THYROID EYE DISEASE
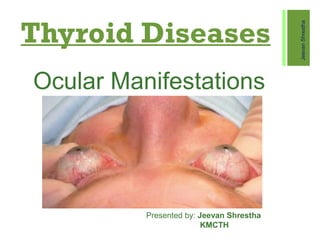
- 1. Thyroid Diseases Ocular Manifestations JeevanShrestha Presented by: Jeevan Shrestha KMCTH
- 2. ÔÅÆ I have no conflict of interest or disclosure in relation to this presentation.
- 3. Thyroid Disorders  Grave’s Disease  Hashimoto's Thyroiditis  Thyroid Carcinoma  Primary Hyperthyroidism  Neck Irradiation JeevanShrestha
- 4. Grave’s Ophthalmopathy  Is an autoimmune inflammatory disorder affecting the orbit around the eye, characterized by upper eyelid retraction, lid lag, swelling, redness, conjunctivitis, and bulging eyes.  Various Names:  Thyroid Eye Disease(TED)  Thyroid-associated Ophthalmopathy (TAO)  Dysthyroid Ophthalmopathy  Thyroid Orbitopathy  Endocrine Ophthalmopathy
- 5. ÔÅÆ Sex: More common in female than male 4:1 ÔÅÆ Smoking ÔÅÆ Middle age ÔÅÆ Autoimmune thyroid disease ÔÅÆ HLA-DR3 and HLA-B8 ÔÅÆ TED associated with Hyperthyroidism(90%), Hypothyroidism(4%), Euthyroidism(6%) Risk factors
- 6. Onset  20% of TED is diagnosed same time as hyperthyroidism  60% of eye disease occur after 1 year of thyroid disease  Only 30% of hyperthyroidism  TED
- 7. Pathogenesis ÔÅÆ Inflammatory targets: ÔÅÆ Primary: Orbital fibroblast ÔÅÆ Secondary: Extraocular muscles ÔÅÆ Activated T-cells act and stimulate adipogenesis, fibroblast proliferation and glycosaminoglycan synthesis. ÔÅÆ Enlargement of extraocular muscles due to edema and infiltration ÔÅÆ Orbital soft tissue infiltrated with lymphocytes, macrophages and mast cells
- 8. Pathogenesis ÔÅÆ Autoimmune disorder(IgG mediated) ÔÅÆ Enlargement of Extraocular Muscles - By Increase in Glycosaminoglycans ÔÅÆ Cellular Infiltration of Interstitial Tissues - With lymohocytes, plasma cells and macrophages, mast cell - Fibrosis ÔÅÆ Proliferation of Orbital fat, Connective tissue and Lacrimal Gland - With retention of fluid and GAG
- 9. Grave’s Ophthalmopathy Axial CT Extraocular Muscle Enlargement (Fusiform Appearance)
- 10. Clinical Features  LID SIGNS - Retraction of Upper Lids (Dalrymple’s Sign) in 90% - Lid Lag in 50% (von Graefe’s Sign) - Fullness of Eyelids(Enroth’s sign) - Difficulty in Eversion of Upper Lid (Gifford’s Sign) - Infrequent Blinking( Stellwag’s Sign)
- 11. Clinical Features  Conjunctival Signs: - Deep Injection and Chemosis  Pupillary Signs: - Unequal dilated pupils  Occular Motility Defects: - - Mobius’s sign  Exophthalmos (60%)  Exposure Keratitis and ocular discomfort  Optic Neuropathy
- 12. Classification - By American Thyroid Association(ATA) ÔÅÆ Class 0: N : No signs and symptoms ÔÅÆ Class 1: O : Only signs( Lid retraction with/without lid lag & proptosis) ÔÅÆ Class 2: S : Soft tissue involvement with signs in class-1 and symptoms like . Lacrimation,photophobia, lid or conjunctival swelling ÔÅÆ Class 3: P : Proptosis well established ÔÅÆ Class 4: E : Extraocular muscle movement limited and diplopia ÔÅÆ Class 5 : C : Corneal involvement( Exposure Keratitis) ÔÅÆ Class 6: S : Sight loss (Optic nerve involvement and visual field defects)
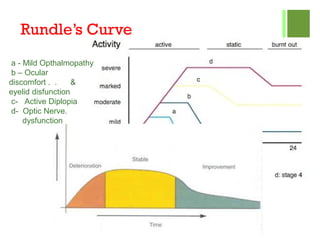
- 13. Rundle’s Curve a - Mild Opthalmopathy b – Ocular discomfort . . & eyelid disfunction c- Active Diplopia d- Optic Nerve. dysfunction
- 14. Diagnosis  Grave’s Ophthalmopathy:  10-20% Precede hyperthyroid  40% Concurrent  30% < 6 months after diagnosis  10-20% > 6 moths after Dx
- 15. Investigations ÔÅÆ Thyroid Function Tests: - Serum T3,T4,TSH ÔÅÆ Positional Tonometry: ÔÅÆ Ultrasonography: - Changes in extraocular muscles ÔÅÆ Computerised tonographic scanning: - Show proptosis, Muscle thickness, Optic Nerve thickening ÔÅÆ MRI(T2- weighed and STIR): ÔÅÆ Orthoptic workup:
- 16. Treatment A) Non- surgical Management: - Smoking Cessation - Head elevation at night & cold compressors in morning(Reduce periorbital edema) - Lubricating artificial tear drops - Eyelid taping - Guanethidine 5% eyedrop ( Decrease lid retraction) - Prisms - Systemic steroids - Radiotherapy - Combined therapy : ( Low dose steroids + Azathioprine + Irradiation)
- 17. Treatment (B) Surgical Management: i)Orbital Decompression: - Two wall Decompression (Orbital floor and medial wall removed) - Three wall Decompression (Floor, medial and lateral wall removed) - Four wall Decompression ( Three wall removal plus lateral half of roof and. . . large portion of sphenoid at apex) ii) Extraocular muscle surgery: - Always done after orbital decompression - To achieve binocular single vision in reading position
- 18. Treatment iii) Eyelid Surgery : - Mullerotomy - Levator recession/disinsertion - Scleral grafts - Recession of lower eyelid retractors - Blepheroplasty
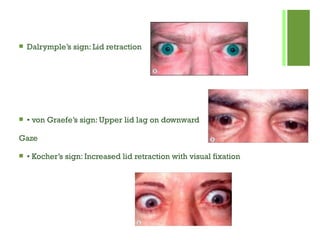
- 21.  Dalrymple’s sign: Lid retraction  • von Graefe’s sign: Upper lid lag on downward Gaze  • Kocher’s sign: Increased lid retraction with visual fixation
- 22.  • Ballet’s sign: Palsy of one or more extraocular muscles  • Suker’s sign:Weakness of fixation on lateral gaze  • Cowen’s sign: Jerky papillary contraction to consensual light  • Knies’ sign: Unequal dilatation of the pupils  • Jeffrey’s sign: Absence of forehead wrinkling on upward gaze  Griffith’s sign: Lower lid lag on downward gaze  • Stellwag’s sign: Infrequent blinking  • Enroth’s sign: Puffy swelling of the lids  • Mobius’ sign:Weakness of convergence mobius
- 23. THANK YOU Marty Feldman Presented By : Jeevan Shrestha