Is looking at consumers' brain the ultimate solution?
- 1. the quest for the truth with neurosciences is looking at consumers’ brain
 the ultimate solution? Esteban Ribero Strategy Director
- 2. how can we really understand consumer behavior…? …we need to influence it we usually have inaccurate or partial understanding of it
- 3. client bias …they only see what they want to see “the consumer said...”
- 4. consumer bias they tell you what you want to hear… “consumers tell you one thing but they do other”
- 5. consumer bias consumer’s inability to know the true causes of their behavior …they don’t need to know them in order to behave!
- 6. we’ve tried… …borrowed techniques and theories from behavioral sciences
- 7. …from psychology and anthropology traditional consumer research… projective techniques ethnographies word association collages psycho drawing metaphor elicitation personification personal diaries photo sort perceptual mapping sentence completion apperception test storytelling laddering visualization
- 8. …from psychology and anthropology the pros • no need to fully articulate an answer • consumers give cues, the planner interprets them • “bypassing” the rational filters • a way to get to the “unconscious” • usually affordable
- 9. …from psychology and anthropology however… • too open to personal interpretation • little power to generalize • still depends on consumer’s input • too biased by the consumer …and the researcher
- 10. …from physiology getting consumer’s body reactions… …an attempt to infer their emotional and motivational states
- 11. …from physiology heart rate measures
- 12. …from physiology galvanic skin response (GSR) …gives an overall measure of arousal by tracking changes in the autonomic nervous system
- 13. …from physiology eye tracking …what catches consumer’s attention?
- 14. …from physiology pupil dilatation …assessing the level of interest pupil dilates in response to: light but also, • emotional state • interest and novelty • cognitive workload
- 15. …from physiology pupil dilatation …windows to the soul Eckhard H. Hess 1960
- 16. …from physiology pupil dilatation Eckhard H. Hess 1960
- 17. …from physiology gaze tracking …what are they looking at
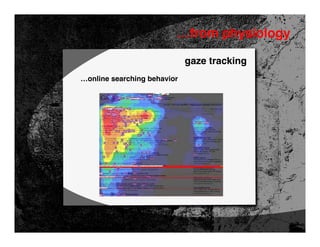
- 18. …from physiology gaze tracking …usability studies
- 19. …from physiology gaze tracking …online searching behavior
- 20. …from physiology gaze tracking …product design
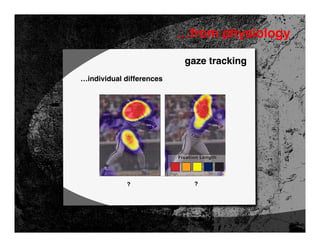
- 21. …from physiology gaze tracking …individual differences regular people artists
- 22. …from physiology gaze tracking …individual differences ? ?
- 23. …from physiology gaze tracking …individual differences men women
- 24. …from physiology gaze tracking …individual differences are they comparing themselves? do they feel threatened? men
- 25. …from physiology face recognition …emotional states are reflected in the face Paul Ekman
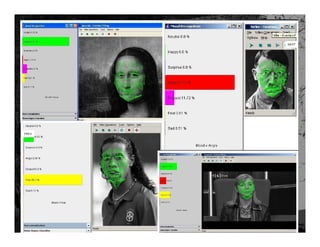
- 26. …from physiology face recognition …the six basic emotions anger fear disgust surprise joy sadness
- 27. …from physiology face recognition …a methodology to assess the emotions
- 28. …from physiology face recognition …emotion recognition software university of amsterdam
- 30. …from physiology the pros • no need to “ask” the consumer • get “true” reactions to different stimuli • assess different degrees of arousal in an “objective” way • “avoid” the subjectivity of the researcher
- 31. …from physiology however… • too vague • hard to interpret • can’t really know what it means (too many variables working at the same time) not specific enough to get to “the truth”
- 32. opening the black box… “asking the brain, not the person”
- 33. the mind and the brain… …putting cognitive psychology under context “if we can see the brain, we can see the mind”
- 34. the mind and the brain… …the mind is a set of modules that process different types of information those modules have identifiable neurological structures…
- 35. the field of neuromarketing… …a discipline that incorporates the knowledge about the brain processes in order to improve the effectiveness of the marketing activities
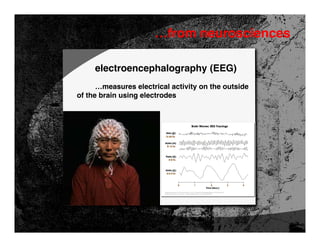
- 36. …from neurosciences electroencephalography (EEG) …measures electrical activity on the outside of the brain using electrodes
- 37. …from neurosciences electroencephalography (EEG) • records timing of activity very precisely (~1 millisecond) but spatial resolution is poor (ERP)
- 38. …from neurosciences electroencephalography (EEG) • it’s “cheap” and portable • can be combined with eye tracking Dr. A.K. Pradeep, President and Chief Executive Officer
- 39. …from neurosciences it looks something like… VW - The Force
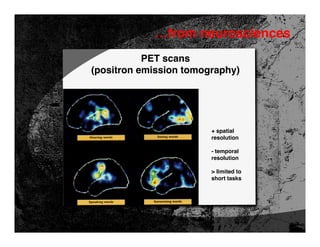
- 40. …from neurosciences PET scans (positron emission tomography) …measures blood flow in the brain after an injection of a radioactive substance
- 41. …from neurosciences PET scans (positron emission tomography) + spatial resolution - temporal resolution > limited to short tasks
- 42. …from neurosciences fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging) …measures changes in blood oxygenation
- 43. …from neurosciences fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging) Princeton’s fMRI equipment
- 44. …from neurosciences “we can tell generally what parts of the brain are active when you're doing different things, but no, I can't tell you what you're thinking" Dr. Reich
- 45. some examples… the Pepsi/Coke challenge vs. Dr. Read Montague Neuron, October 14, 2004
- 46. some examples… the Pepsi/Coke challenge preference fMRI = =
- 47. some examples… the Pepsi/Coke challenge preference fMRI > >
- 48. some examples… the Pepsi/Coke challenge confirmed what we already knew… …brand associations strongly bias our preferences!
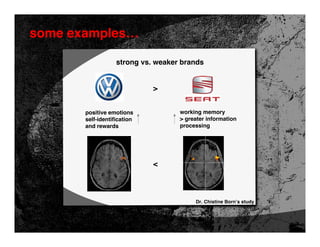
- 49. some examples… strong vs. weaker brands > positive emotions working memory self-identification > greater information and rewards processing < Dr. Chistine Born’s study
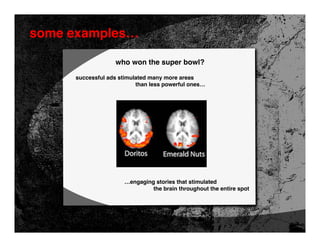
- 50. some examples… who won the super bowl? Dr. Marco Iacoboni UCLA Brain Mapping Center
- 51. some examples… who won the super bowl? “the winners” “the big flops” I’m going to Disney caveman Disney FedEx airport security wopperettes Sierra Mist Burger King approved GoDaddy.com
- 52. some examples… who won the super bowl? “the winners” “the big flops” live the flavor Robert Goulet Doritos Emerald Nuts grand theft auto crave CocaCola Honda CR-V hitchhiker connectile dysfunction Bud Light Sprint
- 53. some examples… who won the super bowl? successful ads stimulated many more areas than less powerful ones… …engaging stories that stimulated the brain throughout the entire spot
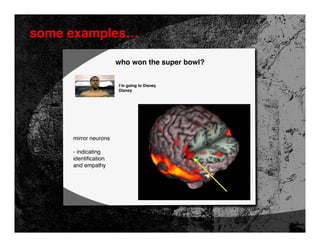
- 54. some examples… who won the super bowl? I’m going to Disney Disney mirror neurons - indicating identification and empathy
- 55. some examples… who won the super bowl? I’m going to Disney Disney ventral striatum - indicating reward processing
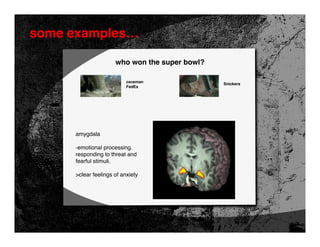
- 56. some examples… who won the super bowl? caveman Snickers FedEx amygdala -emotional processing. responding to threat and fearful stimuli. >clear feelings of anxiety
- 57. some examples… who won the super bowl? caveman FedEx amygdala activity “the scene looks funny and has been described as funny by lots of people, but your amygdala still perceives it as threatening” Dr. Iacoboni
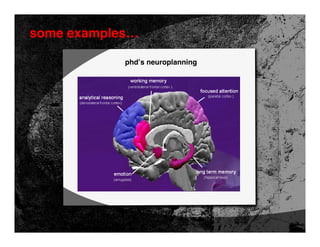
- 58. some examples… phd’s neuroplanning strategic planning process neuroplanning allows the user to identify the most appropriate model of behavior within the communication channels
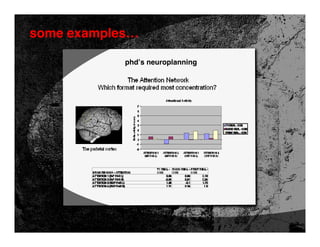
- 59. some examples… phd’s neuroplanning …a channel evaluation tool influence vs. reach different areas of the brain are “stimulated” by different media…
- 60. some examples… phd’s neuroplanning
- 61. some examples… phd’s neuroplanning
- 62. some examples… phd’s neuroplanning
- 63. some examples… phd’s neuroplanning
- 64. the promises of neurosciences… …for planners • better understanding of consumers and their relationships with brands • better understanding of their decision making processes • better understanding of their reactions to commercial stimuli • bypassing the consumer
- 65. …it has created a lot of controversy
- 66. ˛úłÜłŮ… …is it the ultimate solution?
- 67. proximate causes… ….ultimate causes neuromarketing is concerned mostly in understanding how? what? where? …but to get to the truth we need to understand why?!
- 68. and the answer is not in their brains…
- 70. ˛ő´Ç… ...don’t ask consumers for the causes of their behavior, infer them!
- 71. ˛ő´Ç… …consumers aren’t usually right they don’t know the true reasons for their behavior observe their behavior!
- 72. ˛ő´Ç… …use cues to inform the strategy don’t give up your responsibility to research use your intuition and expertise!
- 73. ˛ő´Ç… …refer to theories of human behavior read!
- 74. ˛ő´Ç…