Thermal properties of matter
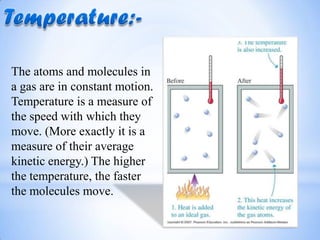
- 3. The atoms and molecules in a gas are in constant motion. Temperature is a measure of the speed with which they move. (More exactly it is a measure of their average kinetic energy.) The higher the temperature, the faster the molecules move.
- 4. Measurement Of temperature:- Temperature can be measured by the following devices:- Mercury Thermometer Ideal Gas Thermometer Pyrometer Electrical Resistance Thermometer
- 6. PV = nRT (Macroscopic Form) Basically says that the state of a gas is also dependent on the number of particles in the sample of gas. So, by adding a term for the number of moles of particles and proportionality constant ŌĆ£RŌĆØ to the combined gas law, we get Ideal Gas Law. ’é¦ŌĆ£nŌĆØ is the number of moles of the gas. ’é¦ŌĆ£RŌĆØ the Universal Gas Constant is the same for all gases.
- 7. The heat capacity C of an object is the heat energy needed to raise its temperature by 1 kelvin (or 1 degree celsius). When different substances undergo the same temperature change they can store or release different amounts of heat. Something with high heat capacity heats up slower and cools down faster. Heat Capacity = Q / T Q ŌĆō thermal energy (J) ╬öT ŌĆō temperature change (K)
- 8. Defined as the amount of thermal energy required to produce unit temperature rise in unit mass of the material.Unit mass is normally 1kg, and unit temperature rise is normally 1K Specific Heat Capacity = Q / (m T) Unit:-J kg-1 K-1,where m is the mass of the material
- 11. Calorimetry means measurement of heat.When a body at higher temperature is brought in contact with another body at lower temperature, the heat lost by the hot body is equal to the heat gained by the colder body, provided no heat is allowed to escape to the surroundings. A device in which heat measurement can be made is called a calorimeter.
- 12. The change of state from solid to liquid is called melting and from liquid to solid is called fusion. The temperature at which the solid and the liquid states of the substance in thermal equilibrium with each other is called its melting point. The melting point of a substance at standard atomspheric pressure is called its normal melting point.
- 13. Some important terms The change of state from liquid to vapour (or gas) is called vaporisation. The temperature at which the liquid and the vapour states of the substance coexist is called its boiling point. The boiling point of a substance at standard atmospheric pressure is called its normal boiling point. The change from solid state to vapour state without passing through the liquid state is called sublimation, and the substance is said to sublime.
- 14. The amount of heat per unit mass transferred during change of state of the substance is called latent heat of the substance for the process. Q=mL Where, Q is the heat required, m is the mass of the substance L is known as latent heat Its SI unit is J kgŌĆō1. The latent heat for a solidliquid state change is called the latent heat of fusion (Lf), and that for a liquid-gas state change is called the latent heat of vaporisation (Lv).
- 16. Conduction is the mechanism of transfer of heat between two adjacent parts of a body because of their temperature difference. Gases are poor thermal conductors while liquids have conductivities intermediate between solids and gases. Heat conduction may be described quantitatively as the time rate of heat flow in a material for a given temperature difference.
- 18. Convection is a mode of heat transfer by actual motion of matter. It is possible only in fluids. Convection can be natural or forced. In natural convection, gravity plays an important part. Convection involves bulk transportof different parts of the fluid. In forced convection, material is forced to move by a pump or by some other physical means.
- 19. Conduction and convection require some Material as a transport medium. These modes Of heat transfer cannot operate between bodies Separated by a distance in vacuum. But the Earth does receive heat from the sun across a Huge distance and we quickly feel the warmth Of the fire nearby even though air conducts Poorly and before convection can set in. The Third mechanism for heat transfer needs no Medium; it is called radiation and the energy So radiated by electromagnetic waves is called Radiant energy. The electromagnetic radiation emitted by a body by virtue of its temperature like the radiation by a red hot iron or light from a filament lamp is called thermal radiation.
- 20. NewtonŌĆÖs Law of Cooling says that the rate of cooling of a body is proportional to the excess temperature of the body over the surroundings: T(t) = TA + (TH-TA) e-kt where T(t) = Temperature at time t TA = Ambient temperature (temp of surroundings) TH = Temperature of hot object at time 0 k = positive constant t = time .