The solar system
- 1. UNIVERSIDAD NACIONAL ABIERTA Y A DISTANCIA ESCUELA DE CIENCIAS DE LA EDUCACIÃN . ECEDU DIDÃCTICA âĒ UNIDAD DIDÃCTICA: EL UNIVERSO âĒ TRABAJO PRESENTADO POR: âĒ JORGE ELIECER FERNÃNDEZ âĒ ALBERTO MORENO âĒ JOHN JADER CARMONA âĒ JAIME PULGARÃN âĒ BÃLMER ANTONIO GARCÃA
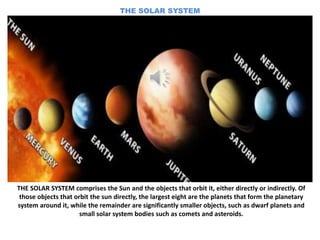
- 2. THE SOLAR SYSTEM THE SOLAR SYSTEM comprises the Sun and the objects that orbit it, either directly or indirectly. Of those objects that orbit the sun directly, the largest eight are the planets that form the planetary system around it, while the remainder are significantly smaller objects, such as dwarf planets and small solar system bodies such as comets and asteroids.
- 3. THE SUN The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System and is by far the most important source of energy for life on Earth. It is a nearly perfect spherical ball of hot plasma, with internal connective motion that generates a magnetic field via a dynamo process. Its diameter is about 109 times that of Earth, and it has a mass about 330000 times that of Earth, accounting for about 99.86% of the total mass of the Solar System. Chemically, about three quartes of the SunÂīs mass consists of hydrogen, whereas the rest is mostly helium, and much smaller quantities of heavier elements, including oxygen, carbon, neon, and iron.
- 4. MERCURY Mercury is the smallest and closest to the Sun of the eight planets in the Solar System, with an orbital period of about 88 Earth days. Seen from Earth, it appears to move around its orbit in about 116 days, which is much faster than any other planet in the Solar System. It has no known natural satellites. The planet is named after the Roman deity Mercury, the messenger to the gods.
- 5. VENUS Venus is the second planet from the Sun, orbiting it every 224.7 Earth days. It has no natural satellite. It is named after the Roman goddess of love and beauty. After the Moon, it is the brightest natural object in the night sky, reaching an apparent magnitude of â4.6, bright enough to cast shadows. Because Venus is an inferior planet from Earth, it never appears to venture far from the Sun: its elongation reaches a maximum of 47.8°.
- 6. EARTH Earth, also called the worldand, less frequently, Gaia (and Terra in some works of science fiction) is the third planet from the Sun, the densest planet in the Solar System, the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets, and the only astronomical object known to accommodate life. The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago. Earth's biodiversity has expanded continually except when interrupted by mass extinctions. Although scholars estimate that over 99 percent of all species that ever lived on the planet are extinct, Earth is currently home to 10â14 million species of life, including over 7.3 billion humans who depend upon its biosphere and minerals. Earth's human population is divided among about two hundred sovereign states which interact through diplomacy, conflict, travel, trade and communication media.
- 7. MARS Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second smallest planet in the Solar System, after Mercury. Named after the Roman god of war, it is often referred to as the "Red Planet" because the iron oxide prevalent on its surface gives it a reddish appearance. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin atmosphere, having surface features reminiscent both of the impact craters of the Moon and the volcanoes, valleys, deserts, and polar ice caps of Earth. The rotational period and seasonal cycles of Mars are likewise similar to those of Earth, as is the tilt that produces the seasons. Mars is the site of Olympus Mons, the largest volcano and second- highest Known Mountain in the Solar System, and of Valles Marineris, one of the largest canyons in the Solar System. The smooth Borealis basin in the northern hemisphere covers 40% of the planet and may be a giant impact feature. Mars has two moons, Phobos and Deimos, which are small and irregularly shaped. These may be captured asteroids.
- 8. JUPITER Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest planet in the Solar System. It is a giant planet with a mass one-thousandth of that of the Sun, but is two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined. Jupiter is a gas giant, along with Saturn (Uranus and Neptune are ice giants). Jupiter was known to astronomers of ancient times. The Romans named it after their god Jupiter. When viewed from Earth, Jupiter can reach an apparent magnitude of â2.94, bright enough to cast shadows, and making it on average the third-brightest object in the night sky after the Moon and Venus. (Mars can briefly match Jupiter's brightness at certain points in its orbit.)
- 9. SATURN Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius about nine times that of Earth. Although only one-eighth the average density of Earth, with its larger volume Saturn is just over 95 times more massive. Saturn is named after the Roman god of agriculture, its astronomical symbol (â) represents the god's sickle.
- 10. URANUS Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. It has the third-largest planetary radius and fourth- largest planetary mass in the Solar System. Uranus is similar in composition to Neptune, and both have different bulk chemical composition from that of the larger gas giants Jupiter and Saturn. Therefore, astronomers increasingly place them in a separate category called "ice giants".
- 11. NEPTUNE Neptune is the eighth and farthest planet from the Sun in the Solar System. It is the fourth- largest planet by diameter and the third-largest by mass. Among the gaseous planets in the Solar System, Neptune is the most dense. Neptune is 17 times the mass of Earth and is slightly more massive than its near-twin Uranus, which is 15 times the mass of Earth, and not as dense as Neptune.
- 12. BRAILLE READINGS THE SOLAR SYSTEM
- 13. THE SOLAR SYSTEM
- 14. THE SUN
- 15. THE SUN
- 16. THE SUN
- 17. MERCURY
- 18. MERCURY
- 19. VENUS
- 20. EARTH
- 21. EARTH
- 22. EARTH
- 23. EARTH
- 24. EARTH
- 25. MARS
- 26. JUPITER
- 27. SATURN
- 28. URANUS
- 29. NEPTUNE