes, intensity of nursing care, and referral for further nursing services. 8. Contribution toward advancing nursing as a research-based discipline.