The periodic table presentation for 4050 [autosaved]
- 2. • Essential Standard 8.P.1: Understand the properties of matter and changes that occur when matter interacts in an open and closed container. • Clarifying Objective 8.P.1.2: Explain how the physical properties of elements and their reactivity have been used to produce the current model of the Periodic Table of elements.
- 3. Why is the periodic table important to • The periodic table is me? the most useful tool to a chemist. • It organizes lots of information about all the known elements.
- 4. The Arrangement of the Periodic Table •The elements are arranged in rows according to their atomic number and in columns according to their valence electrons or number of electrons in the outer shell. Elements in a given column have similar chemical characteristics. •A detailed periodic table typically gives information on the name, symbol, atomic Advance number, atomic weight, shell to page 5 configuration and other material.
- 5. The History of the Periodic Table Dmitri Mendeleev Lothar Meyer
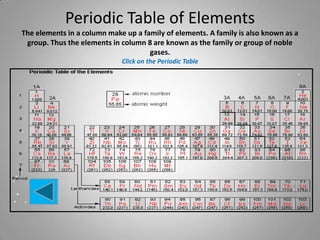
- 6. Periodic Table of Elements The elements in a column make up a family of elements. A family is also known as a group. Thus the elements in column 8 are known as the family or group of noble gases. Click on the Periodic Table
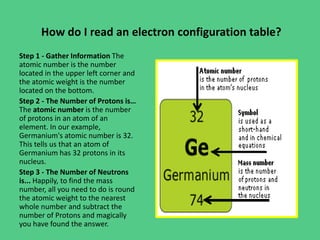
- 7. How do I read an electron configuration table? Step 1 - Gather Information The atomic number is the number located in the upper left corner and the atomic weight is the number located on the bottom. Step 2 - The Number of Protons is… The atomic number is the number of protons in an atom of an element. In our example, Germanium's atomic number is 32. This tells us that an atom of Germanium has 32 protons in its nucleus. Step 3 - The Number of Neutrons is... Happily, to find the mass number, all you need to do is round the atomic weight to the nearest whole number and subtract the number of Protons and magically you have found the answer.
- 8. Let us see what you have learned. Use the information provided to answer the questions. 2 5 11 17 He B Na Cl Helium Boron Sodium Chlorine 4.003 10.81 22.990 35.453 1. What is the atomic number for Chlorine? 2. What is the atomic mass for Boron? 3. How many protons are in an atom of Na? 4. How many neutrons are in an atom of He? 5. How many electrons are in an atom of Cl? 6. How many protons and neutrons would be in an atom of Chlorine? 7. How many neutrons are in an atom of Na? 8. How many protons and neutrons are in an atom of Helium?
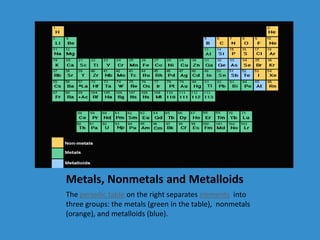
- 9. Metals, Nonmetals and Metalloids The periodic table on the right separates elements into three groups: the metals (green in the table), nonmetals (orange), and metalloids (blue).
- 10. Metals Most elements are metals. They Are usually shiny, very dense, and only Melt at high temperatures. Their shape can be easily changed into thin wires or sheets without breaking. Metals will corrode, Gradually Wearing away, like rusting iron. Heat And electricity travel easily through metals, which is why it is not wise to stand next a flagpole during a thunderstorm!
- 11. Nonmetals Nonmetals, on the right side of the periodic table, are very different from metals. Their surface is dull and they don’t conduct heat and electricity. As compared to metals, they have low density and will melt at low temperatures. The shape of nonmetals cannot be changed easily because they are brittle and will break.
- 12. Metalloids Elements that have properties of both metals and nonmetals are called metalloids.
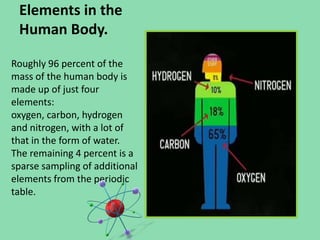
- 13. Elements in the Human Body. Roughly 96 percent of the mass of the human body is made up of just four elements: oxygen, carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen, with a lot of that in the form of water. The remaining 4 percent is a sparse sampling of additional elements from the periodic table.
- 14. Elements in the Earth’s surface. Even though there are 92 elements that are naturally found, only eight of them are common in the rocks that make up the Earth’s outer layer, the crust. Together, these 8 elements make up more than 98% of the crust. Together, the elements oxygen and silicon make up most of the Earth’s crust including silicate minerals such as quartz and feldspar.
- 15. Physical and Chemical Changes It is important to understand the difference between chemical and physical changes. Physical changes are about energy and states of matter. Chemical changes happen on a molecular level when you have two or more molecules that interact and create a new molecule or two.
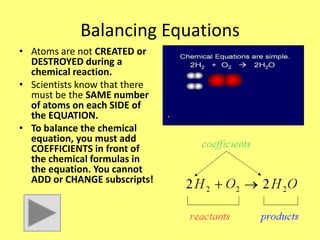
- 16. Balancing Equations • Atoms are not CREATED or DESTROYED during a chemical reaction. • Scientists know that there must be the SAME number of atoms on each SIDE of the EQUATION. • To balance the chemical equation, you must add COEFFICIENTS in front of the chemical formulas in the equation. You cannot ADD or CHANGE subscripts!
- 17. Balancing Act: Step-by-Step Example Problem: • Step 1: Determine number of atoms for each element. • Step 2: Pick an element that is not equal on both sides of the equation. • Step 3: Add a coefficient in front of the formula with that element and adjust your counts. • Step 4: Continue adding coefficients to get the same number of atoms of each element on each side.
- 18. Use the formulas provided to determine the number of atoms of each element in each compound. • 1. CO2 • List each element by symbol and tell how many atoms • 2. 2H2O there are in the compound. • 3. Mg(OH)2 • C = ____ O = ____ • 4. 3NaHCO3 • 5. 2H2SO4
- 19. The periodic table is the most important tool in the chemist’s toolbox!
- 20. References • http://www.tutorvista.com/content/science/science-ii/chemical- reactions-equations/chemical-change.php • http://www.tutorvista.com/content/science/science-ii/chemical- reactions-equations/physical-change.php http://sciencespot.net/Pages/startersphysci.html • http://www.chem4kids.com/files/matter_chemphys.html • http://www.chemistry.co.nz/mendeleev.htm • http://science.howstuffworks.com/dictionary/famous- scientists/chemists/julius-lothar-meyer-info.htm • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d0zION8xjbM
- 21. Mrs. K • On slide 5 is my voice recording and if you click on the pictures you will be directed to additional information. • On slide 6 if you click on the periodic table you will be directed to a youtube video. • On slide 9 if you click on the words periodic table and elements, you will be directed to additional information. • On slide 10 if you click on the word elements, you will be directed to additional information. • On slide 11 if you click on the word density, you will be directed to additional information. • On slide 15 if you click on the word states and both the pictures, you will be directed to additional information (websites).
Editor's Notes
- The pictures have hyperlinks

![The periodic table presentation for 4050 [autosaved]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theperiodictablepresentationfor4050autosaved-130327134237-phpapp02/85/The-periodic-table-presentation-for-4050-autosaved-1-320.jpg)