Theroy of Production.pptx
- 1. Theory of Production BHARAT POUDEL Author and co âauthor of several text books, from +2 level to Masterâs level
- 2. Production âĒ Production is the process of transforming inputs into output. âĒ The term âproductionâ means a process by which tangible and intangible inputs or factors of production (land, labour, capital, etc) are converted or transformed to useful tangible and intangible output.
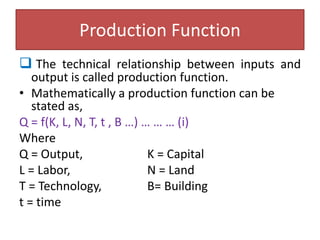
- 3. Production Function ïą The technical relationship between inputs and output is called production function. âĒ Mathematically a production function can be stated as, Q = f(K, L, N, T, t , B âĶ) âĶ âĶ âĶ (i) Where Q = Output, K = Capital L = Labor, N = Land T = Technology, B= Building t = time
- 4. Short-run Production Function ïą Short-run production function refers to the relationship between output and the variables factors of production only like labor, raw materials etc., which can be instantly changed. âĒ In short-run, labour is supposed to be variable factor. The firm can change its output by changing units of variable factor keeping other factor constant. It can be written as Qx = f(K ,L)
- 5. Long-run Production Function ïą The input-output relationship when the quantity of all factor input is varied, is known as long-run production function. ïą The long-run production function can be written as; Q = f (L, K, N, T )......(ii)
- 6. Total Product âĒ It refers to the total amount of a commodity produced by the combination of all inputs in a given period of time. âĒ Total product is cumulative values of marginal products. It is defined as follows. âĒ â TP = AP Ã N Where N = Total number of inputs employed
- 7. TP Curve 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 TP X Y Unit of labor
- 8. Average Product âĒ An average product is the outcome of the total product divided by the total units of the input employed. âĒ It is also known as output per unit factor input. AP = TP/N
- 9. AP Curve 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 AP X Y Unit of Labor A
- 10. Marginal Product âĒ Marginal product may be defined as the change in total product resulting from one additional unit of the variable factor. MP = âTP/âN
- 11. MP Curve -2 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Y X MP Unit of labor