Topological methods
- 1. Topological methods Presented by: Sukhpal Singh Thapar University
- 2. Topological methods Topological methods are based on the simple premise that, given a query that describes some required features, we are interested in identifying library assets that come closest to providing these features. Such methods are critically dependent on what it means to come closest, which in turn depends on some definition of distance between the query and candidate assets [1].
- 3. Categories of Topological methods • Exclusive approximate retrieval: Methods that fall into this category make a distinction between two retrieval goals: exact retrieval and approximate retrieval, whereby we seek to identify library assets that completely satisfy all the requirements of the query. • Inclusive approximate retrieval: Methods that fall into this category make no distinction between exact retrieval and approximate retrieval. Rather, they focus on identifying library assets that minimize some measure of distance to the query.
- 4. Measures of distance can be divided into two broad classes • Measures of functional (semantic) distance, which reflect the extent of similarity between the functional properties of the query and those of candidate components. • Measures of structural (syntactic) distance, which reflect the extent of similarity between the structure of (solutions to) the query and the structure of candidate components.
- 6. The Google PageRank Algorithm is used in Topological methods to retrieve a software assets from software repository.
- 7. What is PageRank? • In short PageRank is a “vote”, by all the other pages on the Web, about how important a page is [3]. • A link to a page counts as a vote of support • PR(A) = (1-d) + d(PR(T1)/C(T1) +…+PR(Tn)/C(Tn))
- 8. Breaking Down the Equation • PR(Tn) - Each page has a notion of its own self-importance. That’s “PR(T1)” for the first page in the web all the way up to “PR(Tn)” for the last page • C(Tn) - Each page spreads its vote out evenly amongst all of it’s outgoing links. The count, or number, of outgoing links for page 1 is “C(T1)”, “C(Tn)” for page n, and so on for all pages. • PR(Tn)/C(Tn) - so if our page (page A) has a backlink from page “n” the share of the vote page A will get is “PR(Tn)/C(Tn)” • d(… - All these fractions of votes are added together but, to stop the other pages having too much influence, this total vote is “damped down” by multiplying it by 0.85 (the factor “d”) • (1 - d) - The (1 – d) bit at the beginning is a bit of probability math magic so the “sum of all web pages’ PageRank's will be one”: it adds in the bit lost by the d(…. It also means that if a page has no links to it (no backlinks) even then it will still get a small PR of 0.15 (i.e. 1 – 0.85).
- 9. How is it Calculated? • The PR of each page depends on the PR of the pages pointing to it. • But we won’t know what PR those pages have until the pages pointing to them have their PR calculated and so on. • So what we do is make a guess.
- 10. Simple Example • Each page has one outgoing link (backlink). So that means [2] : • C(T1) = 1 for A and • C(T2) = 1 for B
- 11. We don’t know what their PR should be to begin with, so we will just guess 1 as a safe random number. • d (damping factor) = 0.85 • PR(A)= (1 – d) + d(PR(T1)/C(T1))= (1 – d) + d(1/1) i.e. • PR(A)= 0.15 + 0.85 * 1 =1 • PR(B)= 0.15 + 0.85 * 1 =1
- 12. Let’s Do It Again with Another Number. Let’s try 0 and re- calculate… • PR(A)= 0.15 + 0.85 * 0 = 0.15 = 0.15 + 0.85 * • PR(B) 0.15 = 0.2775 • Now we have calculated a “next best guess” so we just plug it in the equation again… • PR(A)= 0.15 + 0.85 * 0.2775 = 0.385875 • PR(B)= 0.15 + 0.85 * 0.385875 = 0.47799375 And again… • PR(A)= 0.15 + 0.85 * 0.47799375 = 0.5562946875 • PR(B)= 0.15 + 0.85 * 0.5562946875 = 0.622850484375
- 13. Principle • It doesn’t matter where you start your guess, once the PageRank calculations have settled down, the “normalized probability distribution” (the average PageRank for all pages) will be 1.0 • In software repository we are using software assets instead of pages and also using relationships among software assets based on their keywords instead of links.
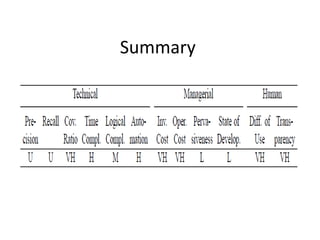
- 14. Summary
- 15. References: [1] A survey of software reuse libraries A. Mili a,_, R. Mili b and R.T. Mittermeir Annals of Software Engineering 5 (1998) 349–414 349 [2] http://wwwdb.stanford.edu/~backrub/google.html http://www-db.stanford.edu/~backrub/google.html [3] Semantic Component Retrieval in Software Engineering Inaugural dissertation zur Erlangung des akademischen Grades eines Doktors der Naturwissenschaften der, Universitat Mannheim, Mannheim, 2008


![Topological methods
Topological methods are based on the simple
premise that, given a query that describes
some required features, we are interested in
identifying library assets that come closest to
providing these features. Such methods are
critically dependent on what it means to come
closest, which in turn depends on some
definition of distance between the query and
candidate assets [1].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topologicalmethodsppt-120927011701-phpapp02/85/Topological-methods-2-320.jpg)




![What is PageRank?
• In short PageRank is a “vote”, by all the other
pages on the Web, about how important a
page is [3].
• A link to a page counts as a vote of support
• PR(A) = (1-d) + d(PR(T1)/C(T1)
+…+PR(Tn)/C(Tn))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topologicalmethodsppt-120927011701-phpapp02/85/Topological-methods-7-320.jpg)


![Simple Example
• Each page has one outgoing link (backlink). So that
means [2] :
• C(T1) = 1 for A
and
• C(T2) = 1 for B](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topologicalmethodsppt-120927011701-phpapp02/85/Topological-methods-10-320.jpg)



![References:
[1] A survey of software reuse libraries A. Mili a,_, R. Mili
b and R.T. Mittermeir Annals of Software
Engineering 5 (1998) 349–414 349
[2] http://wwwdb.stanford.edu/~backrub/google.html
http://www-db.stanford.edu/~backrub/google.html
[3] Semantic Component Retrieval in Software
Engineering Inaugural dissertation zur Erlangung des
akademischen Grades eines Doktors der
Naturwissenschaften der, Universitat Mannheim,
Mannheim, 2008](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topologicalmethodsppt-120927011701-phpapp02/85/Topological-methods-15-320.jpg)