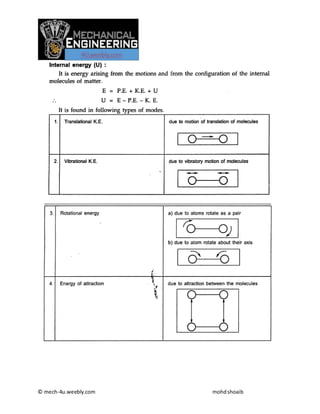
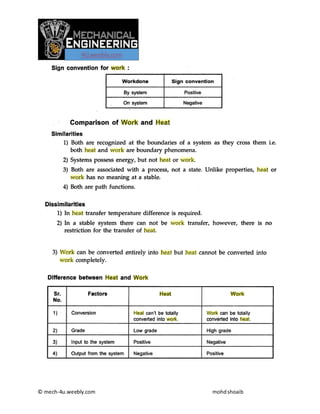
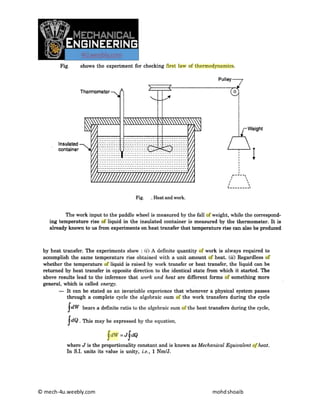
Thermodynamics notes
- 16. © mech-4u.weebly.com mohdshoaib Work refers to an activity involving a force and movement in the directon of the force. A force of 20 newtons pushing an object 5 meters in the direction of the force does 100 joules of work. Energy is the capacity for doing work. You must have energy to accomplish work - it is like the "currency" for performing work. To do 100 joules of work, you must expend 100 joules of energy. Power is the rate of doing work or the rate of using energy, which are numerically the same. If you do 100 joules of work in one second (using 100 joules of energy), the power is 100 watts. Power Power is the rate at which work is done. It is the work/time ratio. Mathematically, it is computed using the following equation.
- 17. © mech-4u.weebly.com mohdshoaib The standard metric unit of power is the Watt. As is implied by the equation for power, a unit of power is equivalent to a unit of work divided by a unit of time. Thus, a Watt is equivalent to a Joule/second. For historical reasons, the horsepower is occasionally used to describethe power delivered by a machine. One horsepower is equivalent to approximately 750 Watts. The expression for power is work/time. And since the expression for work is force*displacement, the expression for power can be rewritten as (force*displacement)/time. Since the expression for velocity is displacement/time, the expression for power can be rewritten once more as force*velocity. This is shown below.
- 31. © mech-4u.weebly.com mohdshoaib First Law of Thermodynamics: Energy can be changed fromone form to another, but it cannot be created ordestroyed. The total amount of energy and matter in the Universe remains constant, merely changing fromone form to another. The First Law of Thermodynamics (Conservation) states that energy is always conserved, it cannot be created or destroyed. In essence, energy can be converted fromone form into another. 2nd Law of Thermodynamics The second law is concerned with entropy, which is a measure of disorder. The second law says that the entropy of the universe increases There are two classical statements of the second law of thermodynamics: Kelvin & Planck "No (heat) engine whose working fluid undergoes a cycle can absorb heat from a single reservoir, deliver an equivalent amount of work, and deliver no other effect" Clausius "No machine whose working fluid undergoes a cycle can absorb heat from one system, reject heat to another system and produce no other effect"