The management of organizational information
- 1. EysteinMathisenHHBTirsdag 27. september, 2011The management of organizational informationManaging information resources and information practices20.09.20111Information & Information Management
- 2. Information and information managementInformation is an intrinsic part of nearly everything that an organization does, especially in connection with decision making. Two essential functions:it facilitates communication and coordination between different parts of the organization (its sub-systems), and between the organization and its environment;it provides a basis for informed decision-making at all levels of the organization20.09.20112Information & Information Management
- 3. Information and information management20.09.2011Information & Information Management3In today’s organizations it is necessary with a clear understanding of the organizational and human processes through which information becomes selected and expressed as insight, knowledge and action.without it an organization is unable to handle an increasingly complex environment.Some possible definitions:Information management: The management of the processes and systems that create, acquire, organize, store, distribute, and use information (i.e. an information value chain or information lifecycle).Information architecture: The structural design of shared information environments and information services.
- 4. Information and IT20.09.2011Information & Information Management4It is proposed that: information is the missing link between business and IT andinformation is a business resource, independent of the supporting IT and Information (being interpreted data) is, unlike IT and data an intangible asset.
- 5. Managing information resources and processes20.09.2011Information & Information Management5By managing information resources and information practices, an organization is able to: sense and respond to a changing environment, but also shape and influence changes in the environment that are advantageous; extend its base of knowledge and capabilities, but also unlearn old assumptions and beliefs; make decisions that are sometimes rational and sometimes creative in order to meet increasingly complex challenges;
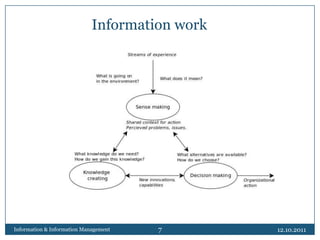
- 6. Information work20.09.2011Information & Information Management6Information work in organizations, generally, aims at accomplishing three outcomes:create a shared context for action and reflection - sense makingdevelop new knowledge and new capabilities - knowledge creationmake decisions that commit resources and capabilities to purposeful action - decision making
- 7. 20.09.2011Information & Information Management7Information work
- 8. Information work20.09.2011Information & Information Management8The coordinated management of these three activities may be termed information governance:Information governance involves establishing an environment and opportunities, rules and decision-making rights for the valuation, creation, collection, analysis, distribution, storage, use and control of information;it answers the question “what information do we need, how do we make use of it and who is responsible for it?”.